
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172517
Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 32, Problem 3VCQ
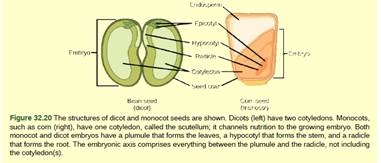
Figure 32.20 What is the function of the
cotyledon?
- It develops into the root.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A banana contains both a fleshy endocarp and mesocarp but the exocarp is skin-like. Bananas also cannot expel their seeds through
dehiscence. Which type of fruit is a banana?
Pepo
Berry
Hesperidium
Drupe
Even before a seed germinates, it already has a root; what is the name of this embryonic root? In eudicots, what does this embryonic root usually develop into? In most monocots, this embryonic root does a strange thing during or immediately after germination. What does it do?
Do you agree that it is the stem that
is growing? Why or why not?
Notebook Entry 1
My seed has begun to
grow. I think the thing
coming out of the split seed
is the stem. It will begin to
grow up in a few more
days. Later, the root will
begin to grow.
Chapter 32 Solutions
Biology 2e
Ch. 32 - Figure 32.3 If the anther is missing, what type of...Ch. 32 - Figure 32.8 An embryo sac is missing the...Ch. 32 - Figure 32.20 What is the function of the...Ch. 32 - In a plant’s male reproductive organs, development...Ch. 32 - The stamen consists of a long stalk called the...Ch. 32 - Theare collectively called the calyx sepals petals...Ch. 32 - The pollen lands on which part of the flower?...Ch. 32 - After double fertilization: a zygote and ______...Ch. 32 - The fertilized ovule gives rise to the fruit seed...Ch. 32 - What is the term for a fruit that develops from...
Ch. 32 - The is the outermost covering of a______ fruit....Ch. 32 - _______ is a useful method of asexual reproduction...Ch. 32 - Which of the following is an advantage of asexual...Ch. 32 - Plants that flower once in their lifetime are...Ch. 32 - Plant species that complete their lifecycle in one...Ch. 32 - Describe the reproductive organs inside a flowerCh. 32 - Describe the two-stage lifecycle of plants: the...Ch. 32 - Describe the four main parts, or whorls, of a...Ch. 32 - Discuss the differences between a complete flower...Ch. 32 - Why do some seeds undergo a period of dormancy,...Ch. 32 - Discuss some ways in which fruit seeds are...Ch. 32 - What are some advantages of asexual reproduction...Ch. 32 - Describe natural and artificial methods of asexual...Ch. 32 - Discuss the life cycles of various plantsCh. 32 - How are plants classified on the basis of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A bullet is accelerated down the barrel of a gun by hot gases produced in the combustion of gun powder. What is...
College Physics
Meiosis II is similar to mitosis because a. sister chromatids separate. b. homologous chromosomes line up indep...
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
4. What five specific threats to biodiversity are described in this chapter? Provide an example of each.
Biology: Life on Earth
Where is transitional epithelium found and what is its importance at those sites?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
1. ___ Mitosis 2. ___ Meiosis 3. __ Homologous chromosomes 4. __ Crossing over 5. __ Cytokinesis A. Cytoplasmic...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (4th Edition)
Body, Heal Thyself The precision of mitotic cell division is essential for repairing damaged tissues like those...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Figure 25.24 Which of the following statements about the fern life cycle is false? Sporangia produce haploid spores. The sporophyte grows from a gametophyte The sporophyte is diploid and the gametophyte is haploid. Sporangia form on the underside of the gametophyte.arrow_forwardWhich of the following is not a characteristic of plants? (a) cuticle (b) unicellular gametangia (c) stomata (d) multicellular embryo (e) alternation of generationsarrow_forwardFigure 23.28 Which of the following statements about the Laminaria life cycle is false? In zoospores form in the sporangia. The sporophyte is the 2n plant. The gametophyte is diploid. Both the gametophyte and sporophyte stages are multicellular.arrow_forward
- Roots that enable a plant to grow on another plant are called.______ epiphytic roots prop roots adventitious roots aerial rootsarrow_forwardFigure 32.3 If the anther is missing, what type of reproductive structure will the flower be unable to produce? What term is used to describe a flower that is normally lacking the androecium? What term describes a flower lacking a gynoecium?arrow_forwardFigure 14.26 If a flower lacked a megasporangium, what type of gamete would it not be able to form? If it lacked a microsporangium, what type of gamete would not form?arrow_forward
- In a germinating seed, the downward growth of roots and upward growth of stems are the plant’s responses to gravity. Which statement best describes this phenomenon? * downward growth of roots – positive response to gravity ; upward growth of stems – negative response to gravity downward growth of roots – negative response to gravity ; upward growth of stems – positive response to gravity downward growth of roots – positive response to gravity ; upward growth of stems – positive response to gravity No answer downward growth of roots – negative response to gravity; upward growth of stems – negative response to gravityarrow_forwardUnlike animals, plants continue to grow in their oldest stage of development Which type of plant tissue produces new, undifferentiated cells? ANSWER CHOICES ARE IN THE PHOTO. thanks.arrow_forwardPut the following 3 fictional plants in order from earliest to most recent according to their characteristics: A. The Terpad Plant: This plant reproduces using spores and has proper leaves and vascular tissue. B. The Feltris Plant: The Feltris plant lives in moist environments since it doesn't have any vascular tissue to maintain hydration throughout the plant. This plant has no roots either but has small root-like structures called rhizoids which help anchor them to the ground. Water is also required in order for fertilization. C. The Lancelot Plant: This plant can grow in either moist or dry environments, has true roots, stems and leaves and reproduces via seeds which develop within an ovary.arrow_forward
- Theophrastus of Lesbos, Aristotle’s successor as head of the Lyceum, improved upon Aristotle’s botany by classifying all dicotyledons as flowering plants with: two seed-leaves in the embryo, branching leaf veins, and flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5 one seed-leaf in the embryo, branching leaf veins, and flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5 one seed-leaf in the embryo, parallel leaf veins, and flower parts in multiples of 3 or 6 two seed-leaves in the embryo, parallel leaf veins, and flower parts in multiples of 3 or 6 two seed-leaves in the embryo, branching leaf veins, and flower parts in multiples of 3 or 6arrow_forwardThe presence of the vascular tissue allows a plant to grow much larger than its gametophyte counterpart and non-vascular plants. What are two functions (not structures) of the vascular tissue that allow for this?arrow_forwardThe center of the woody stem is called the pith. Over the years it gets very hard and becomes clogged with resin. This seals out moisture. This center wood is called heartwood. The outer, newer wood is called sapwood. The bark of the tree is very interesting. Different trees have different bark. You can sometimes tell a tree by its bark. Bark is all the tissue between the cambium and the outer surface of the stem. Bark is divided into two sections, inner and outer bark. The outer bark, which is what you see, protects the tree from disease and the environment. This outer bark is actually dead cork tissues. The inner bark is living tissues like cork cambium, cortex, and phloem. As new cork tissue develops from the cork cambium, it pushes out on the dead cork tissue of the outer bark. This causes the outer bark to crack. This forms the unique patterns on the barks of trees. Check-Up word bank phloem herbaceous meristematic bud scales xylem support heartwood pith terminal lenticels 1. The…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax


Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College
General Embryology Review in 20 minutes; Author: Medical Animations;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4YKvVeVMmEE;License: Standard youtube license