
Concept explainers
School days: The following table presents the numbers of students enrolled in grades 1 through 8 in public schools in the United States.
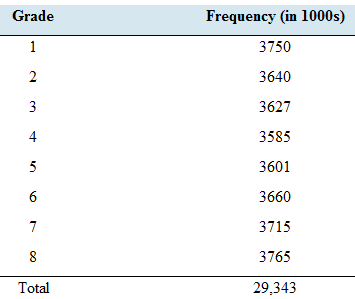
Consider these students to be a population. Let X be the grade of a student randomly chosen from this population.
Construct the
Find the probability that the student is in fourth grade.
Find the probability that the student is seventh or eighth grade.
Compute the
Compute the standard
a.
To construct: The probability distribution of the given random variable.
Explanation of Solution
The enrollment of students from grade
Calculation:
The random variable
To calculate the probability of each value of the random variable, the frequency should be divided by the total number of individuals according to the formula,
As an example,
The all calculation can be expressed in a table as follows. Because both values in the numerator and the denominator is in thousands, in the division those are cancelled out.
The probability distribution can be constructed by the first and third columns of the above table.
b.
To find: The probability to a selected student is from grade four.
Answer to Problem 49E
The probability that the student is in fourth grade is found to be
Explanation of Solution
The probability distribution for the grade of
Calculation:
When a student is fin grade four, the random variable
The relevant probability is calculated in a precious part as,
Conclusion:
The probability of
c.
To find: The probability to a selected student is in grade seven or eight.
Answer to Problem 49E
The probability that the student is seventh or eighth grade is found to be
Explanation of Solution
The probability distribution for the grade of
Calculation:
Same student cannot enroll to two different grades. Hence, being a grade seven student and being a grade eight student are two mutually exclusive events.
Therefore, the probability for this combination can be written as,
By the addition rule, this probability should be equal to
The total probability can be determined as,
Conclusion:
The probability of
d.
To find: The mean of grade of the student.
Answer to Problem 49E
The mean is found to be,
Explanation of Solution
The probability distribution for the grade of
Calculation:
The mean of a random variable, or equivalently the expected value is given by the sum of the product of the values and the corresponding probabilities.
Here, for each value of
Conclusion:
The mean is found to be
e.
To find: The standard deviation of
Answer to Problem 49E
The standard deviation is found to be,
Explanation of Solution
The probability distribution for the grade of
Calculation:
The variance of a random variable
By constructing a table we can do the calculations clearly using the mean of
The sum of right-most column gives the variation of
The standard deviation
Conclusion:
The standard deviation is found to be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Elementary Statistics (Text Only)
- AP1.2 A child is 40 inches tall, which places her at the 90th percentile of all children of similar age. The heights for children of this age form an approximately Normal distribution with a mean of 38 inches. Based on this information, what is the standard deviation of the heights of all children of this age? 0.20 inches (c) 0.65 inches (e) 1.56 inches 0.31 inches (d) 1.21 inchesarrow_forwardAP1.1 You look at real estate ads for houses in Sarasota, Florida. Many houses range from $200,000 to $400,000 in price. The few houses on the water, however, have prices up to $15 million. Which of the following statements best describes the distribution of home prices in Sarasota? The distribution is most likely skewed to the left, and the mean is greater than the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the left, and the mean is less than the median. The distribution is roughly symmetric with a few high outliers, and the mean is approximately equal to the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the right, and the mean is greater than the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the right, and the mean is less than the median.arrow_forwardDuring busy political seasons, many opinion polls are conducted. In apresidential race, how do you think the participants in polls are generally selected?Discuss any issues regarding simple random, stratified, systematic, cluster, andconvenience sampling in these polls. What about other types of polls, besides political?arrow_forward
- Please could you explain why 0.5 was added to each upper limpit of the intervals.Thanksarrow_forward28. (a) Under what conditions do we say that two random variables X and Y are independent? (b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) = E(X)E(Y); (e) Show by a counter example that the converse of (ii) is not necessarily true.arrow_forward1. Let X and Y be random variables and suppose that A = F. Prove that Z XI(A)+YI(A) is a random variable.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
