
Concept explainers
(A)
To draw:
The graph of the given function
(A)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
f(x)=3−x+1g(x)=3x−2
Concept used:
Definition of the
The derivative of a function y=f(x) of a variable x is a measure of the rate at which the value y of the function changes with respect to x
Calculation:
The function
f(x)=3−x+1g(x)=3x−2...................(1)
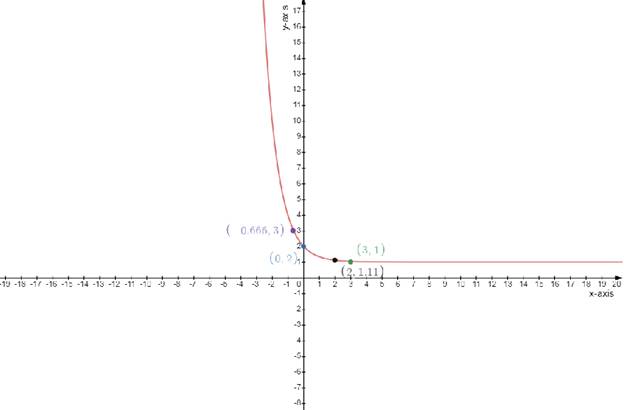
Draw the table
f(x)=3−x+1
Test one point in each of the region formed by the graph
If the point satisfies the function then shade the entire region to denote that every point in the region satisfies the function
| x−axis | 0 | 3 | −0.66 | 2 |
| y−axis | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1.11 |
(B)
To draw:
The graph of the given function
(B)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
f(x)=3−x+1g(x)=3x−2
Concept used:
Definition of the differentiation:-Differentiation is the action of computing a derivative
The derivative of a function y=f(x) of a variable x is a measure of the rate at which the value y of the function changes with respect to x
Calculation:
The function
f(x)=3−x+1g(x)=3x−2...................(1)
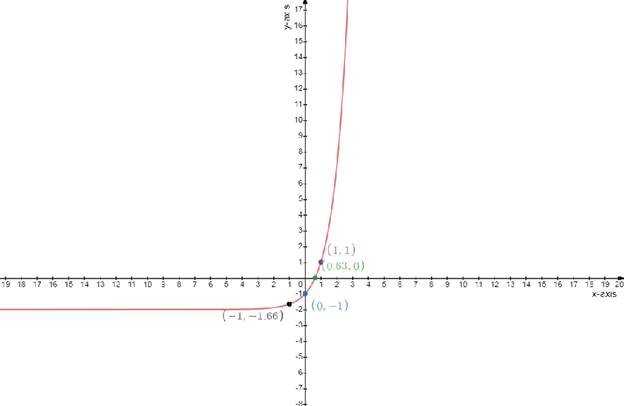
Draw the table
g(x)=3x−2
Test one point in each of the region formed by the graph
If the point satisfies the function then shade the entire region to denote that every point in the region satisfies the function
| x−axis | 0 | 0.63 | 1 | −1 |
| y−axis | −1 | 0 | 1 | −1.66 |
(C)
To draw:
The graph of the given function
(C)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
f(x)=3−x+1g(x)=3x−2
Concept used:
Definition of the differentiation:-Differentiation is the action of computing a derivative
The derivative of a function y=f(x) of a variable x is a measure of the rate at which the value y of the function changes with respect to x
Calculation:
The function
f(x)=3−x+1g(x)=3x−2...................(1)
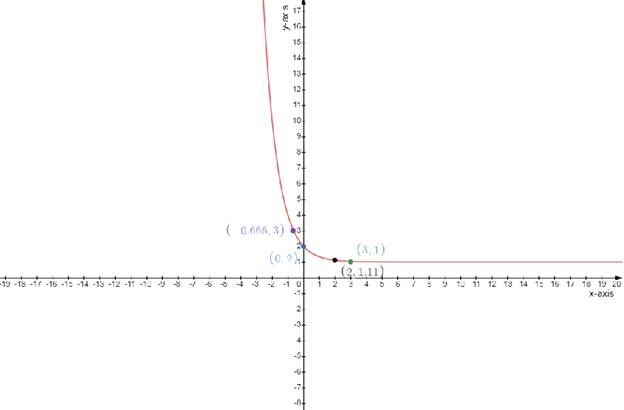
Draw the table
f(x)=3−x+1
Test one point in each of the region formed by the graph
If the point satisfies the function then shade the entire region to denote that every point in the region satisfies the function
| x−axis | 0 | 3 | −0.66 | 2 |
| y−axis | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1.11 |
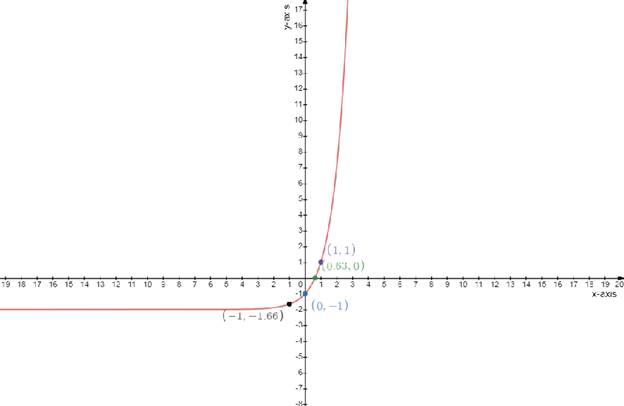
Draw the table
g(x)=3x−2
Test one point in each of the region formed by the graph
If the point satisfies the function then shade the entire region to denote that every point in the region satisfies the function
| x−axis | 0 | 0.63 | 1 | −1 |
| y−axis | −1 | 0 | 1 | −1.66 |
Chapter 5 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
- 5:38 Video Message instructor Submit Question ||| Darrow_forward8:38 *** TEMU TEMU -3 -2 7 B 2 1 & 5G. 61% 1 2 -1 Based on the graph above, determine the amplitude, period, midline, and equation of the function. Use f(x) as the output. Amplitude: 2 Period: 2 Midline: 2 ☑ syntax error: this is not an equation. Function: f(x) = −2 cos(πx + 2.5π) +2× Question Help: Worked Example 1 ☑ Message instructor Submit Question ||| <arrow_forward8:39 *** TEMU 5G 60% A ferris wheel is 28 meters in diameter and boarded from a platform that is 2 meters above the ground. The six o'clock position on the ferris wheel is level with the loading platform. The wheel completes 1 full revolution in 4 minutes. The function h = f(t) gives your height in meters above the ground t minutes after the wheel begins to turn. What is the amplitude? 14 meters What is the equation of the Midline? y = 16 What is the period? 4 meters minutes The equation that models the height of the ferris wheel after t minutes is: f(t): = ƒ (3) = ·−14(0) + 16 syntax error: you gave an equation, not an expression. syntax error. Check your variables - you might be using an incorrect one. How high are you off of the ground after 3 minutes? Round your answe the nearest meter. ||| <arrow_forward
- Use Laplace transform to find L{f(t)} f(t) = tsin(t)arrow_forward√3/2 1 √1-x2 arcsinx 1/2 dx = 2arrow_forwardThe evolution of a population of Hippos, R(t), in hundreds, time in years, in an African National Park is given by the equation, dR dt (a) Solve the system exactly for R(t). = R(7 – R); R(0) = 3 2 (b) What happens as the time t → ∞o, i.e. what is the population a long time in the future? (c) Write an Euler scheme and compute until the population levels off (using Excel, Matlab, Octave, LibreCalc or similar). Do it twice, once with At = 0.1 and once with At = 0.05. (d) Plot all of your solutions on the same set of axes and comment.arrow_forward
- find For triangle ABC, with vertices A = (3,-1,2), B = (-5,4,-4) and C = (6, −1, −1), (a) the length of side AB, (b) the equation of the line that passes through A and B, (c) the angle at vertex B, (d) a vector perpendicular to the plane containing the triangle ABC, (e) the area of the triangle ABC. (f) the equation of a plane passing through A, B and C.arrow_forwardShowing all working, use the row reduction method to find the inverse of B, given by 5 -1 B = -3 1 3 1 -3 2arrow_forwardConsider the matrix A, given by +63) A = 1 -3 4 -3 4 5 -105 (a) Find the determinant of the matrix, A. (b) Find all possible solutions, x, to the system Ax = b, where b is the column vector, (1,2, −4).arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





