
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.26P
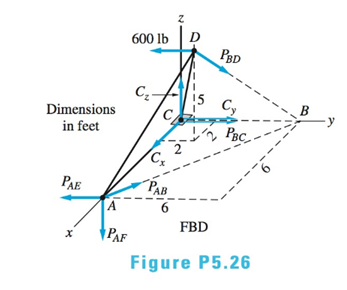
The figure shows the FBD of a portion of the space truss shown in Fig. P5.25. Use this FBD to find the force in member BD.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q1: For the following force system, find the moments with respect to axes x, y, and z
Q10) Body A weighs 600 lb contact with smooth surfaces at D and E. Determine the tension in the cord
and the forces acting on C on member BD, also calculate the reaction at B and F.
Cable
6'
3'
www
Help ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤال
Chapter 5 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
Ch. 5 - Bar AB of negligible weight is supported by a...Ch. 5 - Draw the FBD for the bar described in Prob. 5.1 if...Ch. 5 - The space truss ABCD in the shape of a tetrahedron...Ch. 5 - Draw the FBD of the portion BCD of the space truss...Ch. 5 - The homogeneous plate of weight W is supported by...Ch. 5 - The bar ABCD of negligible weight is supported by...Ch. 5 - The shaft-pulley assembly is supported by the...Ch. 5 - The 60-lb homogeneous door is supported by hinges...Ch. 5 - Draw the FBD for bar BCD. The connections at A and...Ch. 5 - The homogeneous 360-lb plate with a rectangular...
Ch. 5 - The L-shaped rod, supported by slider bearings at...Ch. 5 - The homogeneous 240-lb bar is supported by a rough...Ch. 5 - In Sample Problem 5.4, determine the tension TAC...Ch. 5 - In Sample Problem 5.5, compute the tension TAD...Ch. 5 - In Sample Problem 5.5, determine Oy with one...Ch. 5 - Determine the tension TB in Sample Problem 5.6...Ch. 5 - Compute the tension TAE in Sample Problem 5.7...Ch. 5 - The 80-lb homogeneous plate is suspended from four...Ch. 5 - The three bars are welded together to form a rigid...Ch. 5 - The compound bar is supported by a thrust bearing...Ch. 5 - The homogeneous 20-kg door is held in the...Ch. 5 - The light boom AB is attached to the vertical wall...Ch. 5 - The homogeneous 80-kg sign is suspended from a...Ch. 5 - The bar ABC is supported by a ball-and-socket at A...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members PAE,PAF, and PBG...Ch. 5 - The figure shows the FBD of a portion of the space...Ch. 5 - Calculate all forces acting on the bar AB...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members AD, BD, and CD of...Ch. 5 - Find the tension in cable BE that supports the bar...Ch. 5 - For the structure in Prob. 5.9, determine the...Ch. 5 - Calculate the reaction at D for the structure...Ch. 5 - Calculate the reaction at D for the structure...Ch. 5 - Determine the tension in each of the three ropes...Ch. 5 - Using only one equilibrium equation, compute the...Ch. 5 - The homogeneous 25-kg bar AB is supported by a...Ch. 5 - The shaft AB is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 5 - The bar ABCD has a built-in support at A....Ch. 5 - The total weight of the L-shaped beam of constant...Ch. 5 - The bent rod of negligible weight is supported by...Ch. 5 - A 120-lb weight is attached to the cable that is...Ch. 5 - Calculate the force in cable CD and the reaction...Ch. 5 - The 350-lb homogeneous plate has the shape of an...Ch. 5 - The bent rod ABCD is supported by a...Ch. 5 - A hoist is formed by connecting bars BD and BE to...Ch. 5 - The crank arm OD of the winch is connected by a...Ch. 5 - The 80-lb homogeneous plate is supported by a...Ch. 5 - The frame is built into the wall at D and G. The...Ch. 5 - The bent bar of negligible weight is supported by...Ch. 5 - Determine the reactions at ball-and-socket joints...Ch. 5 - The 180-lb homogeneous bar is supported by a...Ch. 5 - The bent rod is supported by a ball-and-socket...Ch. 5 - Find the maximum load P that can be supported by...Ch. 5 - The vertical mast OA, which weighs 1.5 kN, is...Ch. 5 - The homogeneous bar AB weighs 50-lb. End B leans...Ch. 5 - The 500-kg crate is supported by the three cables....Ch. 5 - The uniform bars AB and BC each weigh 4 lb/ft....Ch. 5 - The rigid body of negligible weight is supported...Ch. 5 - The homogeneous 860-kg bar AB is supported by a...Ch. 5 - The triangular plate is supported by three...Ch. 5 - The connections at the ends of bars AB and BC arc...Ch. 5 - The bar AEB is supported by a ball-and-socket...Ch. 5 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q3: Find the resultant of the force system.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 A three-blade propeller of a diameter of 2 m has an activity factor AF of 200 and its ratio of static thrust coefficient to static torque coefficient is 10. The propeller's integrated lift coefficient is 0.3.arrow_forward(L=6847 mm, q = 5331 N/mm, M = 1408549 N.mm, and El = 8.6 x 1014 N. mm²) X A ΕΙ B L Y Marrow_forward
