
Concept explainers
To review:
The classification of the following amino acids according to theirstructuresas nonpolar, polar, acidic, or basic.
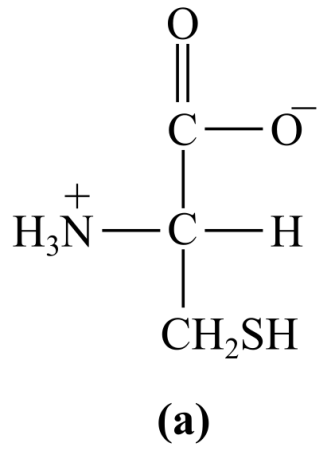
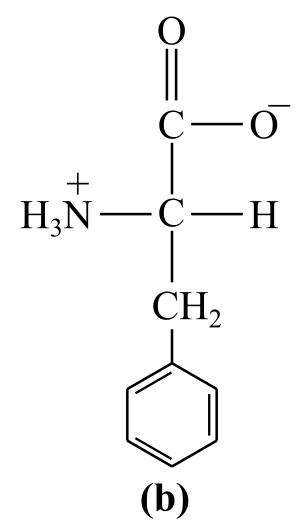
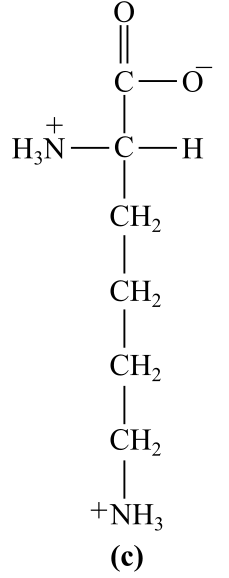
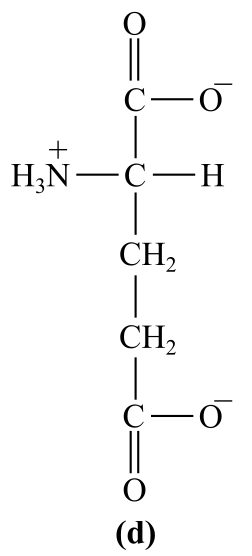
Introduction:
Amino acids are the basic unit of a protein. The chain of an amino acid is calledpolypeptide. Each amino acid has a carboxylic end and an amino end. One amino acid is linked to another via a peptide bond. There are 20 amino acids that are found naturally in our body and are known as standard amino acids.
Explanation of Solution
The amino acids can be classified as polar, nonpolar, acidic, and basic. The nonpolar amino acids have hydrocarbonscontaining R group (side chain), and they lack any type of charge. The polar amino acids have a polar hydroxyl group (-OH). The -SH group (sulfhydryl group) is also polar in nature. The acidic amino acids have R chain containing carboxylate group (-COOH), while the basic amino acid has an amino group in the side chain.
The structure (a) in the given question is the amino acid, cysteine. It has a polar group of -SH in its R-chain (side chain). Thus, it is a polar amino acid.
The structure (b) in the given question is the amino acid, phenylalanine. It has a nonpolar group:a benzene ring, as its side chain, which bear no positive or negative charges. Thus, it is a nonpolar amino acid.
The structure (c) in the given question is the amino acid, lysine. The amino group is present in the R-chain, which bears positive charge at physiological pH, which is basic in nature. Thus, it is a basic amino acid.
The structure (d) in the given question is the amino acid, glutamate. It has a carboxylic group as the R-chain, which bears negative charge at physiological pH, which is acidic in nature.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the given structures are classified as
a) Polar (cysteine)
b) Nonpolar (phenylalanine)
c) Basic (lysine)
d)Acidic (glutamate)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Biochemistry: The Molecular Basis of Life
- For the amino acids listed below, what tertiary/quaternary interaction can each of the amino acids participate in? 1)Alanine 2)Asparagine 3) Aspartic Acid 4) Argininearrow_forwardDraw a generic amino acid and identify its α carbon and its substituents.arrow_forwardDescribe how two amino acids are combined to form apolypeptide.arrow_forward
- The biological marcomolecules composed or multiple units of amino acids isarrow_forwardDefine the types of aminoacids in various ways with suitable examples ?arrow_forwardClassify each of the following amino acid as polar or nonpolar. If polar, indicate if the R group is neutral, acidic, it basic. Indicate if each is hydrophobic or hydrophilic. a. lysine b. arginine c. methionine d. tyrosinearrow_forward
- Why are L-amino acids prevalent/common in biological systems?arrow_forwardName and discuss the non-covalent interactions that maintain protein structure. Explain the chirality of amino acid molecules.arrow_forwardDoes the chemical reaction to unite amino acids incorporate or liberate atoms? What are the chemical entities incorporated or liberated in this reaction?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
