
Sketch the budget constraint.
Explanation of Solution
Maximum unit of good Y (0 unit of good X is purchased) that a person can purchase with the given income and price can be calculated by using the following formula:
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the maximum unit of Y that can be purchased.
The maximum unit of Y is 200 units.
Maximum unit of good X (0 unit of good Y is purchased) that a person can purchase with the given income and price can be calculated by using the following formula:
Substitute the respective values in Equation (2) to calculate the maximum unit of X that can be purchased.
The maximum unit of X is 50 units.
Option (a):
Figure 1 shows the budget constraint of case “a”.
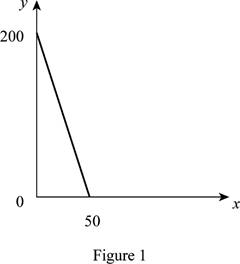
In Figure 1, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (b):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 25 and 40 respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 2 shows the budget constraint of case “b”.
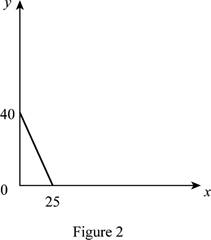
In Figure 2, the vertical axis measure price of good Y and horizontal axis measures price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (c):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 40 and 5, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 3 shows the budget constraint of case “c”.
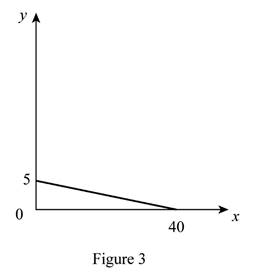
In Figure 3, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (d):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 20 and 50, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 4 shows the budget constraint of case “d”.
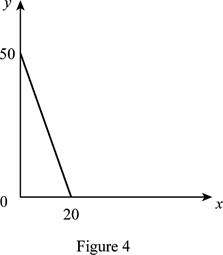
In Figure 4, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (e):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 4 and 6, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 5 shows the budget constraint of case “e”.
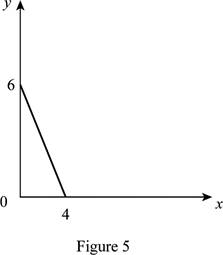
In Figure 5, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (f):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 24 and 4, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 6 shows the budget constraint of case “f”.
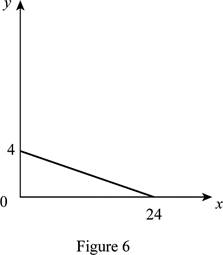
In Figure 6, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (g)
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 4 and 24, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 7 shows the budget constraint of case “g”.
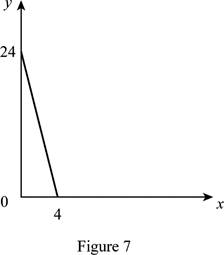
In Figure 7, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Budget constraints: Restrictions imposed on household’s choices by the factors like wealth, income and price of product are termed as the budget constraint.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles Of Microeconomics
- The preferences of a consumer are represented by the following utility function: U = min (×1, 2x2) If income is 100 and p1=p2=1 a) What is the optimal bundle? b) If p₁=4, what is the new optimal bundle? c) If p2=4, what is the new optimal bundle? d) Decompose the price effect into income and substitution effect and provide a graphical representation of your results.arrow_forwardChallenges of Nepal's foreign trade.arrow_forwardSolarrow_forward
- The answer is not Carrow_forwardSocial capital includes: a) labour, produced capital, and natural capital. b) human capital, physical capital, and natural resources. c) labour, physical capital, and human capital. d) labour, physical capital, and produced capital.arrow_forwardGeneral Accounting Question solution and give me Blank ? Carrow_forward
- It is possible to use transformational leadership strategies to reach unethical objectives. Traditional leadership theories and morals standards are not adequate to help employees solve complex organizational issues. For the statement above, argue in position for both in favor or opposed to the statements.arrow_forwardDiscuss the preferred deterrent method employed by the Zambian government to combat tax evasion, monetary fines. As noted in the reading the potential penalty for corporate tax evasion is a fine of 52.5% of the amount evaded plus interest assessed at 5% annually along with a possibility of jail time. In general, monetary fines as a deterrent are preferred to blacklisting of company directors, revoking business operation licenses, or calling for prison sentences. Do you agree with this preference? Should companies that are guilty of tax evasion face something more severe than a monetary fine? Something less severe? Should the fine and interest amount be set at a different rate? If so at why? Provide support and rationale for your responses.arrow_forwardanswerarrow_forward
- Discuss the preferred deterrent method employed by the Zambian government to combat tax evasion, monetary fines. As noted in the reading the potential penalty for corporate tax evasion is a fine of 52.5% of the amount evaded plus interest assessed at 5% annually along with a possibility of jail time. In general, monetary fines as a deterrent are preferred to blacklisting of company directors, revoking business operation licenses, or calling for prison sentences. Do you agree with this preference? Should companies that are guilty of tax evasion face something more severe than a monetary fine? Something less severe? Should the fine and interest amount be set at a different rate? If so at why? Provide support and rationale for your responses.arrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forwardFor the statement below, argue in position for both in favor or opposed to the statement. Incompetent leaders can't be ethical leaders. Traditional leadership theories and moral standards are not adequate to help employees solve complex organizational issues.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





