
figure 4.2 shows a vacuum tank with a flat circular observation window in one end. If the pressure in the tank is 0.12psia when the barometer reads 30.5in of mercury, calculate the total force on the window.
Total force on the window.
Answer to Problem 4.1PP
The required value of the force is 1672.8lb
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
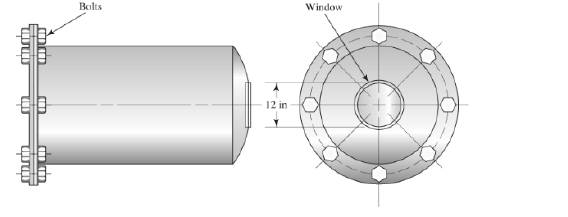
Pressure (P) = 0.12 psiaPressure head (h) = 30.5 in of hgDiameter (D) = 12 in
Formula used:
pressure (P) = force(F)area(A)pressure (P) = γhforce (F) = P×A
Calculation:
We know the standard formula to calculate pressure, i.e.: P = force(F)area(A)
Then, F = P×A(a)
Area (A) = π4(D)2⇒ A = π4(12)2⇒ A = 113.097 in2
Let us assume that the pressure in the tank is Patm= γh
Patm = (0.4889)(30.5)(specific weight of mercury (γ)=0.4889lb/in3)⇒ Patm = 14.911 lb/in2
Net pressure acting in the tank is, P = Patm−Pinside;
P = Patm−Pinside⇒ P = 14.911−0.12⇒ P = 14.791 lb/in2
From equation (a);
F = P×A⇒ F = (14.791)(113.097)⇒ F = 1672.8 lb
Then, the net force acting on the window is;
F = 1672.8 lb
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Applied Fluid Mechanics (7th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
- To save fuel during the heating season it is suggested that glass windows be covered at night with a 1.2 cm layer of polystyrene. Estimate the percent savings in energy and discuss the feasibility of this idea. Show the thermal circuit with and without the insulation panel. Consider a typical case of 0.2 cm thick window glass with inside and outside heat transfer coefficients of 6 and 32 W/m²-ºC. Lg←←Lp h T₁ T。 g kp insulation panelarrow_forwardA plate of thickness L and thermal conductivity k is exposed to a fluid at temperature T1 with a heat transfer coefficient h, on one side and T2 and h₂ on the other side. Determine the one-dimensional temperature distribution in the plate. Assume steady state and constant conductivity. L h h T%2 k Tx1 0xarrow_forwardDetermine the heater capacity needed to maintain the inside temperature of a laboratory chamber at 38°C when placed in a room at 21°C. The chamber is cubical with each side measuring 35 cm. The walls are 1.2 cm thick and are made of polystyrene. The inside and outside heat transfer coefficients are 5 and 22 W/m²-°C.arrow_forward
- (a) Refer to the above figure .What kind of controller is it ? (b) simplify the block diagramto derive the closed loop transfer function of the system. (C) What are the assumptions thatare needed to make to findthe controller gain ? What arethe value of Kp , Ti and Td ?arrow_forwardLonsider a regenerative gas turbine power plant with two stages of compression and two stages of expansion. The compressor pressure ratio of the compressor is 3. Air enters each stage of compressor at 290 K and esch stage of turbine at 1400 K. The regetierator has an effectiveness of 100%, Determine (a) The enthalpy at stage#2 in KJ/kg (b) The enthalpy at stage in KJ/kg" (c) The cathalpy at stager in KJ/kg* (d) The enthalpy at stage#10 in KJ/kg (c) The mass flow rate of air needed to develop a net power output of 50 MW *For all final answers please enter the integer part only, (ie 1234) and do not include the decimal part and the decimal point No rounding in your calculationarrow_forwardConsider a regenerative gas turbine power plant with two stages of compression and two stages of expansion. The compressor pressure ratio of the compressor is 3. Air enters each stage of compressor at 290 K and each stage of turbine at 1400 K. The regenerator has an effectiveness of 100%. Determine (a) The enthalpy at stage#2 in KJ/kg⭑ (b) The enthalpy at stage#6 in KJ/kg* (c) The enthalpy at stage#9 in KJ/kg (d) The enthalpy at stage#10 in KJ/kg (e)The mass flow rate of air needed to develop a net power output of 50 MW* *For all final answers please enter the integer part only, (ie 1234) and do not include the decimal part and the decimal point No rounding in your calculation. Compressor stage 1 Regenerator www HX ww 9 Combustor Reheat Intercooler ww Compressor stage 2 Turbine 1 combustor Turbine 2arrow_forward
- Design a proportional derivitivecontroller for a plant orsystemthat satisfies the following specifications : 1. is steady-state error is less than 2 % for a ramp input. 2.) Damping ratio (zeta) is greater than 0.7have determined the 3. Once youvalue of kp and kd, then plotthe response of the compensated(with controller) and uncompensated( without the controller, only the plantsystem using MATLAB.arrow_forwardExample 2 The particle has a mass of 0.5 kg and is confined to move along the smooth horizontal slot due to the rotation of the arm OA. Determine the force of the rod on the particle and the normal force of the slot on the particle when 0 = 30°. The rod is rotating with a constant angular velocity 2 rad/s. Assume the particle contacts only one side of the slot at any instant. B =2 rad/s 0.5 m 0.5(9.81)N r F 30° Narrow_forwardA gas turbine cycle has two stages of compression, with an intercooler between the stages. Air enters the first stage at 100 kPa, 300 K. The pressure efficiency of 82%. Air exits the intercooler at 330 K. Calculate the temperature at the exit of each compressor stage and the total specific work required.arrow_forward
- For problem 13, your answer should be the same as problem 12. Calculate the flow velocity and the heat transfer/area of the outer surfaces for both duct geometries to see the performance difference of the two designs.arrow_forwardOne end of a thin uniform rod of mass m and length 31 rests against a smooth vertical wall. The other end of the rod is attached by a string of length 1 to a fixed point O which is located a distance 21 from the wall. A horizontal force of magnitude F₁ is applied to the lower end of the rod as shown. Assuming the rod and the string remain in the same vertical plane perpendicular to the wall, find the angle 0 between the rod and the wall at the position of static equilibrium. Notes: This quiz is going to walk you through a sequence of steps to do this. It won't give you the answers, but it will hopefully get you to see how to approach problems like this so that you have a working reference/template in the future. This is actually a modified version of a problem from the textbook (6.3). Note that in that problem, is not actually given. It has been introduced for convenience as we move through solving the problem, and should not show up in the final answer. DO NOT DO PROBLEM 6.3. It is…arrow_forwardvarrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
