
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified whether the given molecule is chiral.
Concept introduction:
The molecule with at least one chiral center having no plane of symmetry is called a chiral molecule. A chiral center is a tetrahedral stereocenter. The atom at the chiral center must be
Answer to Problem 5.38P
The given molecule is not a chiral molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
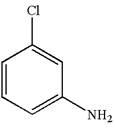
A chiral center must be an
The given molecule is identified as achiral on the basis of the presence of a chiral center.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified whether the given molecule is chiral.
Concept introduction:
The molecule with at least one chiral center having no plane of symmetry is called a chiral molecule. A chiral center is a tetrahedral stereocenter. The atom at the chiral center must be
Answer to Problem 5.38P
The given molecule is a chiral molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
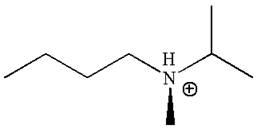
In this molecule, the nitrogen atom is a chiral center bonded to four different groups
The given molecule is identified as chiral on the basis of the presence of a chiral center.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified whether the given molecule is chiral.
Concept introduction:
The molecule with at least one chiral center having no plane of symmetry is called a chiral molecule. A chiral center is a tetrahedral stereocenter. The atom at the chiral center must be
Answer to Problem 5.38P
The given molecule is a chiral molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
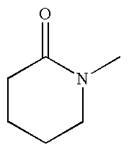
The molecule consists of a ring made up of five carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom. The nitrogen atom is bonded to three different groups having pyramidal shape and a non-bonded electron pair pointing to the unoccupied tetrahedral corner. This makes the nitrogen a chiral center.
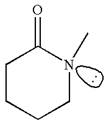
As this molecule has only one chiral center, it cannot possess any symmetry, and hence, this is a chiral molecule.
The given molecule is identified as chiral on the basis of the presence of a chiral center.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified whether the given molecule is chiral.
Concept introduction:
The molecule with at least one chiral center having no plane of symmetry is called a chiral molecule. A chiral center is a tetrahedral stereocenter. The atom at the chiral center must be
Answer to Problem 5.38P
The given molecule is not a chiral molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
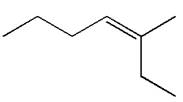
A chiral center must be an
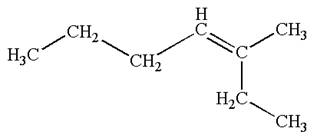
Therefore, these carbon atoms are also not chiral centers. Hence this is not a chiral center.
The given molecule is identified as achiral on the basis of the presence of a chiral center.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified whether the given molecule is chiral.
Concept introduction:
The molecule with at least one chiral center having no plane of symmetry is called a chiral molecule. A chiral center is a tetrahedral stereocenter. The atom at the chiral center must be
Answer to Problem 5.38P
The given molecule is not a chiral molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
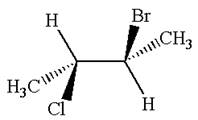
The given molecule possesses two chiral carbons. One carbon is bonded to four different groups,
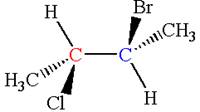
As the bonded atoms are not exactly same, the molecule does not have a symmetry plane; hence, it is a chiral molecule.
The given molecule is identified as chiral on the basis of the presence of a chiral center.
(f)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified whether the given molecule is chiral.
Concept introduction:
The molecule with at least one chiral center having no plane of symmetry is called a chiral molecule. A chiral center is a tetrahedral stereocenter. The atom at the chiral center must be
Answer to Problem 5.38P
The given molecule is not a chiral molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
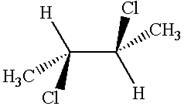
The given molecule possesses an inversion center indicated by the blue dot, which reflects all the atoms into identical atoms through
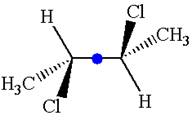
As the molecule has an inversion center, it is not a chiral molecule.
The given molecule is identified as achiral on the basis of the presence of a chiral center.
(g)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified whether the given molecule is chiral.
Concept introduction:
The molecule with at least one chiral center having no plane of symmetry is called a chiral molecule. A chiral center is a tetrahedral stereocenter. The atom at the chiral center must be
Answer to Problem 5.38P
The given molecule is not a chiral molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
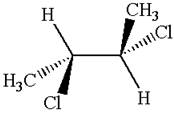
The given molecule possesses two chiral carbons bonded to four different groups,
The given molecule is identified as chiral on the basis of the presence of a chiral center.
(h)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified whether the given molecule is chiral.
Concept introduction:
The molecule with at least one chiral center having no plane of symmetry is called a chiral molecule. A chiral center is a tetrahedral stereocenter. The atom at the chiral center must be
Answer to Problem 5.38P
The given molecule is not a chiral molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
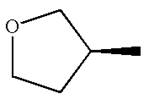
The molecule consists of a ring made up of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom with a substituted methyl group. The carbon having the methyl substituent is a chiral center that has four different groups bonded.
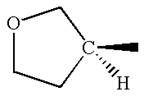
The molecule does not possess any symmetry plane; hence, it is a chiral molecule.
The given molecule is identified as chiral on the basis of the presence of a chiral center.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- Indicate the correct option.a) Graphite conducts electricity, being an isotropic materialb) Graphite is not a conductor of electricityc) Both are falsearrow_forward(f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
- (c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- reaction scheme for C39H4202 Hydrogenation of Alkyne (Alkyne to Alkene) show reaction (drawing) pleasearrow_forwardGive detailed mechanism Solution with explanation needed. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardShow work with explanation needed....don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

