
Part A
(a)
Prepare
Part A
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Share Based Payments:
Sometimes organizations offer to issue equity shares as a consideration, to employees or other parties such consideration is referred as share based payment. IFRS recognizes three types of share based payments that are, equity-settled, cash-settled or having choice of settlement.
Journalizing:
Journalizing is the process of recording the transactions of an organization in the order of happening of events. Based on these journal entries recorded, the accounts are posted to the relevant ledger accounts.
Accounting rules for journal entries:
- To increase balance of the account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To decrease balance of the account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Recording compensation expense:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 31/12/01 | Compensation expense | 1,867 | ||
| Share based payment liability | 1,867 | |||
| (to record compensation) |
Table (1)
- Since, compensation expense is an expense and expense is increased. Hence, compensation expense account is debited.
- Since, share based payment liability is a liability and liability is increased. Hence, share based payment liability account is credited.
Recording compensation expense:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 31/12/02 | Compensation expense | 1,867 | ||
| Share based payment liability | 1,867 | |||
| (to record compensation) |
Table (2)
- Since, compensation expense is an expense and expense is increased. Hence, compensation expense account is debited.
- Since, share based payment liability is a liability and liability is increased. Hence, share based payment liability account is credited.
Recording compensation expense:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 31/12/03 | Compensation expense | 2,566 | ||
| Share based payment liability | 2,566 | |||
| (to record compensation) |
Table (3)
- Since, compensation expense is an expense and expense is increased. Hence, compensation expense account is debited.
- Since, share based payment liability is a liability and liability is increased. Hence, share based payment liability account is credited.
Recording settlement, if company chooses cash alternative:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 31/12/03 | Share based payment liability | 6,300 | ||
| Cash | 6,300 | |||
| (to settle compensation) |
Table (4)
- Since, share based payment liability is a liability and liability is decreased. Hence, share based payment liability account is debited.
- Since, cash is an asset and asset is decreased. Hence, cash account is credited.
Working Note:
Computation of option expense:
Computation of Year 1 expense:
Computation of Year 2 expense:
Computation of Year 3 expense:
(b)
Prepare journal entries to record settlement of share based payment under share alternative.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Compensation entries would remain same as in cash alternative however, settlement entry would differ which is presented as follows:
Recording settlement, if company chooses share alternative:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 31/12/03 | Share based payment liability | 6,300 | ||
| Common stock | 700 | |||
| Additional paid-in capital | 5,600 | |||
| (to settle compensation) |
Table (5)
- Since, share based payment liability is a liability and liability is decreased. Hence, share based payment liability account is debited.
- Since, common stock is capital and capital is increased. Hence, common stock account is credited.
- Since, additional paid-in capital is capital and capital is increased. Hence, additional paid-in capital account is credited.
Part B
Compute the fair value of the stock options at the grant date and the amount to be recognized as compensation expense in Year 1.
Part B
Explanation of Solution
Since, under equity option, fair value is different from cash option due to discount; therefore, fair value of equity component would be greater than zero.
Computation of fair value of options at the grant date:

Table (6)
Computation of option expense in Year 1:
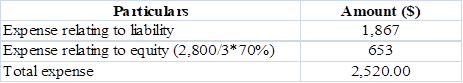
Table (7)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
International Accounting

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





