
Mathematics for Machine Technology
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781133281450
Author: John C. Peterson, Robert D. Smith
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 57, Problem 1A
Trace this line segment two times. On one copy construct a perpendicular bisector of the segment. On the other copy divide the segment into three equal segments.
Expert Solution & Answer
To determine
To construct:
A perpendicular bisector of the line segment.
To divide: The line segment into three equal parts.
Answer to Problem 1A
Area
Explanation of Solution
Steps of construction:
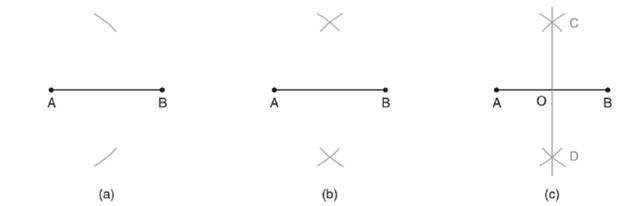
- Taking A as a centre and radius more than half of AB, draw arcs on both the above and below the line segment AB as shown in figure (a).
- Similarly, taking B as a centre and radius same as above draw another arc on both the sides of the line segment that intersects the first pair of arcs as shown in the diagram (b).
- Join both the arcs by drawing a straight line. Line CD as shown in figure (c), is the perpendicular bisector of line segment AB with O as a centre.
Divide the line segment into three equal parts:
Steps of construction:
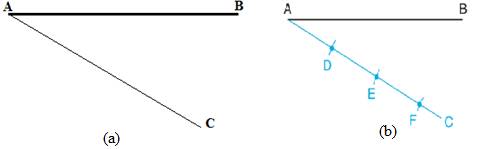
- From point A, draw a line segment AC forming an angle with AB as shown in fig(a).
- On line segment AC with the help of a compass mark three equal arcs D, E and F of any length (b).
- Connect point F with point B.
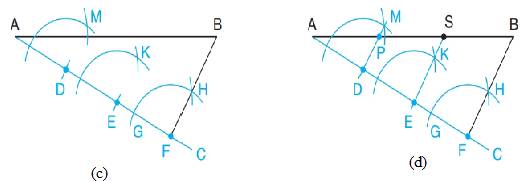
- Now taking F as a centre, draw arcs which intersect the line segment AC at G and BF at H.
- Repeat the procedure by taking D and E as centre and mark an arc of same radii as shown in figure.
- With the help of a compass measure the distance GH and mark the same distance from other two arcs as well which intersects the arcs at point K and M respectively.
- Join E with K and D with M and extending the lines past AB. Thus, line segment AB is divided into three equal parts.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
Consider a simplified two-joint robotic arm where the two joints are connected by rigid links.Each joint has a mass, and the links are modeled as idealized rods. The motion of each jointaffects the other through the coupling of forces. The system can be modeled by the followingsecond-order coupled ODEs:
m1θ1" + k1(θ1 − θrest) + k3(θ1 − θ2) = 0 (equation 1)m2θ2" + k2(θ2 − θrest) + k3(θ2 − θ1) = 0 (equation 2)
where θ1(t) and θ2(t) represent the angular positions of the first and second joints, respec-tively. m1 and m2 are the effective masses at each joint. k1, k2 and k3 are the stiffnessconstants representing the elastic restoring forces in the joints and links. θrest = 0 representsthe equilibrium position for each joint.The parameters are:m1 = 1, m2 = 1, θrest = 0, k1 = 1, k2 = 2, k3 = 3, θrest = 0The initial conditions are:θ1(0) = 1, θ2(0) = 2Please solve by hand to get θ1(t) and θ2(t) using eigenvectors and eigenvalues. Show all steps/calculations, and provide a written description…
3feet in 1secound; 21feet in x seconds
(15 pts) Show your work to get full credit! Compute a QR factorization of the
matrix
Chapter 57 Solutions
Mathematics for Machine Technology
Ch. 57 - Trace this line segment two times. On one copy...Ch. 57 - Find the length of x. Round the answer to 2...Ch. 57 - Prob. 3ACh. 57 - Prob. 4ACh. 57 - Prob. 5ACh. 57 - Prob. 6ACh. 57 - Prob. 7ACh. 57 - Prob. 8ACh. 57 - Prob. 9ACh. 57 - Prob. 10A
Ch. 57 - Prob. 11ACh. 57 - Prob. 12ACh. 57 - Prob. 13ACh. 57 - Express each area as indicated. Round each answer...Ch. 57 - Prob. 15ACh. 57 - Prob. 16ACh. 57 - Prob. 17ACh. 57 - Prob. 18ACh. 57 - Prob. 19ACh. 57 - Prob. 20ACh. 57 - Prob. 21ACh. 57 - Prob. 22ACh. 57 - Prob. 23ACh. 57 - Prob. 24ACh. 57 - Prob. 25ACh. 57 - Prob. 26ACh. 57 - Prob. 27ACh. 57 - Prob. 28ACh. 57 - Prob. 29ACh. 57 - Prob. 30ACh. 57 - Prob. 31ACh. 57 - Prob. 32ACh. 57 - Prob. 33ACh. 57 - Prob. 34ACh. 57 - Prob. 35ACh. 57 - Prob. 36ACh. 57 - Prob. 37ACh. 57 - Prob. 38ACh. 57 - Prob. 39ACh. 57 - Prob. 40ACh. 57 - Prob. 41ACh. 57 - Prob. 42ACh. 57 - Prob. 43ACh. 57 - Prob. 44ACh. 57 - Prob. 45ACh. 57 - Prob. 46ACh. 57 - Prob. 47ACh. 57 - Prob. 48ACh. 57 - Prob. 49ACh. 57 - Prob. 50ACh. 57 - Prob. 51ACh. 57 - Prob. 52ACh. 57 - Prob. 53ACh. 57 - Prob. 54ACh. 57 - Prob. 55ACh. 57 - Prob. 56ACh. 57 - Prob. 57ACh. 57 - Prob. 58ACh. 57 - Prob. 59ACh. 57 - Prob. 60ACh. 57 - Prob. 61ACh. 57 - Prob. 62ACh. 57 - Prob. 63ACh. 57 - Prob. 64ACh. 57 - Prob. 65ACh. 57 - Prob. 66ACh. 57 - Prob. 67ACh. 57 - Prob. 68ACh. 57 - Prob. 69ACh. 57 - Prob. 70ACh. 57 - Prob. 71ACh. 57 - Prob. 72ACh. 57 - Prob. 73ACh. 57 - Prob. 74ACh. 57 - Find the unknown area, height, or base for each of...Ch. 57 - Find the unknown area, height, or base for each of...Ch. 57 - A cross section of an aluminum bar in the shape of...Ch. 57 - Prob. 78ACh. 57 - Prob. 79ACh. 57 - One of the examples showed how to find the area of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (5) Let G be a group. Show that G acts on itself via the action g⚫a (i.e. using the binary operation of G) for all g, a Є G. [ for each of the three axioms, plus 1 for conclusion] = gaarrow_forward= (2) Let H {id, (12) (34), (13)(24), (14)(23)}. Prove that H is a sub- group of the symmetric group S4 of degree 4. each of the four axioms, plus 1 for the conclusion] 1 forarrow_forward(15 pts) Show your work to get full credit! Compute a singular value decomposition of the matrix A-( 7²)arrow_forward
- Sudoku Puzzle Rules Solving a Sudoku puzzle does not require the knowledge of mathematics but it does require logical thinking. A Sudoku puzzle is a grid of nine by nine squares or cells that have been subdivided into nine "regions" of three by three cells. Consider the following diagram: The objective of Sudoku is to enter a digit from 1 through 9 in each cell, in such a way that: Each horizontal row (shown in blue) contains each digit exactly once. Each vertical column (shown in pink) contains each digit exactly once. Each sub grid or region (shown in orange) contains each digit exactly once. In each Sudoku puzzle, some digits have already been entered, you may not change these. Your job is to fill the remaining cells with digits keeping in mind the three rules discussed above. Sudoku puzzles have become so popular that they can be found in newspapers and magazines around the world. If you are ever planning a long trip where you may be stuck in a car, Sudoku can help to pass the…arrow_forward(3) Let G be a group and let gЄ G. Prove that the function f : G→ G given by f(x) = gx is bijective (i.e. injective, and surjective). [ 2 for injectivity, 2 for surjectivity, 1 for bijectivity]arrow_forward(4) Let X = {(a,b) : a,bЄ Z, a on X given by (a, b) R(c, d) if ad 0,60}. Show that the relation R = bc is an equivalence relation. [ 1 for reflexivity, 1 for symmetry, 1 for transitivity, 1 for conclusion]arrow_forward
- (15 pts) Show your work to get full credit! Compute a diagonalization of the matrix -1 0 0 A = 0 1 1 0 20arrow_forward(1) Let G = R \ {1}. the set of all real numbers except 1. Show that G, together with the operation * given by x * y = x + y = xy for all x, y Є G, is a group. [5: 1 for each of the four axioms, and 1 for the conclusion] Hint: See Question 3.2 in the Course Notes for an example of how to write this down formally. See also Exercise 7 in Section 4.7 of [Groups, C. R. Jordan and D. A. Jordan], available online via the Libraryarrow_forwardInstructions: Instructions: Please show as much work as possible to clearly show the steps you used to find the solution. Part 1: In M4LE1 Hand-in Assignment you were to select a vehicle you would like to drive. In this hand-in assignment you are to choose a similar (or same) vehicle and find the cost to lease it. Describe the vehicle by stating make, model, special features, colour, et cetera. Find the price of the vehicle. You may look for the price at a dealer, in a newspaper, on TV, on the Internet, or source of your choice. Be sure to indicate the price and where you found the information. Assume that you have $5000 for a down payment to apply to the lease. Calculate the total cost of leasing the vehicle, including the down payment and applicable taxes. You may want to use a leasing calculator. Be sure to show how you arrived at your answer. Part 2: Compare the cost of buying the vehicle using your information from M4LE1 to the cost of leasing determined in Part 1. Would…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt Asap Upvotearrow_forwardThis problem requires you to apply your skills with fractions and think logically to develop your response. Please show as much work as possible to clearly show the steps you used to find the solution. You must support any results you give with an explanation that makes sense. A wealthy doctor owned 17 expensive cars. Before he died, he prepared a wacky will for his 3 sons. The will stated that his 17 cars be divided among his three sons in a particular way: half of the cars were to go to his eldest son one-third to his middle son one-ninth to his youngest son. Everyone was puzzled. How can 17 cars be divided in such a way? While the sons were arguing about what to do, a mathematics teacher drove up in her new sports car. "Can I be of help?" she asked. After the sons explained the situation, she parked her sports car next to the doctor’s 17 cars and hopped out. "How many cars are there now?" The sons counted 18. Then she carried out the terms of the will. She…arrow_forwardYour task in this assignment is to decide whether owning a vehicle is worth the monthly costs. Follow the steps below to justify your decision: Choose a vehicle that you would be interested in purchasing. It can be a used vehicle or a new vehicle. Provide a description of the vehicle and the purchase price. Determine the monthly payment in order to buy the vehicle. You may want to use one of the payment calculators used in a previous lesson. Estimate how much you will spend on maintenance and repairs per month on the vehicle. Justify your estimates based on information given in the learning experience or perhaps information you have obtained from another source. Estimate your monthly gasoline cost and justify your estimate using the fuel economy of your chosen vehicle and the calculations provided in the learning experience. How much it would cost to purchase a monthly bus pass. Determine how much you would save by travelling by public transportation rather than using your own…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...
Algebra
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9780998625713
Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Points, Lines, Planes, Segments, & Rays - Collinear vs Coplanar Points - Geometry; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dDWjhRfBsKM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Naming Points, Lines, and Planes; Author: Florida PASS Program;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F-LxiLSSaLg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY