
Boxes of various masses are on a friction-free level table.
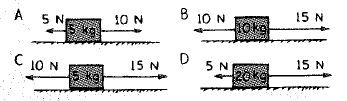
Rank each of the following from greatest to least.
a. the net forces on the boxes
b. the accelerations of the boxes
To rank: The net force on the box of various masses from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 22A
The ranking of forces from greatest to least is,
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given boxes on a friction-free level table are shown below.

Formula used:
Net force on an object, if two forces are travelling in same direction is,
Net force on an object, if two forces are travelling in same direction is,
Calculation:
Right side is considered as positive and left side is considered as negative.
Consider case (A)
Horizontal force acting along positive x-direction = Fx = 10 N
Horizontal force acting along negative x-direction F-x = 5 N
The net force acting on the box is,
Net force acting on box A is 5 N along positive direction of x-axis.
Consider case (B)
Horizontal force acting along positive x-direction = Fx = 15 N
Horizontal force acting along negative x-direction F-x = 10 N
The net force acting on the box is,
Net force acting on box is 5 N along positive direction of x-axis.
Consider case (C).
Horizontal force acting along positive x-direction= Fx = 15 N
Horizontal force acting along negative x-direction F-x = 10 N
The net force acting on the box is,
Net force acting on box is 5 N along positive direction of x-axis.
Consider case (D).
Horizontal force acting along positive x-direction= Fx = 15 N
Horizontal force acting along negative x-direction F-x = 5 N
The net force acting on the box is,
Net force acting on box is 10 N along positive direction of x-axis.
Conclusion:
Therefore, from greatest to least, the net force is
To rank: The net acceleration of the box of various masses from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 22A
Ranking of acceleration from greatest to least is, Case (A) = Case(C) > Case (B) = Case (D)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Given boxes on the friction less lever table is shown below.

Formula used:
Acceleration of box is,
Where, Fnet is the net force acting on the box
Calculation:
Consider Case (A):
Net force acting on box is 5 N along positive direction of x-axis.
Acceleration of 5 kg box along horizontal direction is,
Acceleration of 5 kg box along positive x-direction is 1 m/s2
Consider Case (B):
Net force acting on box 5 N along positive direction of x-axis.
Acceleration of 10 kg box along horizontal direction is,
Acceleration of 10 kg box along positive x-direction is 0.5 m/s2
Consider Case (C):
Net force acting on box is 5 N along positive direction of x-axis.
Acceleration of 5 kg box along horizontal direction is,
Acceleration of 5 kg box along positive x-direction is 1 m/s2
Consider Case (D):
Net force acting on box is 10 N along positive direction of x-axis.
Acceleration of 20 kg box along horizontal direction is,
Acceleration of 20 kg box along positive x-direction is 0.5 m/s2
Conclusion:
Therefore, acceleration from greatest to least, is
Case (A) = Case(C) > Case (B) = Case (D)
Chapter 6 Solutions
Conceptual Physics: The High School Physics Program
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- 10. A light bulb emits 25.00 W of power as visible light. What are the average electric and magnetic fields from the light at a distance of 2.0 m?arrow_forward9. Some 1800 years ago Roman soldiers effectively used slings as deadly weapons. The length of these slings averaged about 81 cm and the lead shot that they used weighed about 30 grams. If in the wind up to a release, the shot rotated around the Roman slinger with a period of .15 seconds. Find the maximum acceleration of the shot before being released in m/s^2 and report it to two significant figures.arrow_forwardIn the movie Fast X, a 10100 kg round bomb is set rolling in Rome. The bomb gets up to 17.6 m/s. To try to stop the bomb, the protagonist Dom swings the counterweight of a crane, which has a mass of 354000 kg into the bomb at 3.61 m/s in the opposite direction. Directly after the collision the crane counterweight continues in the same direction it was going at 2.13 m/s. What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the bomb right after the collision?arrow_forward
- Ultimate Byleth and Little Mac fight. Little Mac, who is a boxer, dashes forward at 26.6 m/s, fist first. Byleth moves in the opposite direction at 3.79 m/s, where they collide with Little Mac’s fist. After the punch Byleth flies backwards at 11.1 m/s. How fast, and in what direction, is Little Mac now moving? Little Mac has a mass of 48.5 kg and Byleth has a mass of 72.0 kg.arrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale as wellarrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale pleasearrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





