
Concept explainers
(a) A luggage carousel at an airport has the form of a section of a large cone, steadily rotating about its vertical axis. Its metallic surface slopes downward toward the outside, making an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. A piece of luggage having mass 30.0 kg is placed on the carousel at a position 7.46 m measured horizontally from the axis of rotation. The travel bag goes around once in 38.0 s. Calculate the force of staticfriction exerted by the carousel on the bag. (b) The drive motor is shifted to turn the carousel at a higher constant rate of rotation, and the piece of luggage is bumped to another position, 7.94 m from the axis of rotation. Now going around once in every 34.0 s, the bag is on the verge of slipping down the sloped surface. Calculate the coefficient of static friction between the bag and the carousel.
(a)
The force of static friction exerted by the carousel on the bag.
Answer to Problem 6.47AP
The force of static friction exerted by the carousel on the bag is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The metallic surface of a luggage carousel slopes downward toward outside at an angle
Formula to calculate the centripetal force is,
The horizontal force acting on the bag in horizontal direction is,
Substitute
Here,
Substitute
Draw the free body diagram for the luggage.
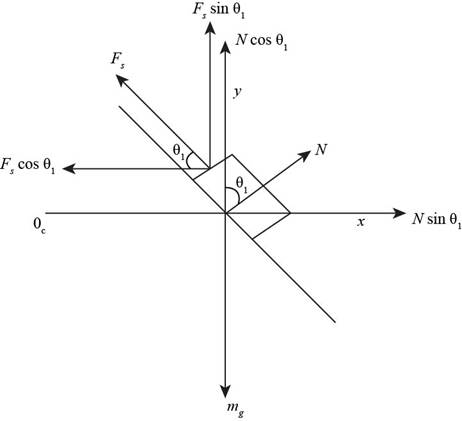
From the Figure (1), the component of force in
From the Figure (1), the component of force in
Substitute
Simplify the above equation.
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the force of static friction exerted by the carousel on the bag is
(b)
The coefficient of friction between the bag and the carousel.
Answer to Problem 6.47AP
The coefficient of friction between the bag and the carousel is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The metallic surface of a luggage carousel slopes downward toward outside at an angle
Substitute
Calculate the centripetal force for the bag.
Substitute
Calculate the normal force for the bag when it is on the carousel.
Substitute
Formula to calculate the coefficient of friction between the bag and the carousel is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the coefficient of friction between the bag and the carousel is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
- Check Your Understanding A car moving at 96.8 km/h travels around a circular curve of radius 182.9 m on a flat county road. What must be the minimum coefficient of static friction to keep the car from slipping?arrow_forwardA boy rides his bicycle 2.00 km. The wheels have radius 30.0 cm. What is the total angle the tires rotate through during his trip?arrow_forward(a) What will an object weigh on the Moon's surface if it weighs 190 N on Earth's surface? (b) How many Earth radii must this same object be from the center of Earth if it is to weigh the same as it does on the Moon? REartharrow_forward
- An object of mass M = 12.0 kg is attached to a cord that is wrapped around a wheel of radius r =10.0 cm (Fig.). The acceleration of the object down the friction-less incline is measured to be a = 2.00 m/s2 and the incline makes ail angle θ = 37.0° with the horizontal. Assuming the axle of the wheel to be frictionless, determine (a) the tension in the rope, (b) the moment of inertia of the wheel, and (c) the angular speed of the wheel 2.00 s alter it begins rotating, starting from rest.arrow_forwardA cylinder having a mass of 40kgs with a radius of 0.5m is pushed to the right without rotation and with an acceleration of 2m/s^2. Determine the location of the horizontal force P if the coefficient of friction is 0.30arrow_forwardA spool of mass 60kg is supported on two rollers at A and B as shown in Figure Q1 (c). Neglect the mass of the inel astic cable, friction and the mass of the rollers at A and B. Knowing that a constant pulling force Pis applied in order to unwind 6m of cable in 3s starting from rest. The radius of gyration for the spool is (600+ 2) mm, (i) Determine the angul ar acceleration of the spool. (ii) Determine the pulling force P. (iii) Explain with calculati on on ways to increase the acceleration of cable being pulled. 900 mm 1000 mm 10° 10 A Barrow_forward
- A uniform sphere of weight 50 N and radius 4 cm is held by a string of length 8 cm, against a smooth wall inclined at an angle of 70 degrees, Find the tension in the string, and the force between the ball and the wallarrow_forwardA cylinder having a mass of 250 kg is to be supported by the cord which wraps over the pipe. Determine the largest vertical force F that can be applied to the cord without moving the cylinder. The cord passes once over the pipe, B = 180° Take us 0.2.arrow_forwardA small bead canslide without friction on a circularhoop that is in a vertical planeand has a radius of 0.100 m. Thehoop rotates at a constant rate of4.00 rev/s about a vertical diameter(Fig. ). (a) Find theangle b at which the bead is invertical equilibrium. (It has a radialacceleration toward the axis.)(b) Is it possible for the bead to“ride” at the same elevation asthe center of the hoop? (c) Whatwill happen if the hoop rotates at1.00 rev/s? Sarrow_forward
- I need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forwardA model airplane of mass 0.700 kg flies with a speed of 35.0 m/s in a horizontal circle at the end of a 64.0-m control wire as shown in Figure (a). The forces exerted on the airplane are shown in Figure (b): the tension in the control wire, the gravitational force, and aerodynamic lift that acts at ? = 20.0° inward from the vertical. Compute the tension in the wire, assuming it makes a constant angle of ? = 20.0° with the horizontal. Answer should be in Newtons.arrow_forwardDetermine the resultant force and its inclination with the force X, if two forces X=90 N, Y=50 N, are acting simultaneously at a point on a particle and they can be represented by the two adjacent sides of the parallelogram. Take the angle between these two forces as 120°. The value of resultant force in N is The resultant force inclination with the force X in degrees isarrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
