
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
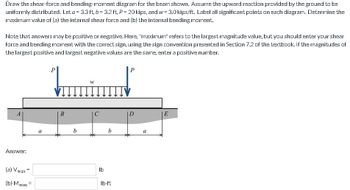
Transcribed Image Text:Draw the shear-force and bending-moment diagram for the beam shown. Assume the upward reaction provided by the ground to be
uniformly distributed. Let a = 3.3ft, b=3.2 ft, P = 20 kips, and w= 3.0 kips/ft. Label all significant points on each diagram. Determine the
maximum value of (a) the internal shear force and (b) the internal bending moment.
Note that answers may be positive or negative. Here, "maximum" refers to the largest magnitude value, but you should enter your shear
force and bending moment with the correct sign, using the sign convention presented in Section 7.2 of the textbook. If the magnitudes of
the largest positive and largest negative values are the same, enter a positive number.
A
Answer:
(a) Vmax
(b) Mmax=
a
P
B
b
W
C
lb
b
lb-ft
P
D
a
E
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A load P.is supported by a structure consisting of rigid bar BDF and three identical 18-mm-diameter steel [E = 195 GPa] rods, as shown in the figure. Use a = 2.0 m, b = 1.2 m, and L= 2.3 m. For a load of P = 82 kN, determine (a) the tension force produced in each rod. (b) the downward vertical deflection of the rigid bar at B. A (1) B Answers: (a) F₁ = F₂= F3 = (b) VB= i i i i b a 92.935 27.334 10.933 Co D (2) a kN 3 2 2 2 kN kN mm F (3) Larrow_forwardDetermine the normal strain EAB in wire AB.arrow_forwardThe beam shown in the Figure q2 below is a continuous beam of 2 spans. Determine the reactions at the supports using a method of stiffness matrix. Assume 1 and 3 are fixed and 2 is a roller. El is constant. 5 6 1 10 kN/m -5 m 2 FIGURE Q2 2 5 kN/m 2 4 m 3 3 4arrow_forward
- For the beam and loading shown,(a) Use discontinuity functions to write the expression for w(x). Include the beam reactions in this expression.(b) Integrate w(x) twice to determine V(x) and M(x).(c) Use V(x) and M(x) to plot the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams.Let a = 3.8 m, b = 1.3 m, wA = 17 kN/m, and wB = 51 kN/m. Label all significant points on each diagram and identify the maximum shear force and bending moment along with their respective locations. Clearly differentiate straight-line and curved portions of the diagrams.Note that answers may be positive or negative. Here, "maximum" refers to the largest magnitude value, but you should enter your shear force and bending moment with the correct sign, using the sign convention presented in Section 7.2 of the textbook. If the magnitudes of the largest positive and largest negative values are the same, enter a positive number.arrow_forwardA 240mm diameter circular simply supported beam carries a concentrated load, uniformly distributed load and a triangular load as shown in the figure. Using Area Moment Method, Solve the following unknowns. Let P = 195KN, a = 2m, and the modulus of elasticity of beam is 100GPA. NOTE: WRONG SIGN IS WRONG. WRONG UNITS IS WRONG. w w B Im If the shear at a point 1m from the roller support is equal to -182.66666666667KN, determine the value of "w". kN/m Determine the deflection at point 2n from the hinge support. (Note: Put a negative sign if the deflection is going down) IIIarrow_forwardSolve with Free body diagramarrow_forward
- For the simply supported beam subjected to the loading shown, derive equations for the shear force V and the bending moment M for any location in the beam. Place the origin at point A. Let a=4.00 m, b=5.25 m, c= 2.50 m, P = 26kN and M = 160kN-m. Construct the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams. Calculate the reaction forces Ay and Cy acting on the beam. Positive values for the reactions are indicated by the directions of the red arrows shown on the free-body diagram below.arrow_forwardA simply supported beam carries a moment applied to one end as shown. El is constant. a) Calculate the support reaction forces for the beam b) Write out the M(x) equation using discontinuity functions. c) Determine the slope and deflection equations by integrating the M(x) equation as needed and using two B.C. to solve for the integration constants, C1 and C2. d) Calculate the deflection at the mid-span of the beam. e) Check: Calculate the deflection at point B (right support). A 12Aarrow_forwardFor the beam and loading shown,(a) Use discontinuity functions to write the expression for w(x). Include the beam reactions in this expression.(b) Integrate w(x) twice to determine V(x) and M(x).(c) Use V(x) and M(x) to plot the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams.Let a = 3.2 m, b = 1.1 m, wA = 25 kN/m, and wB = 55 kN/m. Label all significant points on each diagram and identify the maximum shear force and bending moment along with their respective locations. Clearly differentiate straight-line and curved portions of the diagrams.Note that answers may be positive or negative. Here, "maximum" refers to the largest magnitude value, but you should enter your shear force and bending moment with the correct sign, using the sign convention presented in Section 7.2 of the textbook. If the magnitudes of the largest positive and largest negative values are the same, enter a positive number.arrow_forward
- Part Carrow_forwardSolve the problem by the moment-area method. The beam has constant flexural rigidity EI. A simple beam AB supports two concentrated loads P at the positions shown in the figure. B C 4. 4 A support C at the midpoint of the beam is positioned at distance d below the beam before the loads are applied. Assuming that d = 12 mm, L = 5.4 m, E = 200 GPa, and I = 193 x 10° mm, calculate the magnitude of the loads P (in kN) so that the beam just touches the support at C. 163.87 x kNarrow_forwardDetermine the variation in the width w as a function of x for the cantilevered beam that supports a concentrated force P at its end so that it has a maximum bending stress sallow throughout its length. The beam has aconstant thickness t.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning