The Basic Practice of Statistics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781464142536
Author: David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.20CYS
To determine
To find: The school GPA if one child in this class has IQ score 110.
Expert Solution & Answer
Answer to Problem 5.20CYS
The correct answer is option (b).
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The given
Reason for correct answer:
Justification:
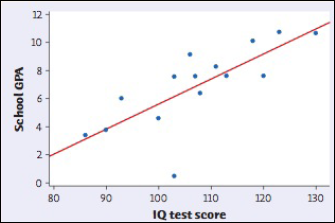
From the output, it is observed that the corresponding value on the School GPA in y axis to the value of 110 on the IQ test score in x-axis meets the regression line on 7.5.
Reason for incorrect answer:
Option (a): 2 are wrong because the calculated predicted value is 7.5.
Option (c): 11 are wrong because the calculated predicted value is 7.5.
Conclusion:
Hence, the predicted school GPA score is, 7.5.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
During busy political seasons, many opinion polls are conducted. In apresidential race, how do you think the participants in polls are generally selected?Discuss any issues regarding simple random, stratified, systematic, cluster, andconvenience sampling in these polls. What about other types of polls, besides political?
Please could you explain why 0.5 was added to each upper limpit of the intervals.Thanks
28. (a) Under what conditions do we say that two random variables X and Y are
independent?
(b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) =
E(X)E(Y);
(e) Show by a counter example that the converse of (ii) is not necessarily true.
Chapter 5 Solutions
The Basic Practice of Statistics
Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.1AYKCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.2AYKCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.3AYKCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.4AYKCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.5AYKCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.6AYKCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.7AYKCh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.8AYKCh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.9AYKCh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.10AYK
Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 5.11AYKCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.12AYKCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.13AYKCh. 5.7 - Prob. 5.14AYKCh. 5.7 - Prob. 5.15AYKCh. 5.7 - Prob. 5.16AYKCh. 5.8 - Prob. 5.17AYKCh. 5.8 - Prob. 5.18AYKCh. 5.8 - Prob. 5.19AYKCh. 5 - Prob. 5.20CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.21CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.22CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.23CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.24CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.25CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.26CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.27CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.28CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.29CYSCh. 5 - Prob. 5.30ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.31ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.32ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.33ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.34ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.35ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.36ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.37ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.38ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.39ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.40ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.41ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.42ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.43ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.44ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.45ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.46ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.47ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.48ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.49ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.50ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.51ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.52ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.53ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.54ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.55ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.56ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.57ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.59ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.60ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.61ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.62ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.63ECh. 5 - Prob. 5.64E
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 19. Let X be a non-negative random variable. Show that lim nE (IX >n)) = 0. E lim (x)-0. = >arrow_forward(c) Utilize Fubini's Theorem to demonstrate that E(X)= = (1- F(x))dx.arrow_forward(c) Describe the positive and negative parts of a random variable. How is the integral defined for a general random variable using these components?arrow_forward
- 26. (a) Provide an example where X, X but E(X,) does not converge to E(X).arrow_forward(b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) E(X)E(Y);arrow_forward(d) Under what conditions do we say that a random variable X is integrable, specifically when (i) X is a non-negative random variable and (ii) when X is a general random variable?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman