
Concept explainers
Consumers were surveyed on the relative number of visits to a Sears store (often, occasional, and never) and if the store was located in an enclosed mall (yes and no). When variables are measured nominally, such as these data, the results are usually summarized in a
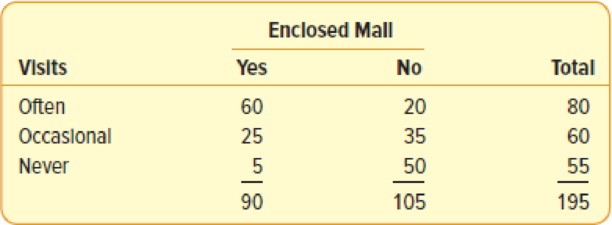
What is the
- (a) Visited a Sears store often?
- (b) Visited a Sears store in an enclosed mall?
- (c) Visited a Sears store in an enclosed mall or visited a Sears store often?
- (d) Visited a Sears store often, given that the shopper went to a Sears store in an enclosed mall?
In addition:
- (e) Are the number of visits and the enclosed mall variables independent?
- (f) What is the probability of selecting a shopper who visited a Sears store often and it was in an enclosed mall?
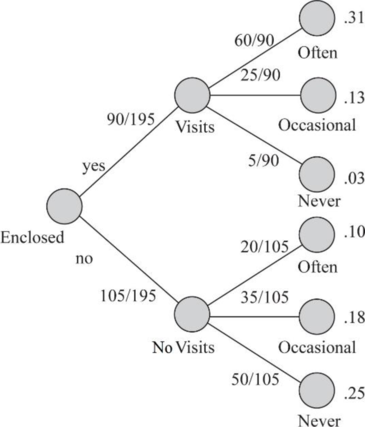
- (g) Draw a tree diagram and determine the various joint probabilities.
a.
Obtain the probability of selecting a shopper who visits a Sears store often.
Answer to Problem 8SR
The probability of selecting a shopper who visits a Sears store often is 0.4103.
Explanation of Solution
Here, number of shopper who visited Sears often is 80. Total number of shoppers is 195.
The required probability is obtained as given below:
Thus, the probability of selecting a shopper who visits a Sears store often is 0.4103.
b.
Obtain the probability of selecting a shopper in an enclosed mall.
Answer to Problem 8SR
The probability of selecting a shopper in an enclosed mall is 0.4615.
Explanation of Solution
Here, number of shopper who visited an enclosed mall is 90.
The required probability is obtained as given below:
Thus, the probability of selecting a shopper in an enclosed mall is 0.4615.
c.
Obtain the probability of selecting a shopper in an enclosed mall or visited Sears store often.
Answer to Problem 8SR
The probability of selecting a shopper in an enclosed mall or visited Sears store often is 0.5641.
Explanation of Solution
Here, number of shopper who visited an enclosed mall and often is 60.
Thus, the probability of selecting a shopper in an enclosed mall or visited Sears store often is 0.5641.
d.
Obtain the probability of selecting a shopper who visited Sears store often given that shopper went to a Sears store in an enclosed mall.
Answer to Problem 8SR
The probability of selecting a shopper who visited Sears store often given that shopper went to a Sears store in an enclosed mall is 0.6667.
Explanation of Solution
The required probability is obtained as given below:
Thus, the probability of selecting a shopper who visited Sears store often given that shopper went to a Sears store in an enclosed mall is 0.6667.
e.
Check whether number of visits and the enclosed mall variables independent.
Answer to Problem 8SR
Number of visits and the enclosed mall variables are not independent.
Explanation of Solution
Two events A and B are independent if
From part (d),
From part (a),
Thus,
f.
Obtain the probability of selecting a shopper in an enclosed mall and visited Sears store often.
Answer to Problem 8SR
The probability of selecting a shopper in an enclosed mall and visited Sears store often is 0.3077.
Explanation of Solution
Here, number of shopper who visited an enclosed mall and often is 60.
Thus, the probability of selecting a shopper in an enclosed mall and visited Sears store often is 0.3077.
g.
Construct a tree diagram that shows probabilities, conditional probabilities and joint probabilities.
Explanation of Solution
The first branch represents the shoppers visited enclosed mall which is divided into two categories. In the second branch, each category is subdivided into three different visits. The probabilities under the second branch represents conditional probabilities. The product of the probabilities in two branches represent joint probabilities.
The tree diagram is as given below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics
- Theorem 3.5 Suppose that P and Q are probability measures defined on the same probability space (2, F), and that F is generated by a л-system A. If P(A) = Q(A) for all A = A, then P = Q, i.e., P(A) = Q(A) for all A = F.arrow_forward6. Show that, for any random variable, X, and a > 0, Lo P(x -00 P(x < xarrow_forward5. Suppose that X is an integer valued random variable, and let mЄ N. Show that 8 11118 P(narrow_forward食食假 6. Show that I(AUB) = max{1{A}, I{B}} = I{A} + I{B} - I{A} I{B}; I(AB)= min{I{A}, I{B}} = I{A} I{B}; I{A A B} = I{A} + I{B}-21{A} I{B} = (I{A} - I{B})². -arrow_forward11. Suppose that the events (An, n ≥ 1) are independent. Show that the inclusion- exclusion formula reduces to P(UAL)-1-(1-P(Ak)). k=1 k=1arrow_forward8. Show that, if {Xn, n≥ 1} are independent random variables, then sup X,, A) < ∞ for some A.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill

 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill

 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL