
Fundamentals Of Physics - Volume 1 Only
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119306856
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 82P
In Fig. 6-57, a stuntman drives a car (without negative lift) over the top of a hill, the cross section of which can be approximated by a circle of radius R = 250 m. What is the greatest speed at which he can drive without the car leaving the road at the top of the hill?
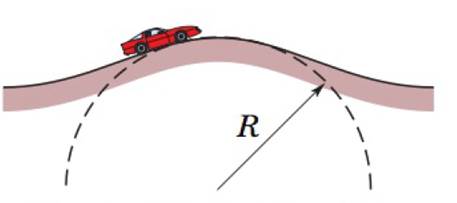
Figure 6-57 Problem 82.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Physics - Volume 1 Only
Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-12, if the box is stationary and the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 2QCh. 6 - In Fig. 6-13, horizontal force F1 of magnitude 10...Ch. 6 - In three experiments, three different horizontal...Ch. 6 - If you press an apple crate against a wall so hard...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-14, a block of mass m is held stationary...Ch. 6 - Reconsider Question 6 but with the force F now...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-15, a horizontal force of 100 N is to be...Ch. 6 - Prob. 9QCh. 6 - Prob. 10Q
Ch. 6 - A person riding a Ferris wheel moves through...Ch. 6 - During a routine flight in 1956, test pilot Tom...Ch. 6 - A box is on a ramp that is at angle to the...Ch. 6 - The floor of a railroad flatcar is loaded with...Ch. 6 - In a pickup game of dorm shuffleboard, students...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW A bedroom bureau with a mass of 45 kg,...Ch. 6 - A slide-loving pig slides down a certain 35 slide...Ch. 6 - GO A 2.5 kg block is initially at rest on a...Ch. 6 - A baseball player with mass m 79 kg, sliding into...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW A person pushes horizontally with a force...Ch. 6 - The mysterious sliding stones. Along the remote...Ch. 6 - GO A 3.5 kg block is pushed along a horizontal...Ch. 6 - Figure 6-20 shows an initially stationary block of...Ch. 6 - SSM A 68 kg crate is dragged across a floor by...Ch. 6 - In about 1915, Henry Sincosky of Philadelphia...Ch. 6 - A worker pushes horizontally on a 35 kg crate with...Ch. 6 - Figure 6-22 shows the cross section of a road cut...Ch. 6 - The coefficient of static friction between Teflon...Ch. 6 - A loaded penguin sled weighing 80 N rests on a...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-24, a force P acts on a block weighing...Ch. 6 - GO You testify as an expert witness in a case...Ch. 6 - A 12 N horizontal force F pushes a block weighing...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-27, a box of Cheerios mass mC = 1.0...Ch. 6 - An initially stationary box of sand is to be...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-23, a sled is held on an inclined...Ch. 6 - When the three blocks in Fig. 6-29 are released...Ch. 6 - A 4.10 kg block is pushed along a floor by a...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW Block B in Fig. 6-31 weighs 711 N. The...Ch. 6 - GO Figure 6-32 shows three crates being pushed...Ch. 6 - GO Body A in Fig. 6-33 weighs 102 N, and body B...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-33, two blocks are connected over a...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-34, blocks A and B have weights of 44...Ch. 6 - A toy chest and its contents have a combined...Ch. 6 - SSM Two blocks, of weights 3.6 N and 7.2 N, are...Ch. 6 - GO A block is pushed across a floor by a constant...Ch. 6 - SSM A 1000 kg boat is traveling at 90 km/h when...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-37, a slab of mass m1= 40 kg rests on...Ch. 6 - ILW The two blocks m = 16 kg and M = 88 kg in Fig....Ch. 6 - The terminal speed of a sky diver is 160 km/h in...Ch. 6 - Continuation of Problem 8. Now assume that Eq....Ch. 6 - Assume Eq. 6-14 gives the drag force on a pilot...Ch. 6 - Calculate the ratio of the drag force on a jet...Ch. 6 - In downhill speed skiing a skier is retarded by...Ch. 6 - A cat dozes on a stationary merry-go-round in an...Ch. 6 - Suppose the coefficient of static friction between...Ch. 6 - ILW What is the smallest radius of an unbanked...Ch. 6 - During an Olympic bobsled run, the Jamaican team...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW A student of weight 667 N rides a steadily...Ch. 6 - A police officer in hot pursuit drives her car...Ch. 6 - A circular-motion addict of mass 80 kg rides a...Ch. 6 - A roller-coaster car at an amusement park has a...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-39, a car is driven at constant speed...Ch. 6 - An 85.0 kg passenger is made to move along a...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW An airplane is flying in a horizontal...Ch. 6 - An amusement park ride consists of a car moving in...Ch. 6 - An old streetcar rounds a flat corner of radius...Ch. 6 - In designing circular rides for amusement parks,...Ch. 6 - A bolt is threaded onto one end of a thin...Ch. 6 - GO A banked circular highway curve is designed for...Ch. 6 - GO A puck of mass m = 1.50 kg slides in a circle...Ch. 6 - Brake or turn? Figure 6- 44 depicts an overhead...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW In Fig. 6-45, a 1.34 kg ball is connected...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-46, a box of ant aunts total mass m1...Ch. 6 - SSM A block of mass mt = 4.0 kg is put on top of a...Ch. 6 - A 5.00 kg stone is rubbed across the horizontal...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-49, a 49 kg rock climber is climbing a...Ch. 6 - A high-speed railway car goes around a flat,...Ch. 6 - Continuation of Problems 8 and 37. Another...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-50, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-51, a crate slides down an inclined...Ch. 6 - Engineering a highway curve. If a car goes through...Ch. 6 - A student, crazed by final exams, uses a force P...Ch. 6 - GO Figure 6-53 shows a conical pendulum, in which...Ch. 6 - An 8.00 kg block of steel is at rest on a...Ch. 6 - A box of canned goods slides down a ramp from...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-54, the coefficient of kinetic friction...Ch. 6 - A 110 g hockey puck sent sliding over ice is...Ch. 6 - A locomotive accelerates a 25-car train along a...Ch. 6 - A house is built on the top of a hill with a...Ch. 6 - What is the terminal speed of a 6.00 kg spherical...Ch. 6 - A student wants to determine the coefficients of...Ch. 6 - SSM Block A in Fig. 6-56 has mass mA = 4.0 kg, and...Ch. 6 - Calculate the magnitude of the drag force on a...Ch. 6 - SSM A bicyclist travels in a circle of radius 25.0...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-57, a stuntman drives a car without...Ch. 6 - You must push a crate across a floor to a docking...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-58, force F is applied to a crate of...Ch. 6 - In the early afternoon, a car is parked on a...Ch. 6 - A sling-thrower puts a stone 0.250 kg in the...Ch. 6 - SSM A car weighing 10.7 kN and traveling at 13.4...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-59, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and...Ch. 6 - SSM A filing cabinet weighing 556 N rests on the...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-60, a block weighing 22 N is held at...Ch. 6 - Prob. 91PCh. 6 - A circular curve of highway is designed for...Ch. 6 - A 1.5 kg box is initially at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 6 - A child weighing 140 N sits at rest at the top of...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-61 a fastidious worker pushes directly...Ch. 6 - A child places a picnic basket on the outer rim of...Ch. 6 - SSM A warehouse worker exerts a constant...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-62, a 5.0 kg block is sent sliding up a...Ch. 6 - An 11 kg block of steel is at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 6 - A ski that is placed on snow will stick to the...Ch. 6 - Playing near a road construction site, a child...Ch. 6 - A 100 N force, directed at an angle above a...Ch. 6 - A certain string can withstand a maximum tension...Ch. 6 - A four-person bobsled total mass = 630 kg comes...Ch. 6 - As a 40 N block slides down a plane that is...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Why are the top predators in food chains most severely affected by pesticides such as DDT?
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
WHAT IF? Is allopatric speciation more likely to occur on an island close to a mainland or on a more isolated i...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
4.1 Write the symbols for the following elements.
a. copper
b. platinum
c. calcium
d. manganese
e. Iron
...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
2.37 Identify all of the functional groups in paclitaxel (Taxol), an important drug used to fight breast cance...
Organic Chemistry
10. Zack is driving past his house in FIGURE Q4.1O. He wants to toss his physics book out the window and have i...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Conservative and Non Conservative Forces; Author: AK LECTURES;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vFVCluvSrFc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY