
Concept explainers
Consider the double-slit arrangement shown in Figure P37.60, where the slit separation is d and the distance from the slit to the screen is L. A sheet of transparent plastic having an index of refraction n and thickness t is placed over the upper slit. As a result, the central maximum of the interference pattern moves upward a distance y′ Find y′.
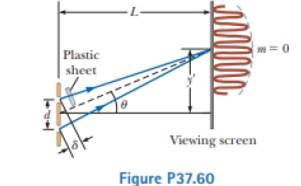
The position
Answer to Problem 37.60AP
The position
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The separation between the slits is
The path difference due to the slit is given by,
Here,
The value of sine of angle is,
Here,
Substitute
The path difference due to the transparent plastic sheet is,
Here,
The net path difference is given by,
Substitute
The condition of central maxima is,
Substitute
Take square on both sides of the above equation.
Simplify the above equation for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the position
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 37 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 1
- Coherent light rays of wavelength strike a pair of slits separated by distance d at an angle 1, with respect to the normal to the plane containing the slits as shown in Figure P27.14. The rays leaving the slits make an angle 2 with respect to the normal, and an interference maximum is formed by those rays on a screen that is a great distance from the slits. Show that the angle 2 is given by 2=sin1(sin1md) where m is an integer.arrow_forwardTable P35.80 presents data gathered by students performing a double-slit experiment. The distance between the slits is 0.0700 mm, and the distance to the screen is 2.50 m. The intensity of the central maximum is 6.50 106 W/m2. What is the intensity at y = 0.500 cm? TABLE P35.80arrow_forwardIn Figure P27.7 (not to scale), let L = 1.20 m and d = 0.120 mm and assume the slit system is illuminated with monochromatic 500-nm light. Calculate the phase difference between the two wave fronts arriving at P when (a) = 0.500 and (b) y = 5.00 mm. (c) What is the value of for which the phase difference is 0.333 rad? (d) What is the value of for which the path difference is /4?arrow_forward
- Figure P35.24 shows the diffraction patterns produced by a slit of varying width. What is the relative width of the slit in each case, from narrowest to widest? FIGURE P35.24 Problems 24 and 32.arrow_forwardInterference fringes are produced using Lloyds mirror and a source S of wavelength = 606 nm as shown in Figure P36.41. Fringes separated by y = 1.20 mm are formed on a screen a distance L = 2.00 m from the source. Find the vertical distance h of the source above the reflecting surface. Figure P36.41arrow_forwardLaser light of wavelength 627.0 nm passes through a double-slit arrangement at the front of a lecture room, reflects off a mirror 29.2 m away at the back of the room, and then produces an interference pattern on a screen at the front of the room. The distance between adjacent bright fringes is 9.52 cm. What is the slit separation in meters? Number i 0.000192 Units marrow_forward
- In an interference experiment using a monochromatic source emitting light of wavelength 1, the fringes are produced by two long, narrow slits separated by a distance d 0.5 mm. The fringes are formed on a screen which is situated at a distance D = 5 m from the slits. Determine å, if the fringe width w = 6 mm. Provide your answer in nanometers (10° m).arrow_forwardA student performs a multiple-slit interference experiment. A coherent light source illuminates multiple slits in a barrier, and the resulting interference pattern is projected on a screen that is separated from the barrier by 2.2 m. The uniform spacing between the slits is 5.0μm5.0μm. A light sensor is used to measure the intensity of the light at the screen, and the student makes the following graph of the intensity as a function of the position along the screen as measured from the center of the central maximum. What is the wavelength, in nm, of the light source?arrow_forwardA monochromatic light beam coming from a point source illuminates two parallel horizontal slits. The center of the two slits is a = 0.80 mm, as illustrated in the figure. An interference pattern is produced on a target at 50 cm. In this pattern, the dark and light fringes are equally spaced. The distance y1 is 0.304 mm.Calculate the wavelength of the incident light.arrow_forward
- The figure shows the interference pattern that appears on a distant screen when coherent light is incident on a mask with two identical, very narrow slits. Points P and Q are maxima; Point R is a minimum. The wavelength of the light that created the interference pattern is λ=678nm, the two slites are separated by rm d=6 μm, and the distance from the slits to the center of the screen is L=80cm . The difference in path length at a point on the screen is Δs=|s1−s2|, where s1s1 and s2s2 are the distances from each slit to the point. What is ΔsΔs (in nm) at Point P? What is ΔsΔs (in nm) at Point Q? What is ΔsΔs (in nm) at Point R?arrow_forwardCoherent light of frequency f travels in air and is incident on two narrow slits. The interference pattern is observed on a distant screen that is directly opposite the slits. The frequency of light f can be varied. For f = 5.60 x 1012 Hz there is an interference maximum for θ = 60.0°. The next higher frequency for which there is an interference maximum at this angle is 7.47 x 1012 Hz. What is the separation d between the two slits?arrow_forwardLight Emitting Diodes (LEDS) are semiconductor devices that emit light at specific wavelengths without emitting at any other wavelengths. LEDS can be used to create lasers that are very compact since they are a solid state device. A pair of narrow, parallel slits separated by 0.266 mm are illuminated by the green LED laser (A = 546.1 nm). The interference pattern is observed on a screen 1.20 m from the plane of the parallel slits. (a) Calculate the distance from the central maximum to the first bright region. (b) What is the distance between the first and second dark fringes? marrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





