
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
A reaction roadmap have to be made for the reactions in the study Guide section of chapters 6-11.
Concept Introduction:
Markovnikov addition: The addition reaction of parotic acids to a different alkene or alkyne, the hydrogen atom of
Anti-Markovnikov addition: These rules describe the regiochemistry where the substituent is bonded to a less substituted carbon, rather than the more substituted carbon. This placed is quite unusual as carbon cations which are commonly formed during alkene or alkyne reactions tend to favor the more substituted carbon.
Unsaturated compound: The nucleophile reacts with
The alkylation at the β carbon of ketone or aldehyde is done by the following mechanism;
(1) Alkylating the β carbon via enamine intermediate.
(2) Alkylating the β carbon via a Michael reaction.
Osmium tetroxide
The reaction mechanism involves the concentrated addition of the osmium tetroxide to the
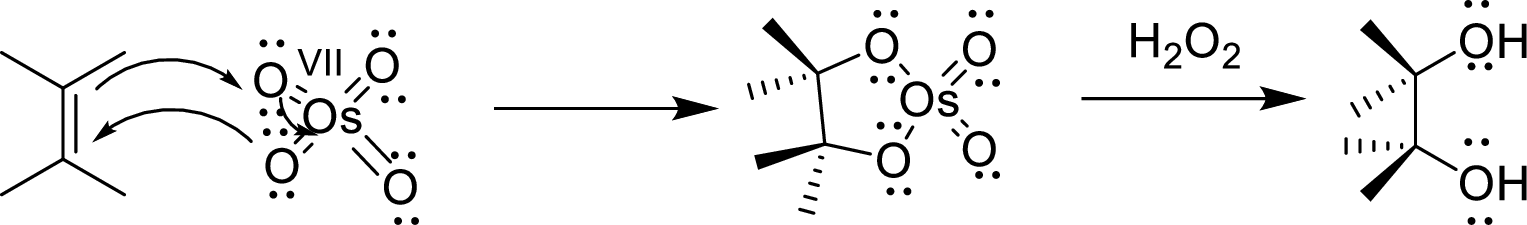
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of
Ozonolysis Reaction: It is an oxidative reaction which is used to oxidize the carbon-carbon double and triple bond.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
OWLv2 with MindTap Reader, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card for Brown/Iverson/Anslyn/Foote's Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition
- What is the major organic product of this reaction sequence? Type its systematic IUPAC name in the box below. 1) HNO3, H,SO, 2) H2, Pd/C 3) NaNO,, HCI, 0 °C 4) H20, heatarrow_forwardWorksheet 2: Formulae and structures of organic compounds Complete the table below to identify the general formulae and structures of the organic compounds. Give reasons why. Name Homologous series General formula Structural formula (homologous series) Propan-1-ol Alcohol Reasons Propan-2-ol Reasons 2-methypropan-2-ol Worksheet 2: Formulae and structures of organic compounds Reasons 2-Bromopropane Reasons Propanone Reasons 1-Propanal Reasonsarrow_forwardPlease help in answering the organic chemistry questions given below. Explanations are welcome.arrow_forward
- 3. How would you separate these to compounds using acid-base chemistry? (a) Identify all functional groups; and (b) Draw a flow diagram of your separation process. H3N HOarrow_forward9. Your plane crashes in the Rocky Mountains. Miraculously you survive, and find yourself stranded on a deserted mountain slope. While out gathering berries, you stumble across an abandoned but well-stocked organic laboratory! Mentally thanking your chemistry teacher, you immediately begin making the useful compounds listed below. Show equations with structures and names and give type of reaction) a) pentan-2-ol (to use as a disinfectant for cuts and scrapes) Type of Reaction: Structures and Names:arrow_forwardFirst, draw your chosen compounds including any non-bonding electrons and non-zero formal charges Circle and name any pH-sensitive functional groups. Choose an organic solvent that will dissolve both or your compounds and an aqueous solution (i.e. conc. aqueous NaOH, 5% aq. NaHCO3, or 3M HCl) that would successfully separate the two compounds selected.arrow_forward
- I. Name the following benzene derivatives in accordance to General Nomenclatures and IUPAC rules. NO2 NO2 CaHs Co ty 1. 4. CH-CH2 CH-CH NO cOcty CH2 NO2 NOz 5. NO cOcto I 3. 6. NH, 2. NO2 Authored by: Sensei Wilmark Palacios 7. 8. NH, cooH OH CAg 9. 10. COH I 2.arrow_forwardCarbonyl-containing compounds are equally important in biological molecules. The following line diagram is one example: What is the IUPAC name of the above molecule? Type your answer in, ignoring any isomerism that may exist in this line diagram. You will need to submit a handwritten response to the next part of this question (see below). Label the question number (Q7) and show your answer legibly and clearly. Your handwritten response for this question will be awarded up to Handwritten response Question 7: a. Write a reaction equation between the above compound and propan-1-ol to form a hemiacetal. b. Combine the hemiacetal from part (a) with a second molecule of propan-1-ol and draw the structure of the resulting acetal. In your answer include the structural formulas, preferably as line diagrams, of all organic reactants and products.arrow_forwardThe careful choice of an appropriate solvent will play a major role in whether organic reactions will be successful. For example, reagents such as CH3CH2Li and NaNH2 will be incompatible with solvents such as water and ethanol. Why is this?arrow_forward
- I want clear handwritten solution only....i will up votearrow_forwardOrganic Chemistry 1 Here is the professor's solution to the problem. The assignment has been turned in and the answer key has been shared with the class. So, this is the official answer key. However, I do NOT understand the solution. Please explain the answer in a clear step-by-step fashion to me. Explain the answer provided in the image in a clear fashion and as if I did not know much about organic chemistry. It seems to me like the professor is making the problem more complicated than it has to be. Can you demystify or simplify this problem about D glucose?arrow_forwardHow toarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
