
a)
To find: Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market.
a)
Explanation of Solution
Introduction: Exchange rate refers to the rate of conversion of one currency into another. This is usually determined for the trading of goods and services with one country and the rest of the world.
b)
To find: The impact on country U interest rate and international capital flows due to
b)
Explanation of Solution
If Fed follows an expansionary monetary policy, the money supply will increase which causes the interest rate to fall. This makes us a less attractive destination for investment, reducing international capital inflow to the country U.
Introduction: Exchange rate refers to the rate of conversion of one currency into another. This is usually determined for the trading of goods and services with one country and the rest of the world.
c)
To draw: Graphical representation of foreign exchange rate showing the effect of the Fed’s policy.
c)
Explanation of Solution
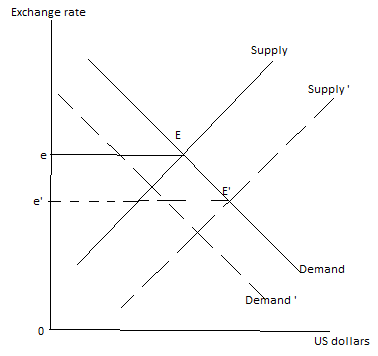
Demand for the US dollar decreases. Also with a lower interest rate in country U, country U’s investors may invest more abroad which increases US dollar supply.
Demand curve shifts left, hence, the supply curve will shift right, leading to a decrease in e (depreciation of USD) (Point E1 in the diagram).
Introduction: Exchange rate refers to the rate of conversion of one currency into another. This is usually determined for the trading of goods and services with one country and the rest of the world.
d)
To find: Affect on country U aggregate demand due to Fed’
d)
Explanation of Solution
Fed monetary policy changes interest rates which directly affect consumption and investment expenditure. Also, exchange rate changes (on account of change in interest rate) change aggregate demand through Net exports.
Introduction:
Exchange rate is the rate of conversion of one currency into another. This is usually determined for the trading of goods and services with one country and the rest of the world.
Chapter 43 Solutions
Krugman's Economics For The Ap® Course

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





