
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780137533268
Author: Paula Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON+
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 4, Problem 64P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The reason should be explained for the given compound has four stereoisomers when it has only one asymmetric center.
Concept introduction:
The total number of stereoisomers can be calculated by using following formula,
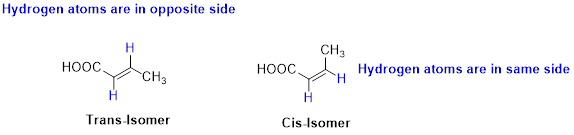
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of
Example:
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
How many asymmetric centers does the following compound have? How many stereocenters does it have?
What is the maximum number of stereoisomers possible for each compound?
The following compound has only one asymmetric center. Why then does it have four stereoisomers?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Ch. 4.1 - Draw the cis and trans isomers for the following:...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 5PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 6PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 7PCh. 4.2 - Tamoxifen slows the growth of some breast tumors...Ch. 4.2 - Draw and label the E and Z isomers for each of the...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 10PCh. 4.2 - Name each of the following:Ch. 4.2 - Draw the structure of (Z)-2,3-dimethyl-3-heptene.
Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 4.4 - Prob. 14PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 16PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 17PCh. 4.7 - Assign relative priorities to the groups or atoms...Ch. 4.7 - Name the following:Ch. 4.7 - Prob. 22PCh. 4.7 - Draw a perspective formula for each of the...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 24PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 27PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 28PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 29PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 30PCh. 4.10 - Prob. 31PCh. 4.10 - Prob. 32PCh. 4.10 - Prob. 33PCh. 4.11 - Prob. 34PCh. 4.11 - a. Draw the stereoisomers of...Ch. 4.11 - Prob. 37PCh. 4.11 - Prob. 38PCh. 4.12 - Which of the following compounds has a...Ch. 4.12 - Draw all the stereoisomers for each of the...Ch. 4.12 - Limonene exists as two different stereoisomers....Ch. 4 - a. Draw three constitutional isomers with...Ch. 4 - Which of the following have an asymmetric center?...Ch. 4 - Prob. 45PCh. 4 - Prob. 46PCh. 4 - Of all the possible cyclooctanes that have one...Ch. 4 - Prob. 48PCh. 4 - Prob. 49PCh. 4 - Prob. 50PCh. 4 - Prob. 51PCh. 4 - Prob. 52PCh. 4 - Draw the stereoisomers of 2,4-dichlorohexane....Ch. 4 - Prob. 54PCh. 4 - Prob. 55PCh. 4 - Prob. 56PCh. 4 - Prob. 57PCh. 4 - Prob. 58PCh. 4 - Prob. 59PCh. 4 - Prob. 60PCh. 4 - Prob. 61PCh. 4 - Prob. 62PCh. 4 - Draw structures for each of the following: a....Ch. 4 - Prob. 64PCh. 4 - a. Draw all the isomers with molecular formula...Ch. 4 - Prob. 66PCh. 4 - Prob. 67PCh. 4 - Prob. 68PCh. 4 - Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic...
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- (A) How many chirality centers does the following molecule contain? (B) How many stereoisomers are possible for this molecule? (C) Assign R,S designation to each chiral carbonarrow_forwardDetermine the relationship between the following compounds if stereoisomers (enantiomer/diastereomers) indicate R or S, E or Z, Cis or Trans for each stereocenter.arrow_forwardHow many chirality centers are there in the molecule shown below? How many stereoisomers are possible?arrow_forward
- Is cis-1,2-dibromocyclohexane a meso compound? In its planar structure, it has a line of symmetry but it has two chiral carbons. However, in its chair conformation, it does not look like it has a line of symmetry but it has two chiral carbons.arrow_forwardHow many chirality centers are there in the following molecule?arrow_forwardGiven the following structure and numbering: (a) Label the stereocenters of A as R or S and draw a Fischer Projection of the enantiomer of A with C1on top and C4 on bottom. (b) Draw a Newman Projection of a diastereomer of A looking down the C2-C3 bond with C2 in front.arrow_forward
- How many chiral centers are in oxanamide? How many stereoisomers are possible for this compound?arrow_forwardIs it possible for a meso compound to contain three chiral centers? Why or why not?arrow_forward3. Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Completely fill in the circle in front of your chosen answer. (a) A compound with a plane of symmetry must be achiral. (b) A compound with two or more stereocenters must be chiral. (a) O True O False True O Falsearrow_forward
- What is the configuration of the asymmetric centers in the following compounds?arrow_forwardDoes methylcyclopentane have a stereogenic center?arrow_forwardI want to know how many chiral centers there are in the structure of artemisinin, which is an antimalarial drug. And how many stereoisomers can there be?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning