
Concept explainers
Neurofibromatosis
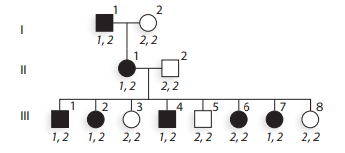
a. Determine the alleles for the
b. Based on the phase of alleles on chromosomes in generation
c. What is the estimated recombination frequency between the
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 5 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Biological Science
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- The DNA of every individual in the pedigree shown below has been sequenced at the causative locus. All the non-shaded individuals are wild type apart from III.1. III.1 has been proven to have the causative mutation for this autosomal dominant condition, but they exhibit no symptoms. Based on this small pedigree, what is the level of penetrance for the condition? Please give your answer as a WHOLE percentage, give the number only, no percentage symbol. Answer: The level of penetrance for the condition shown in the pedigree below is Blank 1 percent. 1:1 1:2 Il:1 I1:2 I1:3 Il:4 I1:5 I1:6 II:1 I:2 III:3 III:4 III:3 III:6 III:7 III:8 III:9 III:10 III:11 III12 II:13 III:14 IV:1 | IV:2 IV:3 IV:4 IV:5 IV:6 IV:7 IV:8 IV:9 IV:10 IV:11 IV:12 IV:13 IV:14 IV:15 IV:16 IV:17 IV:18 IV:19 V:1 V:2 V:3 V:4 V:5 V:6 V:7 V:8 V:9 V:10 V:11 V:12arrow_forwardGiven the following genetic map, predict the chance an offspring would inherit the exact same haplotypes that the parents had. Assume interference in this area of the chromosome is 5%. Please report your value as a percent (%). A |-- 3 mu -- |-- 12 mu -- | Parent 1 Haplotypes: A1 B6 C14/A5 B1 C3 Parent 2 Haplotypes: A8 B3 C2 / A7 B2 C5arrow_forwardConsider the following two nonhomologous wildtype chromosomes, where letters or numbers represent genes, the "-" represents the centromere of each chromosome, and chromosomes are shown on separate lines. ABCDE-FGHIJK 123-45678 Identify the type of rearrangement shown in each of the following (A-C) and then identify whether it is balanced or unbalanced. Assume that the individual is diploid and heterozygous for the rearrangement. A. ABCDE-FGHIJKGH 123-45678 Rearrangement: [Select] • Balanced or Unbalanced: [Select] B. ABCDGF-EHIJK 123-45678 Rearrangement: [Select] Balanced or Unbalanced: [Select]arrow_forward
- Familial Down syndrome is similar to primary Down syndrome in that it is caused by trisomy 21. However, in familial Down syndrome, all or part of the third copy of chromosome 21 has translocated onto another autosome, typically chromosome 14. In cases of familial Down syndrome, one of the parents of the affected child is often a carrier of a translocated chromosome. The translocation carrier parent does not have Down syndrome because he or she has a total of two copies of chromosome 21. Suppose that a woman is a translocation carrier of chromosome 21 on chromosome 14. She conceives six zygotes with a man who carries no aneuploidies. Match the description of the chromosomes inherited by each zygote with the viability and phenotype of the zygote. ✓ Two normal copies of 14, two normal copies of 21 two normal copies of 21, one normal copy of 14 ✓one normal copy of 14, one 21 to 14 translocation, one normal copy of 21 ✓two normal copies of 14, one normal copy of 21, on 21 to 14…arrow_forwardA tomato geneticist attempts to assign five recessivemutations to specific chromosomes by using trisomics.She crosses each homozygous mutant (2n) with each ofthree trisomics, in which chromosomes 1, 7, and 10 takepart. From these crosses, the geneticist selects trisomicprogeny (which are less vigorous) and backcrosses themto the appropriate homozygous recessive. The diploidprogeny from these crosses are examined. Her results, inwhich the ratios are wild type:mutant, are as follows:Which of the mutations can the geneticist assign towhich chromosomes? (Explain your answer fully.)arrow_forwardNeurofibromatosis 1 is considered an autosomal dominant disorder because the gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 17. It is caused by microdeletion at the long arm of chromosome 17 band 11 sub-band 2 involving the NF1 gene. Group of answer choices Statement 1 is correct. Statement 2 is incorrect Statement 1 is incorrect, statement 2 is correct Both statements are incorrect Both statements are correctarrow_forward
- Many genetic disorders exhibit locus heterogeneity. Define andgive two examples of locus heterogeneity. How does locus heterogeneityconfound a pedigree analysis?arrow_forwardIn a cross in Drosophila, a female heterozygous for the autosomallylinked genes a, b, c, d, and e (abcde/ + + + + +) was testcrossedwith a male homozygous for all recessive alleles (abcde/abcde).Even though the distance between each of the loci was at least3 map units, only four phenotypes were recovered, yielding thefollowing data: Phenotype No. of Flies+ + + + + 440a b c d e 460+ + + + e 48a b c d + 52 Total = 1000 Why are many expected crossover phenotypes missing? Can anyof these loci be mapped from the data given here? If so, determinemap distances.arrow_forwardA PORTION OF THE LINKAGE MAP OF CHROMOSOME 2 IN THE TOMATO IS ILLUSTRATED HERE. ci (compound influorescence) o (oblate) - 15 CM 20 CM p (peach) THE OBLATE PHENOTYPE IS A FLATTENED FRUIT, THE PEACH PHENOTYPE IS HAIRY FRUIT (LIKE A PEACH), AND COMPOUND INFLORESCENCE MEANS CLUSTERED FLOWERS. IGNORE THE PEACH LOCUS. AMONG 1000 GAMETES PRODUCED BY A PLANT OF GENOTYPE O CI /+ +, WHAT TYPES OF GAMETES WOULD BE EXPECTED, AND WHAT NUMBER WOULD BE EXPECTED OF EACH?arrow_forward
- In the pedigree below, male II-1 has Klinefelter syndrome, which is the result of an XXY karyotype. On the X chromosome, a gene called G6PD has two codominant alleles, G6PDA and G6PDB. In this pedigree, A, B, and AB refer to the phenotypes associated with the alleles of this gene. (Note: In this family, no individuals have the AB version of the phenotype.) A A B Based on the information in the pedigree, when could nondisjunction have occurred? Select all correct answers. In Il-1's father, during meiosis I In II-1's mother, during meiosis I In II-1's mother, during meiosis II In Il-1's father, during meiosis IIarrow_forwardThe Klinefelter syndrome (disomy of the X chromosome in males) is a genetic disease caused by aneuploidy of the sex chromosomes in humans. Patients with the 47,XXY karyotype are male. Describe two genetic scenarios leading to patients with the Klinefelter syndrome.arrow_forwardIn humans, chromosome 16 sometimes has a heavily stained area near the centromere. This feature can be seen in a microscope, but otherwise has no effect on the phenotype of the person carrying it. When such a “blob" exists on a given copy of chromosome 16, it is a constant feature of that chromosome and is inherited. A couple conceived a child, but the fetus had multiple abnormalities and was miscarried. e.g., The fetus had three copies of chromosome 16, where 2 of the 3 copies of chromosome 16 had large blobs. Both of the mother's copies of chromosome 16 lacked blobs, but the father was heterozygous for blobs. The fetus was formed from a fertilization event that included a gamete produced by the in which nondisjunction occurred during the meiotic division. Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a mother; first. mother; second. father; first. C Your answer d father; second. E3 Fullso L e Insufficient information is provided…arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
