
Fill in the blanks in this concept map to help you tie together key concepts concerning transport in plants.
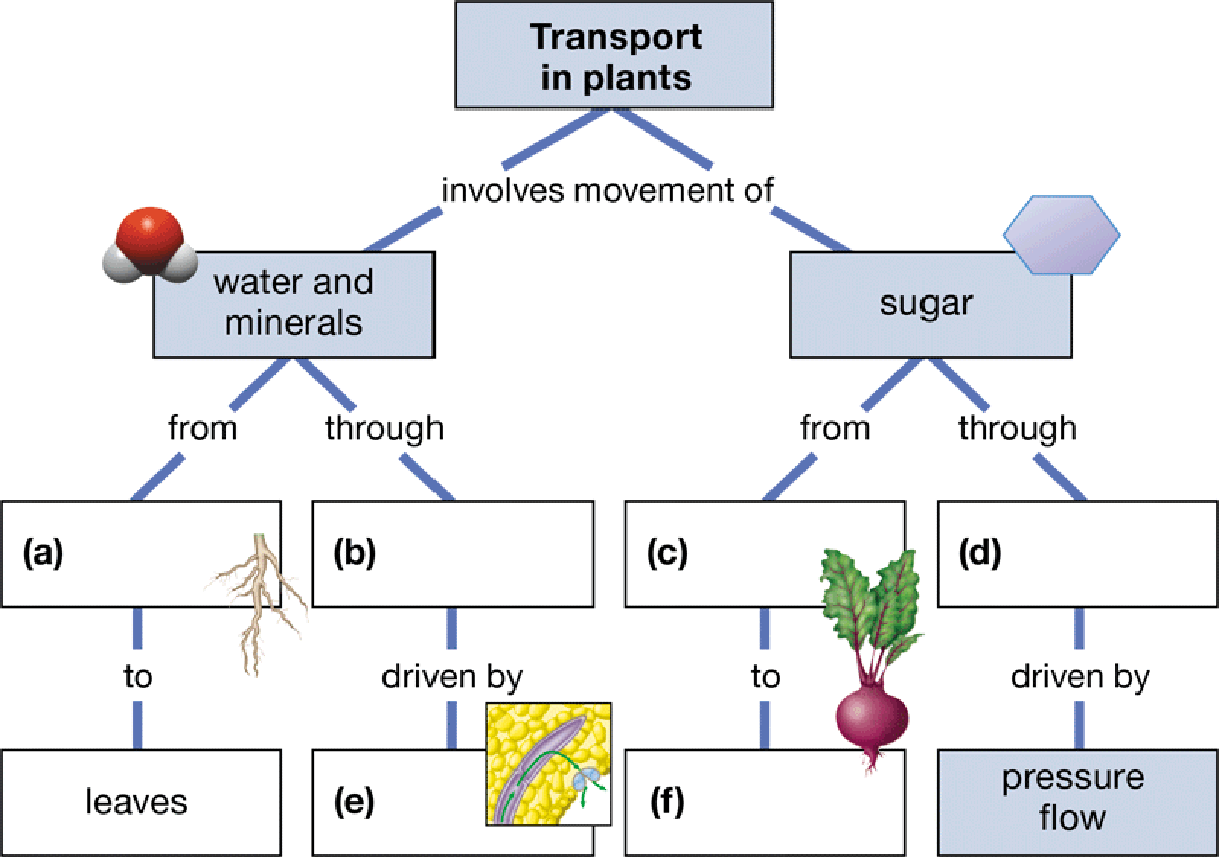
To create: The concept map that depicts transportation in plant.
Introduction: Angiosperms are the most developed group in the plant kingdom. They comprise the root system, root hairs, shoot system, leaves, petioles, blades, stems, nodes, internodes, and flower. They are seed-bearing plants that are covered.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig: 1 shows a complete concept map of transport in plants.
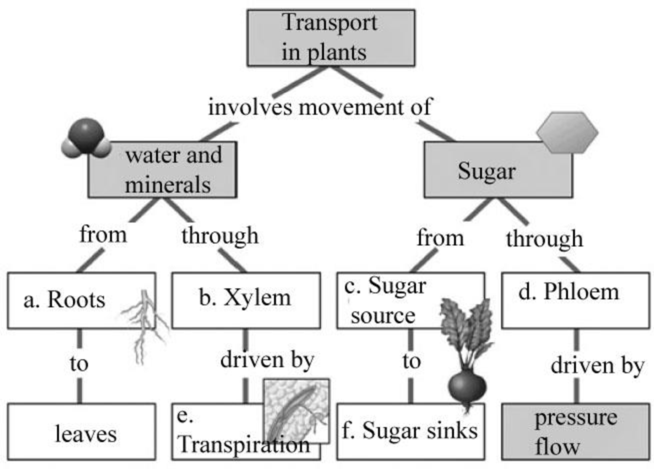
Figure 1: The concept map depicting the concept in transport in plants.
(a)
Correct answer: Roots.
Roots are the part of the root system that helps in uptake of water and minerals from the surrounding to the shoot system. Hence, the correct answer is roots.
(b)
Correct answer: Xylem.
Xylem is the vascular bundles present in the inner region of the stem that sends water and minerals through them to the rest of the plant body. Hence, the correct answer is xylem.
(c)
Correct answer: Sugar source.
Sugar source is the leaves where, by the process of photosynthesis, the sugar is made. Hence, the correct answer is sugar source.
(d)
Correct answer: Phloem.
Phloem is a type of vascular bundle through which the sugar sources are transported to the rest of the plant body. Hence, the correct answer is phloem.
(e)
Correct answer: Transpiration.
It is the process of loss of water from the plant through the leaves. This helps in maintaining the osmotic balance. Hence, the correct answer is transpiration.
(f)
Correct answer: Sugar sinks.
It is the region where the prepared sugar is stored till the plant is in requirement of energy. When such a situation arises, the plant supplies the sugar from these stored regions. Hence, the correct answer is sugar sinks.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 32 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
- Beans increase or decrease the turgidity of Pulvini cells to change the orientation of leaves. In order to raise the leaf blades to a horizontal position (as in the right side of the picture) pulvini cells at the junction between petiole and blade import sugar and potassium ions to increase their Yp from .30 Mpa to 0.67 Mpa. The pulvini cells are at equilibrium both before (leaf held more vertically) and after (leaf held horizontally) moving with an interstitial fluid that is not under pressure and has an unchanging osmotic potential of -3.31 Mpa. What is the osmotic potential of the Pulvini cell when the leaf blade is horizontal?arrow_forwardFigure 2 shows the cross-section of a eudicot root. i. Based on Figure 2, identify the structure that regulates the movement of water and minerals towards the xylem in the root. ii. Name structure of the cell membrane allows it to act as a selective barrier? iii. Predict what will happen to the transportation of water and minerals through the plasma membrane if the root was poisoned and no cellular respiration occurredarrow_forwardIn hot, dry climates, plants have evolved mechanisms to avoid photorespiration. Which of the following is FALSE Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a b с d C3 plants have no mechanism to avoid photorespiration C4 plants reduce photorespiration by separating the light reaction in the mesophyll cells from the light- independent reaction in the bundle-sheath cells CAM plants minimize photorespiration by collecting and storing CO2 at night and keeping their stomata closed during the day C4 plants include corn, sugarcane, and many grasses CAM plants can undergo photophosphorylation in the absence of sunlight 7 Open in Readinarrow_forward
- A) The concentration of CO2 is lower inside a plant cell than in the atmosphere (outside the cell). In your own words, describe how the CO2 levels are kept low inside the plant cell and explain why this is necessary. Assume stomata are open. B) Regarding the situation presented in Part A and assuming that the stomata of the plant leaves are closed, would this favour the induction of photorespiration in a C3 plant? Explain. Make reference to relevant molecule or molecules as needed. Please clearly label your responses as A and Barrow_forwardIn hot, dry climates, plants have evolved mechanisms to avoid photorespiration. Which of the following is FALSE Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a b с d e C3 plants have no mechanism to avoid photorespiration C4 plants reduce photorespiration by separating the light reaction in the mesophyll cells from the light- independent reaction in the bundle-sheath cells CAM plants minimize photorespiration by collecting and storing CO2 at night and keeping their stomata closed during the day C4 plants include corn, sugarcane, and many grasses CAM plants can undergo photophosphorylation in the absence of sunlight Open in Readirarrow_forwardplease help with my biology homework,thank you Once sugar is in the vascular tissue, what forces cause it to move? Name at least two, andexplain how they function in sugar transport in vascular plants.arrow_forward
- Which type of the following play a role in the gravitropic response of plants according to the statolith hypothesis? amyloplasts chloroplasts receptors calcium ions O O O Oarrow_forwardWhat among the following would happen to plant exposed to toxin that made thylakoid membranes permeable to protons? a reverasal of proton gradient across thylakoid membrans would result in higher pH in thylakoid lumen than the surrounding stroma reduction of NADP+ inthe chloroplasts would no longer be possible the proton gradient across the ehylakoid membrane woudl be eliminated the transport of electrons by the protein complexes int eh thylakoids would be prevented.arrow_forwardDefine and compare the terms within each of the following pairs, including an outline of the role of each member of the pair in a typical plant:(a) Channel protein; proton pump(b) Nitrate; potassium(c) Gibberellic acid; abscisic acidarrow_forward
- The image below shows a plant that has one stem wrapped in plastic. You can see the condensation of water on the inside of the plastic bag. Which of the following best explain the processes required for the bag to accrue 1 point condensation? Water from the root to the leaves via the xylem and transpiration from the stomata O Photosynthesis from the leaves via the stomata. O Cellular respiration through the stems. Cellular division within the dermal tissue.arrow_forwardDescribe the hypothesis of pressure flow for the transportation of sugars in the plants.arrow_forwardIf I were to make a transport molecule for plants, what would be the best characteristics that should be part of it?arrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStaxBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStaxBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning




