
Concept explainers
The tension in each brace and the reaction at C.
Answer to Problem 4.110P
The tension in brace BD is TBD=176.8 lb_.
The tension in brace BE is TBE=176.8 lb_.
The reaction at C is C=−(50 lb)j+(216.5 lb)k_.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the flag pole AC is 10 ft.
The inclination of the flag pole AC is 30°.
The distance BC is 3 ft.
Calculation:
Assumption:
Apply the sign convention for calculating the equations of equilibrium as shown below.
- For the horizontal forces equilibrium condition, take the force acting towards right side as positive (→+) and the force acting towards left side as negative (←−).
- For the vertical forces equilibrium condition, take the upward force as positive (↑+) and the downward force as negative (↓−).
- For moment equilibrium condition, take the clockwise moment as negative and counterclockwise moment as positive.
Draw the free body diagram as in Figure (1).
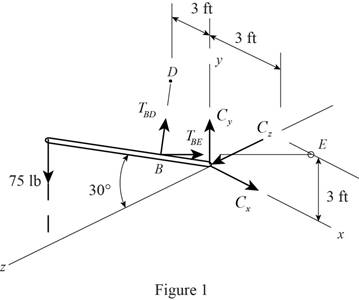
Calculate the position vector (r) as shown below.
The position of A is;
rA=(10sin30°)j−(10cos30°)k=(5 ft)j−(8.66 ft)k
The position of B is;
rB=(3sin30°)j+(3cos30°)k=(1.5 ft)j+(2.598 ft)k
The position of D is;
rD=−(3 ft)i+(3 ft)j
The position of E is;
rE=(3 ft)i+(3 ft)j
Calculate the position of brace BD as shown below.
→BD=rD−rB
Substitute −(3 ft)i+(3 ft)j for rD and (1.5 ft)j+(2.598 ft)k for rB.
→BD=[−(3 ft)i+(3 ft)j]−[(1.5 ft)j+(2.598 ft)k]=−(3 ft)i+(1.5 ft)j−(2.598 ft)k
Calculate the length of brace BD as shown below.
BD=√(−3)2+(1.5)2+(−2.598)2=√17.999604=4.243 ft
Calculate the position of brace BE as shown below.
BE=rE−rB
Substitute (3 ft)i+(3 ft)j for rB and (1.5 ft)j+(2.598 ft)k for rB.
→BE=[(3 ft)i+(3 ft)j]−[(1.5 ft)j+(2.598 ft)k]=(3 ft)i+(1.5 ft)j−(2.598 ft)k
Calculate the length of brace BE as shown below.
BE=√(−3)2+(1.5)2+(−2.598)2=√17.999604=4.243 ft
Calculate the tension in brace BD (TBD) as shown below.
TBD=TBD→BDBD
Substitute −(3 ft)i+(1.5 ft)j−(2.598 ft)k for →BD and 4.243 ft for BD.
TBD=TBD−3i+1.5j−2.598k4.243=TBD(−0.707i+0.3535j−0.6123k)
Calculate the tension in brace BE (TBE) as shown below.
TBE=TBE→BEBE
Substitute (3 ft)i+(1.5 ft)j−(2.598 ft)k for →BE and 4.243 ft for BE.
TBE=TBE3i+1.5j−2.598k4.243=TBE(0.707i+0.3535j−0.6123k)
Apply the Equations of Equilibrium as shown below.
Apply the equilibrium equation of moment about point C and equate to zero for equilibrium.
∑MC=0rB×TBD+rB×TBE+rA×(−75j)=0
Substitute (5 ft)j−(8.66 ft)k for rA, (1.5 ft)j+(2.598 ft)k for rB, TBD(−0.707i+0.3535j−0.6123k) for TBD, and TBE(0.707i+0.3535j−0.6123k) for TBE.
[(1.5j+2.598k)×(TBD(−0.707i+0.3535j−0.6123k))+(1.5j+2.598k)×(TBE(0.707i+0.3535j−0.6123k))+(5j−8.66k)×(−75j)]=0TBD|ijk01.52.598−0.7070.3535−0.6123|+TBE|ijk01.52.5980.7070.3535−0.6123|+|ijk05−8.660−750|=0[TBD(i(−0.9185−0.9184)−j(0+1.8368)+k(0+1.0605))+TBE(i(−0.9185−0.9184)−j(0−1.8368)+k(0−1.0605))+(i(0−649.5)−j(0)+k(0))]=0(TBD(−1.8369i−1.8368j+1.0605k)+TBE(−1.8369i+1.8368j−1.0605k)−649.5i)=0
Multiply by 4.243.
(−1.8369TBDi−1.8368TBDj+1.0605TBDk−1.8369TBEi+1.8368TBEj−1.0605TBEk−649.5i)=0{(−1.8369TBD−1.8369TBE−649.5)i+(−1.8368TBD+1.8368TBE)+(1.0605TBD−1.0605TBEk)}=0
Resolve i, j, and k components as shown below.
Resolve j component.
−1.8368TBD+1.8368TBE=01.8368TBD=1.8368TBETBD=TBE (1)
Resolve i component.
−1.8369TBD−1.8369TBE−649.5=0
Substitute TBE for TAD.
−1.8369TBE−1.8369TBE−649.5=0−3.6738TBE=649.5TBE=−176.79 lbTBE=176.79 lb
Hence, the tension in brace BE is TBE=176.8 lb_.
Calculate the tension in brace BD as shown below.
Substitute 176.8 lb for TBE in Equation (1).
TBD=176.8 lb
Hence, the tension in brace BD is TBD=176.8 lb_.
Apply the Equations of Equilibrium as shown below.
Apply the equilibrium equation of forces in x-direction and equate to zero for equilibrium.
∑Fx=0Cx+176.8×(−0.707)+176.8×0.707=0Cx=0
Apply the equilibrium equation of forces in y-direction and equate to zero for equilibrium.
∑Fy=0Cy+176.8×0.3535+176.8×0.3535−75=0Cy+50=0Cy=−50 lb
Apply the equilibrium equation of forces in z-direction and equate to zero for equilibrium.
∑Fz=0Cz+176.8×(−0.6123)+176.8×(−0.6123)=0Cz−216.5=0Cz=216.5 lb
Calculate the reaction at C as shown below.
C=Cxi+Cyj+Czk
Substitute 0 for Cx, −50 lb for Cy, and 216.5 lb for Cz.
C=(0)i+(−50)j+(216.5)k=−(50 lb)j+(216.5 lb)k
Therefore, the reaction at C is C=−(50 lb)j+(216.5 lb)k_.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- The evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle utilizing R-123 as the refrigerant isbeing used to chill water. The evaporator is a shell and tube heat exchanger with the water flowingthrough the tubes. The water enters the heat exchanger at a temperature of 54°F. The approachtemperature difference of the evaporator is 3°R. The evaporating pressure of the refrigeration cycleis 4.8 psia and the condensing pressure is 75 psia. The refrigerant is flowing through the cycle witha flow rate of 18,000 lbm/hr. The R-123 leaves the evaporator as a saturated vapor and leaves thecondenser as a saturated liquid. Determine the following:a. The outlet temperature of the chilled waterb. The volumetric flow rate of the chilled water (gpm)c. The UA product of the evaporator (Btu/h-°F)d. The heat transfer rate between the refrigerant and the water (tons)arrow_forwardThe blade support of a hacksaw is subject to compression when a blade is installed and tightened. What is the state of stress (total combined stress) at A in MPa if the compression in the support is 1,524 N. Note: pay close attention to what is compression and what is tension and use a negative sign for the former. 100 mm 8 mm 3 mm 75 mm A 8 mm 3 mm B 50 mmarrow_forwardThe answer is not 4.378 ft/sarrow_forward
- The answer is not 0.293 marrow_forwardplease first help me solve this problem find the line of action and them help to find the forces like for example {fx= fy= mz= and determine the shear force in the nailsarrow_forwardAn open channel of square cross section had a flowrate of 17.2 ft³/s when first used. After extended use, the channel became 0.6-filled with silt. Determine the flowrate for this silted condition. Assume the Manning coefficient is the same for all the surfaces. Qs= ! ft³/sarrow_forward
- (Manning equation) The triangular flume shown in the figure below is built to carry its design flowrate, Qo, at a depth of 0.991 m as is indicated. If the flume is to be able to carry up to twice its design flowrate, Q = 2Qo, determine the freeboard, I, needed. ✓ -90°- 0.991 m i marrow_forwardWater flows in a 2-ft-wide rectangular channel at a rate of 10 ft³/s. If the water depth downstream of a hydraulic jump is 2.5 ft, determine (a) the water depth upstream of the jump, (b) the upstream and (c) downstream Froude numbers, and (d) the head loss across the jump. (a) y₁ = i (b) Fr₁ = i (c) Fr₂ = i (d) h₁ = ft ftarrow_forwardA hydraulic jump at the base of a spillway of a dam is such that the depths upstream and downstream of the jump are 0.8 and 3.2 m, respectively (see the Video). If the spillway is 12 m wide, what is the flowrate over the spillway? Q= i m³/sarrow_forward
- (Manning equation) Water flows in a rectangular channel of width b at a depth of b/2. Determine the diameter of a circular channel (in terms of b) that carries the same flowrate when it is half-full. Both channels have the same Manning coefficient, n, and slope. barrow_forward(Manning equation) A weedy irrigation canal of trapezoidal cross section is to carry 20 m³/s when built on a slope of 0.60 m/km. If the sides are at a 45° angle and the bottom is 8 m wide, determine the width of the waterline at the free surface. i marrow_forwardWater flows in a 1.2-m-diameter finished concrete pipe so that it is completely full and the pressure is constant all along the pipe. If the slope is So = 0.0073, (a) determine the flowrate by using open-channel flow methods. Compare this result with (b) that obtained using the pipe flow methods of Chapter 8 (Use Colebrook formula, Table 8.1, Table 10.1 and assume that Re > 10º). (a) Q = i (b) Q = i m³/s m³/sarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





