
a)
Labeled budget line on the graph
a)
Explanation of Solution
To draw budget line, we need:
In the equation form, the budget constraint can be written as:
5X+20Y=100
To find out the intercepts of the budget line and to find the x-intercept (0 for y) of the line:
Now, to find the y-intercept (0 for x) of the line:
From these intercepts, the budget line by on the x- and y-intercepts would be shown on graph as:
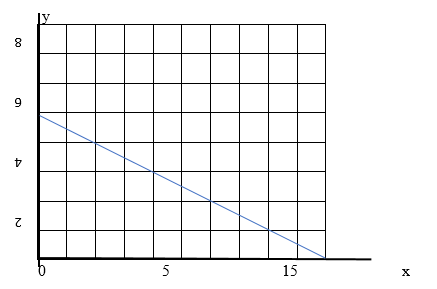
Introduction: A budget line is the graphical presentation of a price line that shows possible combination of goods that can be bought at various costs or different levels of income.
b)
Maximizing total utility if income is $100, good x is of $5, and good y is of $10. And, with current consumption one receives 100 utils from consuming last unit of good x and 400 utils from consuming last unit of good y.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Yes, one can enjoy maximization of utility. Because from good x one can maximize by 100/5 and it can be 400/20 from good y, therefore, per dollar spent on good x, the
Introduction: Marginal utility refers to the benefit or satisfaction of person by consuming one additional unit of the good.
c)
The total and marginal utility by consuming one another unit of good
c)
Explanation of Solution
By consuming another unit of good x, both the marginal utility of and the total utility of good x will decline because according to the law of diminishing marginal utility, an increase consumption of good (good x) at the time when keeping the same consumption of another good (good y), the marginal utility from additional consumption (good x) decreases.
This is the reason which is responsible to decrease the marginal utility per dollar spent on good x. And, from the marginal utility per dollar spent on good x, the additional benefit per dollar spent on good y will be higher but the total utility can be greater if one less unit would be spent on good x.
Introduction: Marginal utility refers to the benefit or satisfaction of person by consuming one additional unit of the good.
Chapter 51 Solutions
Krugman's Economics For The Ap® Course

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





