
Long-term contract; revenue recognition over time vs. upon project completion
• LO5–9
On June 15, 2018, Sanderson Construction entered into a long-term construction contract to build a baseball stadium in Washington, D.C., for $220 million. The expected completion date is April 1, 2020, just in time for the 2020 baseball season. Costs incurred and estimated costs to complete at year-end for the life of the contract are as follows ($ in millions):
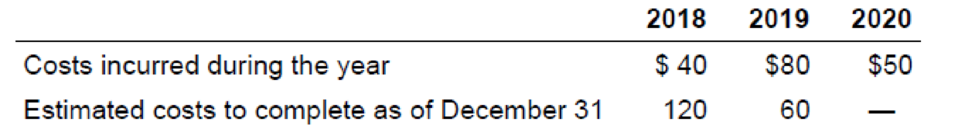
Required:
1. How much revenue and gross profit will Sanderson report in its 2018, 2019, and 2020 income statements related to this contract assuming Sanderson recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion?
2. How much revenue and gross profit will Sanderson report in its 2018, 2019, and 2020 income statements related to this contract assuming this project does not qualify for revenue recognition over time?
3. Suppose the estimated costs to complete at the end of 2019 are $80 million instead of $60 million. Determine the amount of revenue and gross profit or loss to be recognized in 2019 assuming Sanderson recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion.
Requirement – 1
Contract
Contract is a written document that creates legal enforcement for buying and selling the property. It is committed by the parties to performing their obligation and enforcing their rights.
Revenue recognized point of long term contract
A long-term contract qualifies for revenue recognition over time. The seller can recognize the revenue as per percentage of the completion of the project, which is recognized by revenue mines cost of completion until date.
A contract does not meet the performance obligation norm. The seller cannot recognize the revenue till the project complete.
The revenue recognition principle
The revenue recognition principle refers to the revenue that should be recognized in the time period, when the performance obligation (sales or services) of the company is completed.
The amount of revenue and gross profit or loss will report in 2018, 2019, and 2020 income statement of S Contraction, and assume revenue recognize over time according to percentage of completion.
Explanation of Solution
Recognized revenue
In the year 2018:
Given,
The contract price is $220,000,000
Actual cost to date is $4,000,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $160,000,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $55,000,000.
In the year 2019:
Given,
The contract price is $220,000,000
Actual cost to date is $120,000,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $180,000,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $91,670,000.
In the year 2020:
Given,
Contract price is $220,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2018 is $55,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2019 is $91,670,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $73,330,000.
Recognized gross profit
In the year 2018:
Given,
Estimated gross profit in 2018 is $60,000,000 (1)
Total estimated cost is $160,000,000
Actual cost to date is $40,000,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $15,000,000.
In the year 2019:
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2019 is $40,000,000 (1)
Total estimated cost is $180,000,000
Gross profit recognition in 2018 is $15,000,000
Actual cost to date is $120,000,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $11,670,000.
In the year 2020:
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2018 is $50,000,000 (1)
Gross profit recognition in 2016 is $15,000,000
Gross profit recognition in 2017 is $11,670,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $11,670,000.
Working note:
Calculate the value of gross profit (in millions)
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |||
| Contract price | $220 | $220 | $220 | |||
| Actual costs to date | $40 | $120 | $170 | |||
| Estimated costs to complete | $120 | $60 | $0 | |||
| Less: Total estimated cost | $160 | $180 | $170 | |||
| Estimated gross profit | $60 | $40 | $50 | |||
Table (1)
(1)
Requirement – 2
To calculate: The amount of revenue and gross profit or loss to be recognized in 2018, 2019 and 2020 assuming the project does not qualify for revenue recognition over time.
Explanation of Solution
Revenue recognition:
In this case, there is no revenue recognition because the project does not qualify for revenue recognition overtime.
Recognized gross profit:
In the year 2018 and 2019:
In this case, there is no recognized profit, because the contract is not yet completed. Hence, the gross profit in the year 2018 and 2019 is $0.
In the year 2020:
Here,
The contract price is $220,000,000
Actual cost to date is $170,000,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $50,000,000.
Requirement – 3
The amount of revenue and gross profit or loss to be recognized in 2019, and assume S Construction recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion.
Explanation of Solution
Revenue recognition in the year 2019:
Here,
Contract price is $220,000,000
Actual cost to date is $120,000,000
Total estimated cost is $200,000,000
Revenue recognition is $55,000,000
Profit recognizes is $15,000,000.
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $77,000,000.
Recognized gross profit in the year 2019:
Here,
Revenue recognition in 2019 is $77,000,000
Actual cost to date is $80,000,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross loss recognition is $300,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING RMU 9TH EDITION
- 56 On February 20, 2022, ABC Construction Company entered into a fixed-price contract to construct a commercial building for P9,000,000. ABC determined that the performance obligation is satisfied over time. Information relating to the contract is as follows: 2022 2023 Percentage of completion 25% 75% Estimated costs at completion P6,750,000 P7,200,000 How much is the contract costs charged to profit or loss in 2022? On February 20, 2022, ABC Construction Company entered into a fixed-price contract to construct a commercial building for P9,000,000. ABC determined that the performance obligation is satisfied over time. Information relating to the contract is as follows: 2022 2023 Percentage of completion 25% 75% Estimated costs at completion P6,750,000 P7,200,000 How much is the contract costs charged to profit or loss in 2022?arrow_forwardProblem 6-11 (Algo) Long-term contract; revenue recognition upon completion [LO6-9] In 2024, the Westgate Construction Company entered into a contract to construct a road for Santa Clara County for $10,000,000. The road was completed in 2026. Information related to the contract is as follows: Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year- end Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Billings during the year Cash collections during the year Assume that Westgate Construction's contract with Santa Clara County does not qualify for revenue recognition over time. Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year- end Required: 1. Calculate the amount of revenue and gross profit (loss) to be recognized in each of the three years. 2-a. In the journal below, complete the necessary journal entries for the year 2024 (credit "Cash, Materials, etc." for construction costs incurred). 2-b. In the journal below, complete the…arrow_forwardProblem 6-11 (Algo) Long-term contract; revenue recognition upon completion [LO6-9] In 2024, the Westgate Construction Company entered into a contract to construct a road for Santa Clara County for $10,000,000. The road was completed in 2026. Information related to the contract is as follows: Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Billings during the year Cash collections during the year Assume that Westgate Construction's contract with Santa Clara County does not qualify for revenue recognition over time. Required: 1. Calculate the amount of revenue and gross profit (loss) to be recognized in each of the three years. 2-a. In the journal below, complete the necessary journal entries for the year 2024 (credit "Cash, Materials, etc." for construction costs incurred). 2-b. In the journal below, complete the necessary journal entries for the year 2025 (credit "Cash, Materials, etc."…arrow_forward
- Problem 6-11 (Algo) Long-term contract; revenue recognition upon completion [LO6-9] In 2024, the Westgate Construction Company entered into a contract to construct a road for Santa Clara County for $10,000,000. The road was completed in 2026. Information related to the contract is as follows: Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Billings during the year Cash collections during the year Assume that Westgate Construction's contract with Santa Clara County does not qualify for revenue recognition over time. Required: 3. Complete the information required below to prepare a partial balance sheet for 2024 and 2025 showing any items related to the contract. 4. Calculate the amount of revenue and gross profit (loss) to be recognized in each of the three years, assuming the following costs incurred and costs to complete information. Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to…arrow_forwardOn June 15, 2021, Sanderson Construction entered into a long-term construction contract to build a baseball stadium in Washington, D.C., for $220 million. The expected completion date is April 1, 2023, just in time for the 2023 baseball season. Costs incurred and estimated costs to complete at year-end for the life of the contract are as follows ($ in millions): 2021 2022 2023 Costs incurred during the year $ 40 $ 80 $ 50 Estimated costs to complete as of December 31 120 60 — Required:1. Compute the revenue and gross profit will Sanderson report in its 2021, 2022, and 2023 income statements related to this contract assuming Sanderson recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion.2. Compute the revenue and gross profit will Sanderson report in its 2021, 2022, and 2023 income statements related to this contract assuming this project does not qualify for revenue recognition over time.3. Suppose the estimated costs to complete at the…arrow_forwardProblem 6-10 (Algo) Long-term contract; revenue recognition over time [LO6-8, 6-9] [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] In 2021, the Westgate Construction Company entered into a contract to construct a road for Santa Clara County for $10,000,000. The road was completed in 2023. Information related to the contract is as follows: Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Billings during the year Cash collections during the year Westgate recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion. Costs incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Revenue Gross profit (loss) 2021 2022 $2,044,000 $2,628,000 5,256,000 2,628,000 2,170,000 2,502,000 1,885,000 2,600,000 Problem 6-10 (Algo) Part 5 5. Calculate the amount of revenue and gross profit (loss) to be recognized in each of the three years assuming the following costs incurred and costs to complete information. (Do not round intermediate…arrow_forward
- Problem 6-10 (Algo) Long-term contract; revenue recognition over time [LO6-8, 6-9] [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] In 2021, the Westgate Construction Company entered into a contract to construct a road for Santa Clara County for $10,000,000. The road was completed in 2023. Information related to the contract is as follows: Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Billings during the year Cash collections during the year Westgate recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion. Balance Sheet (Partial) Current assets: Accounts receivable Construction in progress Problem 6-10 (Algo) Part 3 3. Complete the information required below to prepare a partial balance sheet for 2021 and 2022 showing any items related to the contract. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Less: Billings Costs and profit in excess of billings Current liabilities: Construction in progress Answer is complete but not entirely…arrow_forwardOn June 15, 2024, Sanderson Construction entered into a long-term construction contract to build a baseball stadium in Washington, D.C., for $330 million. The expected completion date is April 1, 2026, just in time for the 2026 baseball season. Costs incurred and estimated costs to complete at year-end for the life of the contract are as follows ($ in millions): 2024 2025 2026 Costs incurred during the year $ 50 $ 100 $ 60 Estimated costs to complete as of December 31 150 90 — Required: Compute the revenue and gross profit that Sanderson will report in its 2024, 2025, and 2026 income statements related to this contract, assuming Sanderson recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion. Compute the revenue and gross profit that Sanderson will report in its 2024, 2025, and 2026 income statements related to this contract, assuming this project does not qualify for revenue recognition over time. Suppose the estimated costs to complete at the end of 2025…arrow_forwardProblem 6-10 (Algo) Long-term contract; revenue recognition over time [LO6-8, 6-9] [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] In 2021, the Westgate Construction Company entered into a contract to construct a road for Santa Clara County for $10,000,000. The road was completed in 2023. Information related to the contract is as follows: Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Billings during the year Cash collections during the year Problem 6-10 (Algo) Part 3 Westgate recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion. Balance Sheet (Partial) Current assets: Accounts receivable Construction in progress 2021 $2,044,000 5,256,000 2,170,000 1,885,000 Less: Billings Costs and profit in excess of billings Current liabilities: Construction in progress 2021 2022 $2,628,000 2,628,000 2,502,000 2,600,000 3. Complete the information required below to prepare a partial balance sheet for 2021 and 2022 showing any items…arrow_forward
- Problem 6-10 (Algo) Long-term contract; revenue recognition over time [LO6-8, 6-9] [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] In 2024, the Westgate Construction Company entered into a contract to construct a road for Santa Clara County for $10,000,000. The road was completed in 2026. Information related to the contract is as follows: Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Billings during the year Cash collections during the year Problem 6-10 (Algo) Part 5 Westgate recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion. Costs incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Revenue Gross profit (loss) $ $ 2024 $ 2,610,000 6,390,000 2,100,000 1,850,000 5. Calculate the amount of revenue and gross profit (loss) to be recognized in each of the three years, assuming the following costs incurred and costs to complete information. X Answer is complete but not entirely correct. 2026 3,939,962 (110,038)…arrow_forwardProblem 6-11 (Algo) Long-term contract; revenue recognition upon completion [LO6-9] In 2021, the Westgate Construction Company entered into a contract to construct a road for Santa Clara County for $10,000,000. The road was completed in 2023. Information related to the contract is as follows: Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end Billings during the year Cash collections during the year. 2021 $1,584,000 5,616,000 1,200,000 1,000,000 Cost incurred during the year Estimated costs to complete as of year-end) 2022 $3,240,000 2,376,000 3,624,000 2,800,000 Assume that Westgate Construction's contract with Santa Clara County does not qualify for revenue recognition over time. Required: 1. Calculate the amount of revenue and gross profit (loss) to be recognized in each of the three years. 2-a. In the journal below, complete the necessary journal entries for the year 2021 (credit "Various accounts" for construction costs incurred). Cost incurred during the…arrow_forwardOn June 15, 2021, Sanderson Construction entered into a long-term construction contract to build a baseball stadium in Washington, D.C., for $230 million. The expected completion date is April 1, 2023, just in time for the 2023 baseball season. Costs incurred and estimated costs to complete at year-end for the life of the contract are as follows ($ in millions): Costs incurred during the year 2021 2022 2023 $ 25 $75 $35 100 60 Estimated costs to complete as of December 31 Required: 1. Compute the revenue and gross profit will Sanderson report in its 2021, 2022, and 2023 income statements related to this contract assuming Sanderson recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion. 2. Compute the revenue and gross profit will Sanderson report in its 2021, 2022, and 2023 income statements related to this contract assuming this project does not qualify for revenue recognition over time. 3. Suppose the estimated costs to complete at the end of 2022 are $100 million instead…arrow_forward
