Concept explainers
DRAW IT Diagram each of the following flagellar arrangements:
a. lophotrichous
b. monotrichous
c. peritrichous
d. polar
e. amphitrichous
To review:
The bacteria flagella arrangements.
Introduction:
Flagella are present both in prokaryotes and eukaryotes and they facilitate cell motility. It is a whip-like, hollow, cylindrical structure that contains the protein called flagellin. The arrangement of flagella is different in different species. It consists of three different parts, namely filament, hook, and basal body. Flagella eukaryotes derive energy from ATP, whereas flagella in prokaryotes derive energy from proton motive force.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
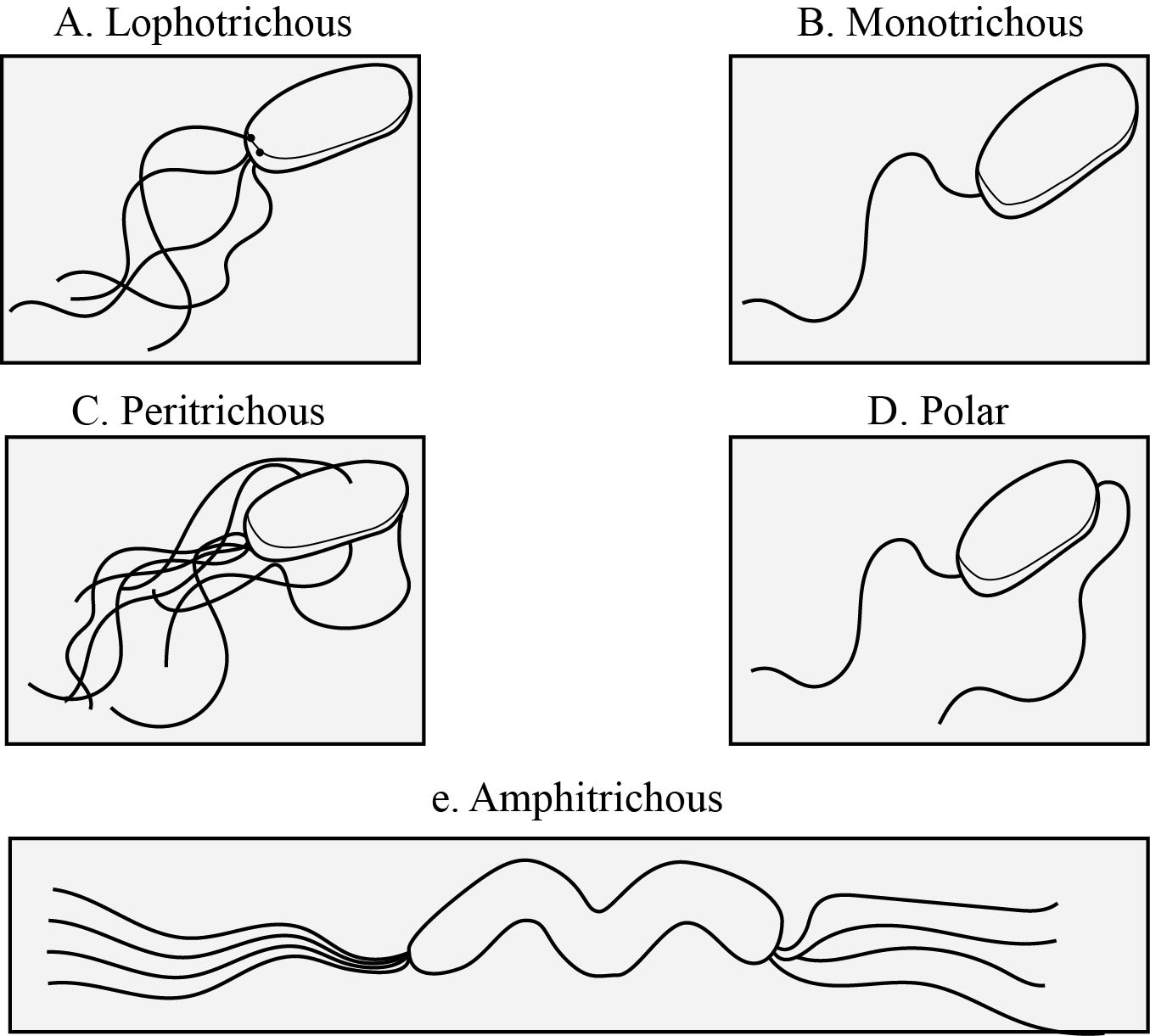
Based on the flagella arrangements, the organisms are classified into different types.
- Lophotrichous: Two or more flagella at one end of the cell.
- Monotrichous: Single flagellum present at one end of the cell.
- Peritrichous: More number of flagella present on the entire surface of the cell.
- Polar: Flagella are present at each pole of the bacterial cell.
- Amphitrichous: A bunch of flagella present at both ends of the bacterial cell.
The flagella present on the cells are useful for locomotion and attachment. It contains filamentous protein which helps to propel a cell through liquid. The flagella also act as sensory organelle and aid in detecting changes in the temperature and pH.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
- 1. Under a microscope, you probably noticed that all of the onions cells were roughly the same shape whereas the squamous cells from your buccal cavity, while roundish, may have been folded or bent. What do you think keeps all of the plant cells the same shape? A) Vaucole B) Cell membrane C) Chloroplasts D) Cell wall 2. When stained with methylene blue (buccal cell) and haemalum acid (onion cell), the nuclei were the only cellular structures that stained. This has to do with the stains being cationic (positively charged). What charge do you think the nuclei are in order to be stained? A) Positive (cationic) B) Negative (anionic) C) Neutral D) Hypotonic 3. FILL IN THE BLACKS USING THE BOLDED BRACKET OPTIONS: Observable physical differences between the three types of simple epithelial tissue are that squamous epithelial cells are _________ (flat, equal, more, less, cube, column, buccal, wider), whereas cuboidal epithelial cells have _____ (flat, equal, more, less, cube, column,…arrow_forwardShort, hairlike structures covering the surface of the cell used only by eukaryotic cells for movement are called O 1) pseudopodia. O 2) fimbriae. O 3) cilia. O 4) pili. O 5) flagella.arrow_forwardLabel the cell wall, chloroplast, and pyrenoid of the Spirogyra. Notice the series of cells making up the filament. Is the filament branched or unbranched? What is the shape of the individual cells that make up the filament?arrow_forward
- Which statement about flagella is false? Question 9 options: a) Eukaryotic flagella are made of a protein called tubulin. b) Eukaryotic flagella move in a wavelike motion. c) Prokaryotic flagella rotate. d) Prokaryotic flagella are composed of a protein called flagellin. e) Prokaryotic flagella can transfer DNA between cells. f) None of the above statements is false.arrow_forwardWhich of the following is NOT a true statement about bacterial structure and function? A. Bacteria can have membrane-enclosed organelles such as mitochondria or chloroplasts B. Bacteria have a single circular chromosome made of double-stranded DNA C. Bacterial cell walls are made of a substance called peptidoglycan D. Bacterial flagella rotate to propel the cell E. Some bacteria have a capsule surrounding the cell, made of a sticky polysaccharide or proteinarrow_forwardDifferences between Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli in terms of: a. Chromatoidal mass b. Description of pseudopode and motility c. Number of nuclein in the mature cyst stage d. Location of the karyosomearrow_forward
- Which of the following does not possess cilia or flagella? a.)Amoeba b.)Paramecium c.)Trypanosoma d.)Mastigamoebaarrow_forwardUse this diagram of a Chlamydomonas cell for the following question. M. CY CL is chloroplast, CY is cytoplasm, M is mitochondrion, N is nucleus. Which of the following locations would be the site of translation of genes involved in the process of cellular respiration? 00arrow_forwardUse this diagram of a Chlamydomonas cell for the following question, 00 OD. N and M O E. CY and M O F. CY and CL O G. CY only OH. No CY CL is chloroplast, CY is cytoplasm, M is mitochondrion, N is nucleus. Which of the following locations would be the site of translation of genes involved in the process of cellular respiration? O A CL, CY, M and N OB. CL. M and N O C. CL and Marrow_forward
- Identify Three subtypes of polar arrangement where the flagella are attached at one or both ends of the cell.arrow_forwardMention one significant function of rhizoids.arrow_forwardWhat term best describes the following organisms: some with tetramembraneous chloroplasts, some with hairy flagellae, some with pseudopods; some with cuplike indentations in the cell membrane? a) Excavata. b) SAR. c) Plantae. d) Unikonta. The term protista refers to : a) A kingdom within the superkingom SAR. b) A kingdom within the superkingdom Excavata. c) It is a descriptive term or common name for unicellular, colonial, and some multicellular organisms that lack true tissues. d) A phylum within the Kingdom Metazoa. Which term best describes the following organism: a unicellular (single celled) eukaryote that has a single large mitochondrion, and causes Chagas disease or sleeping sickness. a) Hypermastigophora. b) Diplomonada. c) Algae. d) Trypanosoma. e) Rhizopoda. 4. What term best describes the following organism: a multicellular eukaryote with a chitinous cell wall that is an absorptive heterotroph? a) Fungi. b)…arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





