Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780134293936
Author: Nivaldo J. Tro
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 38E
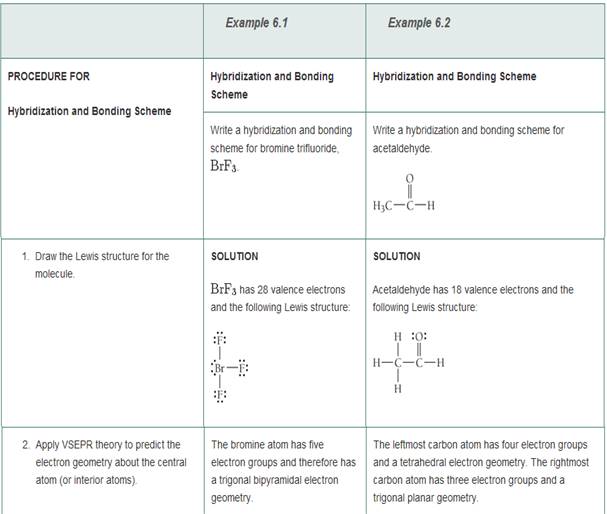
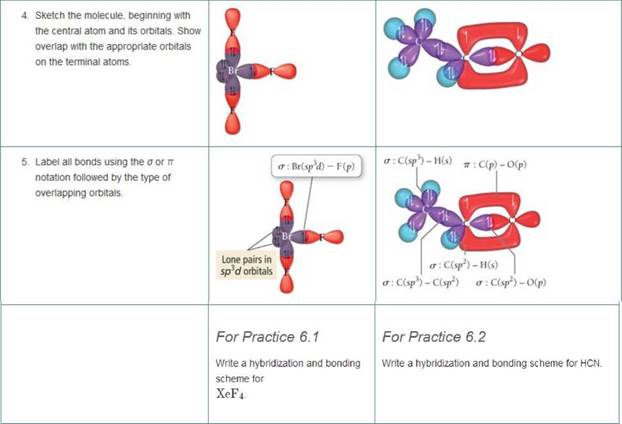
Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each molecule that contains more than one interior atom. Indicate the hybridization about each interior atom. Sketch the structure, including overlapping orbitals, and label all bonds using the notation shown in Examples 6.1 and 6.2.
- C2H2 (skeletal structure HCCH)
- C2H4 (skeletal structure H2CCH2)
- C2H6 (skeletal structure H3CCH3)

Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under
the table.
Molecule 1
Molecule 2
Molecule 3
----|||
Molecule 4
Molecule 5
Molecule 6
none of the above
mm..
Use the vapor-liquid equilibrium data at 1.0 atm. for methanol-water (Table 2-8 ) for the following:
If the methanol vapor mole fraction is 0.600, what is the methanol liquid mole fraction?
Is there an azeotrope in the methanol-water system at a pressure of 1.0 atmospheres?
If water liquid mole fraction is 0.350, what is the water vapor mole fraction?
What are the K values of methanol and of water at a methanol mole fraction in the liquid of 0.200?
What is the relative volatility αM-W at a methanol mole fraction in the liquid of 0.200?
Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under
the table.
||
|II*****
Molecule 1
|
Molecule 4
none of the above
Molecule 2
Molecule 3
Х
mm...
C
---|||
***
Molecule 5
Molecule 6
Chapter 6 Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Ch. 6 - Prob. 1ECh. 6 - What is a chemical bond according to valence bond...Ch. 6 - In valence bond theory, what determines the...Ch. 6 - In valence bond theory, the interaction energy...Ch. 6 - What is hybridization? Why is hybridization...Ch. 6 - How does hybridization of the atomic orbitals in...Ch. 6 - How is the number of hybrid orbitals related to...Ch. 6 - Sketch each hybrid orbital sp sp2 sp3 sp3d sp3d2Ch. 6 - Prob. 9ECh. 6 - Name the hybridization scheme that corresponds to...
Ch. 6 - What is a chemical bond according to molecular...Ch. 6 - Explain the difference between hybrid atomic...Ch. 6 - What is a bonding molecular orbital?Ch. 6 - Prob. 14ECh. 6 - What is the role of wave interference in...Ch. 6 - Prob. 16ECh. 6 - Prob. 17ECh. 6 - Prob. 18ECh. 6 - Prob. 19ECh. 6 - Prob. 20ECh. 6 - Prob. 21ECh. 6 - When applying molecular orbital theory to...Ch. 6 - In molecular orbital theory, what is a nonbonding...Ch. 6 - Write a short paragraph describing chemical...Ch. 6 - The valence electron configurations of several...Ch. 6 - The valence electron configurations of several...Ch. 6 - Draw orbital diagrams (boxes with arrows in them)...Ch. 6 - Draw orbital diagrams (boxes with arrows in them)...Ch. 6 - Prob. 29ECh. 6 - Draw orbital diagrams (boxes with arrows in them)...Ch. 6 - Which hybridization scheme allows the formation of...Ch. 6 - Which hybridization scheme allows the central atom...Ch. 6 - Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each...Ch. 6 - Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each...Ch. 6 - Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each...Ch. 6 - Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each...Ch. 6 - Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each...Ch. 6 - Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each...Ch. 6 - Consider the structure of the amino acid alanine...Ch. 6 - Consider the structure of the amino acid aspartic...Ch. 6 - Sketch the bonding molecular orbital that results...Ch. 6 - Sketch the antibonding molecular orbital that...Ch. 6 - Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond...Ch. 6 - Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond...Ch. 6 - Sketch the bonding and antibonding molecular...Ch. 6 - Sketch the bonding and antibonding molecular...Ch. 6 - Using the molecular orbital energy ordenng for...Ch. 6 - Using the molecular orbital energy ordering for...Ch. 6 - Apply molecular orbital theory to predict if each...Ch. 6 - Apply molecular orbital theory to predict if each...Ch. 6 - According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has...Ch. 6 - According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has...Ch. 6 - Draw an MO energy diagram for CO. (Use the energy...Ch. 6 - Draw an MO energy diagram for HCI. Predict the...Ch. 6 - For each compound, draw the Lewis structure,...Ch. 6 - For each compound, draw the Lewis structure,...Ch. 6 - Amino acids are biological compounds that link...Ch. 6 - The genetic code is based on four different bases...Ch. 6 - The structure of caffeine, present in coffee and...Ch. 6 - The structure of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) is...Ch. 6 - Draw a molecular orbital energy diagram for CIF....Ch. 6 - Draw Lewis structures and MO diagrams for CN+, CN,...Ch. 6 - Bromine can form compounds or ions with any number...Ch. 6 - The compound C3H4 has two double bonds. Describe...Ch. 6 - How many hybrid orbitals do we use to describe...Ch. 6 - Prob. 66ECh. 6 - In VSEPR theory, which uses the Lewis model to...Ch. 6 - The resuts of a molecular orbital calculation for...Ch. 6 - Prob. 69ECh. 6 - cis-2-Butene isomerizes (changes its structure) to...Ch. 6 - The ion CH5 + can form under very special...Ch. 6 - Neither the VSEPR model nor the hybridization...Ch. 6 - Prob. 73ECh. 6 - The most stable forms of the nonmetals in groups...Ch. 6 - Consider the bond energies of three iodine...Ch. 6 - How many atomic orbitals form a set of sp3hybrid...Ch. 6 - Have each group member pick one of these...Ch. 6 - Divide your group into two subgroups. Have one...Ch. 6 - A molecular orbital calculation for Hi results in...Ch. 6 - Determine the hybridization about 0 in CH3OH.Ch. 6 - Determine the hybridization about C in H2CO.Ch. 6 - According to the valance bond theory, which kind...Ch. 6 - Use molecular orbital theory to determine the bond...Ch. 6 - Use molecular orbital theory to predict which...Ch. 6 - Use molecular orbital theory to determine which...Ch. 6 - Which hybridization scheme occurs about nitrogen...Ch. 6 - Prob. 8SAQCh. 6 - Prob. 9SAQCh. 6 - Prob. 10SAQCh. 6 - Which type of orbitals overlap to form the sigma...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- is SiBr4 Silicon (IV) tetra Bromine? is KClO2 potassium dihypochlorite ?arrow_forward"יוון HO" Br CI Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 Br Br Br HO OH H CI OH ✓ Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 CI Br יייון H Br OH OH CI Br ☐ none of the above × Garrow_forwardUS2 Would this be Uranium (II) diSulfide?arrow_forward
- nomenclature for PU(SO4)3arrow_forwardLi2CrO4 is this Lithium (II) Chromatearrow_forwardCheck the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. NH ** Molecule 1 NH Molecule 4 none of the above Х Molecule 3 Molecule 2 H N wwwwww.. HN Molecule 5 Molecule 6 HN R mw... N H ☐arrow_forward
- Nomenclature P4S3 Would this be tetraphsophorus tri sulfide?arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardBenzene-toluene equilibrium is often approximated as αBT = 2.34. Generate the y-x diagram for this relative volatility. Also, generate the equilibrium data using Raoult’s law, and compare your results to these.arrow_forward
- Given the most probable macrostate: s/k (K) Populations 300 4 200 8 100 16 0 32 Indicate how to demonstrate that the population of the levels is consistent with the Boltzmann distribution.arrow_forwardRank the following components in order of decreasing volatility: butane, n-pentane, iso-pentene (e.g., 3-methyl-1-butene), isoprene, pentanol? Briefly explain your answer.arrow_forwardViscosity of a liquid related to the activation energy.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY