
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Determine the equations for shear and bending moment for the beam shown. Use the resulting equations to draw the shear and bending moment diagrams.
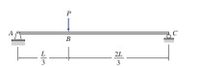
Transcribed Image Text:A
B
2L
3
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- #4 Part II. Beamsarrow_forwardProblem 2: For a given force F=100 kips and a given point C, draw the 1st line and the 2nd line and indicate the two with the clear labs, show the arm or distance and determine the magnitude of the arm, and calculate the magnitude of the moment of the force about A. The distance between the point A and point B, AB=10 ft. The distance between the point B and point C , BC=10 ft and the angle between the force and line BC is 60º. Barrow_forwardDetermine the reactions in pounds the hinge and the rocker exert on the beam supporting the distributed load. (Assume that the +x-axis is to the right and the +y-axis is up along the page. Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations or answers) Magnitude and direction Magnitude in lbs. Ax- Magnitude is 0 Ay- By-arrow_forward
- Q.2 If the (010×10) cylinder compressive strength of O.P.C. concrete at 10-day is (14 MPa). Calculate (20×20×20) cube comp. strength at age of 28 days.arrow_forwardDraw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam shown. After you have the diagrams, answer the questions. The distance x is measured from point A to the right. 300 lb/ft 7.2₁4.0' Questions: At x = 2.8ft, V = At x = 8.5ft, V= i i lbM = lbM = i iarrow_forwardUse the graphical method to construct the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams for the beam shown. Let a = 3.2 ft, b = 9.6 ft, c = 3.6 ft, MA = 6700 lb·ft, P = 3000 lb, and w = 660 lb/ft. Label all significant points on each diagram and identify the maximum moments (both positive and negative) along with their respective locations. Clearly differentiate straight-line and curved portions of the diagrams. Determine the maximum shear force and bending moment in the beam.Note that answers may be positive or negative. Here, "maximum" refers to the largest magnitude value, but you should enter your shear force and bending moment with the correct sign, using the sign convention presented in Section 7.2 of the textbook. If the magnitudes of the largest positive and largest negative values are the same, enter a positive number.arrow_forward
- Please answer attached image.thank youarrow_forwardElaborate the principle of statics to calculate the internal shear force and bending moment as functions of location along an element.arrow_forwardSolve the problem and answer the questions that follow. - If the supports were swapped such that the left support were a roller and the right support a pin, how would your solution change? - If the value of “w” were doubled, what would be the bending moment at the left most point of the beam?arrow_forward
- Calculate the vertical support reaction in support A. When sketching FBD, set the positive directions of both reactions in the positive direction of y axis. Enter your answer in kN to three decimal places.arrow_forward1 ft 3 ft B 3 ft 3 ft (-9002 + 800f + 1000k) Ib.ft 6 ft 3 ft E (-300î – 400ĵ + 100k) Ibs The applied force at point E and the applied couple moment at point D are shown in the figure. Complete/calculate the following: (Where applicable, express the results as the (x, y, z) components of a Cartesian vector) 1. Draw the free-body diagram (FBD), showing the appropriate reaction forces and/or moments at the supports. (You must show the reactions in their component form i.e. show RAx, MRAX etc. on the FBD). Note: The support at point A is not able to resist a moment about the 'X' axis but is able to resist a force in this direction. 2. The unit vector ÅBc 3. The position vector Tɛ/a 4. The position vector īB/aarrow_forwardplease answer correctlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning