
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
To sketch the
Concept Introduction:
The system assigns a vector
Substitute the given system in the equation
The stable manifold of a fixed point is the set of all points in the plane which tends to the fixed point as time goes to positiveinfinity.
The unstable manifold for a fixed point is the set of all points in the plane which tends to the fixed point as time goes to negative infinity.
Answer to Problem 9E
Solution:
a) The vector field of the system
b) It is shown that the trajectories of the system are hyperbolas of the form
c) The equations for the stable and unstable manifolds for origin are
d) The solutions in terms of new variables
e) The equations for the stable and unstable manifolds in terms of
f) The general solution for
Explanation of Solution
a) The vector field of the given system
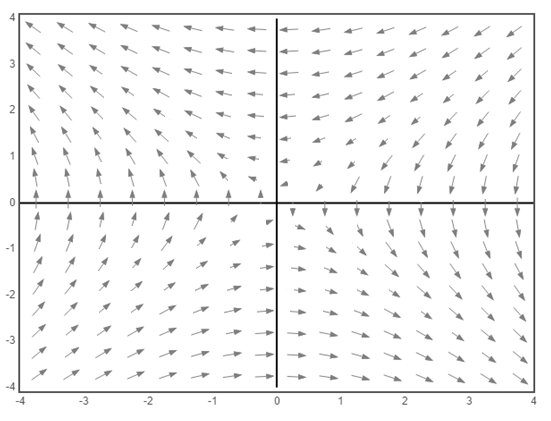
b) Consider the given system,
It can be shown that the trajectories of the system are hyperbolas of the form
Substituting
Thus, the given system implies
Integrating the above equation,
Thus, the trajectory of the given system is the hyperbola of the form
c) The origin is a saddle point for the given system. From the sketch of the vector field, it is clear that the equation
Also, the equation
This can also be proved by substituting
This linear system gives a stable fixed point.
Similarly, substituting
This linear system gives an unstable fixed point.
Therefore, the equations for the stable and unstable manifolds for origin is
d) Introducing new variables
The system can be rewritten as
Substituting
Again, substituting
The above equation can be also represented as
Solving for the initial conditions,
Substituting
Substituting the value of
Similarly substituting
Again, substituting
The above equation can be also represented as
Solving for the initial conditions,
Substituting
Substituting the value of
Hence, the solutions of the linear equation for the initial condition
e) Since the equations of the stable and unstable manifold are
Therefore, substituting
Similarly, substituting
Thus,
f) Since
Solving the above equations to get the values of
Substituting
Again, substituting
Similarly, substituting
Again, substituting
Therefore, the general solution for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos
- Find a system of two equations in two variables, x1 and x2, that has the solution set given by the parametric representation x1=t and x2=3t4, where t is any real number. Then show that the solutions to the system can also be written as x1=43+t3 and x2=t.arrow_forwardIn Exercises 19 and 20, use the x, y, and z-intercepts to sketch the plane for each equation. x+2y+z=6arrow_forwardA Edit oX Create Talking: Consider in an orthonormal system (0; t,j), the straight line (D) of equation: 2x-y+4=0, and the two points A(1; 2) and B(2; 3). 1) Give the directing vector, normal vector and the slope of (D). 2) Calculate the distance from the point B to the straight line (D). 3) Write the system of parametric equations of straight line (D') passing through A and parallel to (D). 4) Write the Cartesian equation of the straight line (D") passing through B and perpendicular to (D). X =-t 5) Let (A) be a straight line defined by: t =t+1' where t is a real parameter. a. Show that (D) and (A) are secant. b. Find the coordinates of I, their point of intersection. TOSHIBA ofarrow_forward
- 1.) is the quantity r(t+h)-r(t) a vector or a scalar? identify this object in the applet. 2.) is (r(t+h)-r(t))/h a vector or a scalar? Describe what represents r(t+h)-r(t)/h 3.) slide h toward to 0. How does r(t+h)-r(t) change? How about (r(t+h)-r(t))/h?arrow_forwardFind the linear equation of the plane through the point (1, 7, 6) and parallel to the plane x + 3y +5z +4 = 0.arrow_forward
 Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,


