
(a)
The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the car.
(a)
Answer to Problem 3SP
The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the car is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The radius of the curve is
Write the equation for the centripetal acceleration.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the car is
(b)
The magnitude of the
(b)
Answer to Problem 3SP
The magnitude of the centripetal force required to produce the centripetal acceleration is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The mass of the car is
Write the equation for centripetal force.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus the magnitude of the centripetal force required to produce the centripetal acceleration is
(c)
The magnitude of the vertical component of the normal force acting upon the car to counter the weight of the car.
(c)
Answer to Problem 3SP
The magnitude of the vertical component of the normal force acting upon the car to counter the weight of the car is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The mass of the car is
The vertical component of the normal force acts to counter the weight of the car so that vertical component of normal force is equal to the weight of the car.
Write the equation for the weight of the car.
Here,
The value of
Substitute
This weight of the car is equal to the vertical component of normal force.
Conclusion:
Thus, the magnitude of the vertical component of the normal force acting upon the car to counter the weight of the car is
(d)
Diagram of the car on the banked curve to scale the vertical component of the normal force and determine the magnitude of the total normal force.
(d)
Answer to Problem 3SP
The diagram of the car on the banked curve is shown in figure 1 and the magnitude of the total normal force is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The angle of banking of the curve is
The diagram of the car in the curve is shown in figure 1.
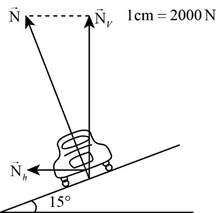
Figure 1
Write the equation for the vertical component of the normal force.
Here,
Rewrite the above equation for
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus the diagram of the car on the curve is drawn in figure 1 and the magnitude of the total normal force is
(e)
The magnitude of the horizontal component of the normal force and whether it is sufficient to provide the centripetal force.
(e)
Answer to Problem 3SP
The magnitude of the horizontal component of the normal force is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The angle of banking of the curve is
Write the equation for the horizontal component of the normal force.
Here,
Substitute
The value of
Conclusion:
Thus the magnitude of the horizontal component of the normal force is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
The Physics of Everyday Phenomena
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