- Calculate the maximum shear stress Tmax at the selected element within the wall (Fig. Q3) if T = 26.7 KN.m, P = 23.6 MPa, t = 2.2 mm, R = 2 m. The following choices are provided in units of MPa and rounded to three decimal places. Select one: ○ 1.2681.818 O 2. 25745.455 O 3. 17163.636 O 4. 10727.273 ○ 5.5363.636arrow_forwardIf L-719.01 mm, = 7839.63 N/m³, the normal stress σ caused by self-weight at the location of the maximum normal stress in the bar can be calculated as (Please select the correct value of σ given in Pa and rounded to three decimal places.) Select one: ○ 1. 1409.193 2. 845.516 O 3. 11273.545 ○ 4.8455.159 ○ 5.4509.418 6. 2818.386 7.5636.772arrow_forwardTo calculate the rotation at Point B, a suitable virtual structure needs to be created. Which equation in the following choices most accurately represents the functional relationship between the bending moment, Mv2 ( Units: N.mm), of the virtual structure and the spatial coordinate x (Units: mm) if the applied unit virtual moment is clockwise? Select one: O 1. Mv2 1.000 O 2. Mv2=x+1.000 O 3. Mv2=x+0.000 4. Mv2 = -x-1.000 O 5. Mv2 -1.000 6. Mv2=-x+0.000arrow_forward
- The vertical deflection at Point B can be calculated as ( The following choices are provided in units of mm and rounded to three decimal places ; the downward deflection is negative and upward deflection is positive. ) Select one: 1. 1703.065 2. -1703.065 3. -2043.679 4.1362.452 5. -1362.452 6. 2043.679arrow_forwardThe second moments of area about z-axis, /z, and the second moments of area about y-axis, ly, can be calculated as Select one: O 1. I = Iz ○ 2. Ly ○ 3. ○ 4. ○ 5. = = Iz = *D' 64 I₁ = D, Iz Ly Ly = 32 *D' = = 3 Iz = *D' 32 = *D' O 6. Iy=D, Ly = D², Iz = 32 O 7. Ly = Iz D = 64 32arrow_forward[If L=3508 mm, W-9189 N, E=80 GPa, Determine the deflection at the free end of the beam.] Step -2 Which equation in the following choices most accurately represents the functional relationship between the value of the slope O (Units: Radian) at half length (x = L/2) of the beam and the second moment of area about z-axis, Izz (Units: mm²), of the cross section? (Please note that " X = L/2" is the same as "X = L ÷ 2" .) Select one: O 1.0 448787.925/Izz O 2.0 279167.292/Izz O 3.0 38871.395/Izz O 4.0 114847.304/Izz O 5.0 176688.160/Izz O 6.0 609574.150/Izz O 7.0 70675.264/Izzarrow_forward
- Use the principle of virtual work to determine the vertical deflection and rotation at tip (Point B) of the cantilever shown below. (L=6847 mm, q = 5331 N/mm, M = 1408549 N.mm, and El = 8.6 x 1014 N. mm²) q Y M X A ΕΙ B L Step -1 Let the coordinates defined with origin located at B and x-axis pointing to the Left and Y-axis pointing upward. The bending moment, M (Units: N.mm), in the beam as a function of spatial coordinate x(Units: mm) can be most accurately described by Select one: 1. M=1126839.200 +2132.400*x*x 2. M=-1408549.000 - 3198.600*x*x 3. M=-1408549.000-2665.500*x*x 4. M=-1408549.000-2132.400*x*x 5. M= -1408549.000+2665.500*x*x 6. M= 1408549.000 + 2665.500*x*x 7. M= 1408549.000-2665.500*x*xarrow_forwardCalculate the principal stress σ at the selected element within the wall (Fig. Q3) if T = 26.7 KN.m, P = 23.6 MPa, t = 2.2 mm, R = 2 m. The following choices are provided in units of MPa and rounded to three decimal places Select one: O 1.5363.64 O 2. 12872.727 3.9118.182 4. 10727.273 5. 16090.909 6. 2681.818arrow_forwardQuestion2 The mission profile for a jet driven aircraft consists of the following segments: engine start and warm-up, taxi, take-off, climb to the cruise altitude of 35000 ft, descend to 10000 ft, one hour loiter at this altitude at 60% of the cruise speed, flight at loiter speed and altitude to an alternate airport (100 nm), descend to landing approach condition followed by the final landing, taxi and shutdown. The cruise Mach number is 0.8. No provisions are made for the reserved fuel or any trapped oil and fuel. The aircraft carries 200 people (including pilots and the cabin crew) at 175 lb each and 90 lb baggage each. This aircraft has a wing area of 2000 ft² L/D at cruise L/D at 10000ft flight Table Q2 20 16 0.43 lb/hr/lb 0.50 lb/hr/lb C: Specific Fuel Consumption at cruise: C: Specific Fuel Consumption at 10000 ft flight: Weight ratios Engine Start and warm-up Taxi Take-off Climb Descent Landing, taxi and shutdown 0.992 0.996 0.996 0.996 0.992 0.992 Question 2 continues on the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Engineering Basics - Statics & Forces in Equilibrium; Author: Solid Solutions - Professional Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQBvQ2hJZFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY