
Concept explainers
Light rays strike a plane mirror at an angle of 45.0° as shown in Figure P37.15. At what angle should a second mirror be placed so that the reflected rays are parallel to the first mirror?
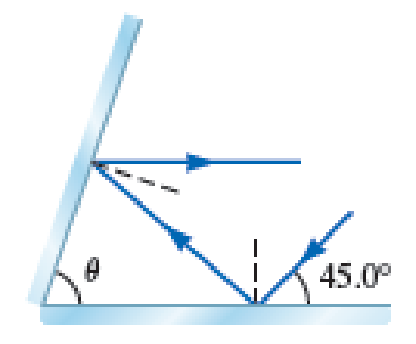
The angle at which the second mirror be placed so that the reflected rays are parallel to the first mirror.
Answer to Problem 15PQ
The angle at which the second mirror be placed so that the reflected rays are parallel to the first mirror is
Explanation of Solution
The following figure shows the reflection diagram.
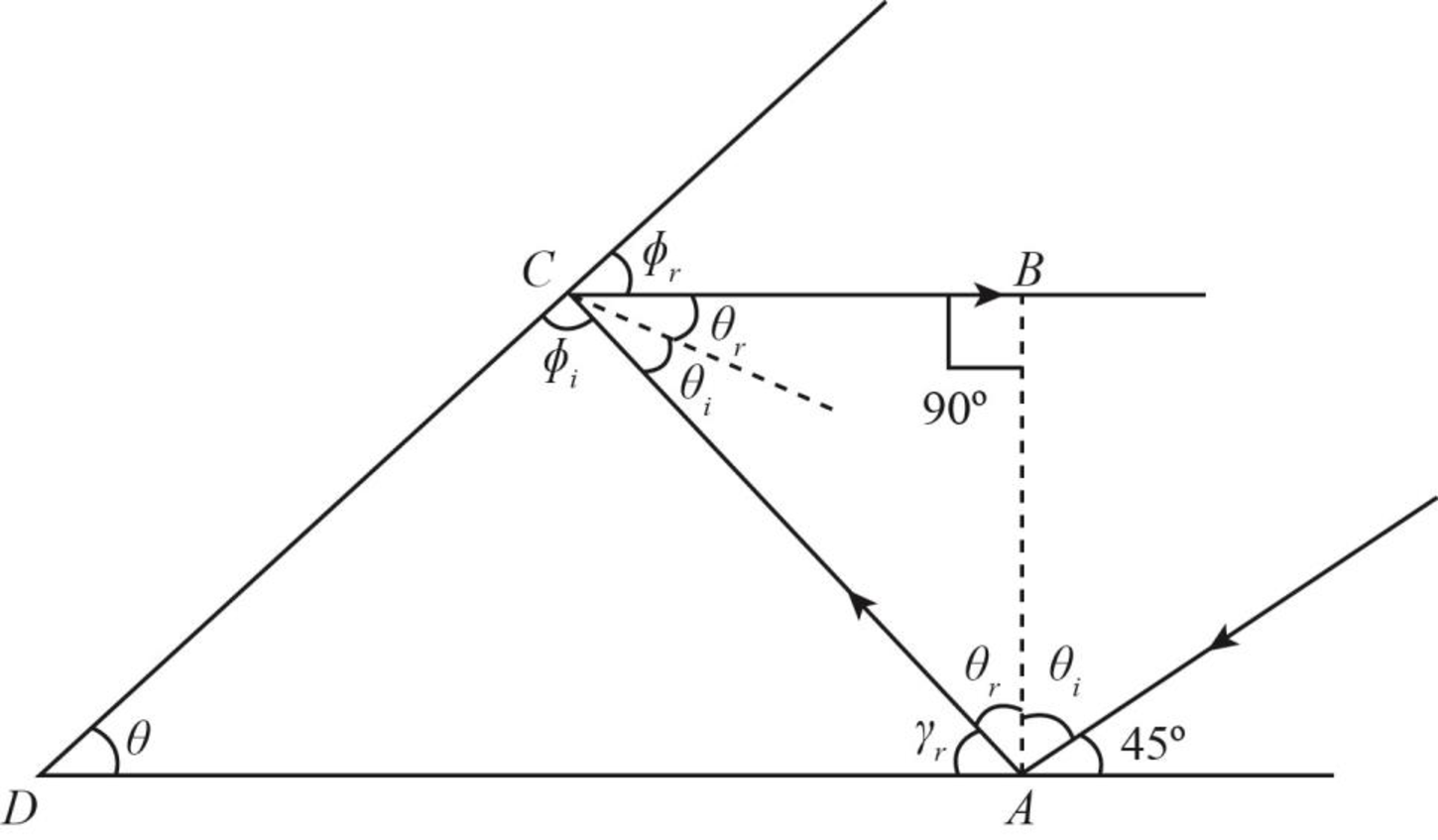
Figure-(1)
Here,
Calculate the angle from the above diagram.
According to law of reflection
Calculate the other angles from the above diagram.
From the above figure, the total angle in the triangle
For the second mirror, the total angle in a straight line is equal to
From the above figure, the total angle in the triangle
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the angle at which the second mirror be placed so that the reflected rays are parallel to the first mirror is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 37 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- If Joshs face is 30.0 cm in front of a concave shaving mirror creating an upright image 1.50 times as large as the object, what is the mirrors focal length? (a) 12.0 cm (b) 20.0 cm (c) 70.0 cm (d) 90.0 cm (e) none of those answersarrow_forwardA floating strawberry illusion is achieved with two parabolic mirrors, each having a focal length 7.50 cm, facing each other as shown in Figure P33.58. If a strawberry is placed on the lower mirror, an image of the strawberry is formed at the small opening at the center of the top mirror, 7.50 cm above the lowest point of the bottom mirror. The position of the eye in Figure P35.58a corresponds to the view of the apparatus in Figure P35.58b. Consider the light path marked A. Notice that this light path is blocked by the upper mirror so that the strawberry itself is not directly observable. The light path marked B corresponds to the eye viewing the image of the strawberry that is formed at the opening at the top of the apparatus. (a) Show that the final image is formed at that location and describe its characteristics. (b) A very startling effect is to shine a flashlight beam on this image. Even al a glancing angle, the incoming light beam is seemingly reflected from the image! Explain. Figure P35.58arrow_forwardIn Figure P35.30, a thin converging lens of focal length 14.0 cm forms an image of the square abed, which is he = hb = 10.0 cm high and lies between distances of pd = 20.0 cm and pa = 30.0 cm from the lens. Let a, b, c. and d represent the respective corners of the image. Let qa represent the image distance for points a and b, qd represent the image distance for points c and d, hb, represent the distance from point b to the axis, and hc represent the height of c. (a) Find qa, qd, hb, and hc. (b) Make a sketch of the image. (c) The area of the object is 100 cm2. By carrying out the following steps, you will evaluate the area of the image. Let q represent the image distance of any point between a and d, for which the object distance is p. Let h represent the distance from the axis to the point at the edge of the image between b and c at image distance q. Demonstrate that h=10.0q(114.01q) where h and q are in centimeters. (d) Explain why the geometric area of the image is given by qaqdhdq (e) Carry out the integration to find the area of the image. Figure P35.30arrow_forward
- A small convex mirror and a large concave mirror are separated by 1.00 m, and an object is placed 1.40 m to the left of the concave mirror (Fig. P37.69). The concave mirror forms an image of this object at distance di = 25.0 cm. This image is then reflected in the convex mirror, which forms an image a distance of 8.00 cm behind the convex mirror. What is the focal length of the small convex mirror? FIGURE P37.69arrow_forwardWhy is the following situation impossible? Consider the lensmirror combination shown in Figure P35.55. The lens has a focal length of fL = 0.200 m, and the mirror has a focal length of fM = 0.500 m. The lens and mirror are placed a distance d = 1.30 m apart, and an object is placed at p = 0.300 m from the lens. By moving a screen to various positions to the left of the lens, a student finds two different positions of the screen that produce a sharp image of the object. One of these positions corresponds to light leaving the object and traveling to the left through the lens. The other position corresponds to light traveling to the right from the object, reflecting from the mirror and then passing through the lens. Figure P35.55 Problem 55 and 57.arrow_forwardAn observer to the right of the mirror-lens combination shown in Figure P36.89 (not to scale) sees two real images that are the same size and in the same location. One image is upright, and the other is inverted. Both images are 1.50 times larger than the object. The lens has a focal length of 10.0 cm. The lens and mirror are separated by 40.0 cm. Determine the focal length of the mirror.arrow_forward
- Use a ruler and a protractor to draw rays to find images in the following cases. (a) A point object located on the axis of a concave minor located at a point within the focal length from the vertex. (b) A point object located on the axis of a concave mirror located at a point farther than the focal length from the vertex. (c) A point object located on the axis of a convex mirror located at a point within the focal length from the vertex. (d) A point object located on the axis of a convex mirror located at a point farther than the focal length from the vertex. (e) Repeat (a)—(d) for a point object off the axis.arrow_forward(i) An object is plated at a position p f from a concave mirror as shown in Figure CQ39.12a, where f is the focal length of the mirror. In a finite time interval, the object is moved to the right to a position at the focal point F of the mirror. Show that the image of the object moves at a speed greater than the speed of light. (ii) A laser pointer is suspended in a horizontal plane and set into rapid rotation as shown in Figure CQ39 12b. Show that the spot of light it produces on a distant screen can move across the screen at a speed greater than the speed of light. (If you carry out this experiment. make sure the direct laser light cannot enter a person's eyes.) (iii) Argue that the experiments in parts (i) and (ii) do not invalidate the principle that no material, no energy, and no information can move faster than light moves in a vacuum. Figure CQ39.12arrow_forwardA 1.80-m-tall person stands 9.00 m in front of a large, concave spherical mirror having a radius of curvature of 3.00 m. Determine (a) the mirrors focal length, (b) the image distance, and (c) the magnification. (d) Is the image real or virtual? (e) Is the image upright or inverted?arrow_forward
- A mirror is designed so that a person 50 cm in front of it sees an erect image magnified by a factor of three. A) What is the radius of curvature of the mirror? B) Is the mirror concave or convex?arrow_forwardA concave makeup mirror is designed so that a person 20 cm in front of it sees an upright image magnified by a factor of two. What is the radius of curvature of the mirror? R = marrow_forwardIn E111, the object is placed in front of a concave mirror, at an object distance 3x the magnitude of the focal length. Which of the following is incorrect? Consider the magnitudes only. The image height is 0.25 times the object height. The image is inverted. The image distance is 1.5 times the focal length. The image distance is 0.5 times the object distance.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





