
Concept explainers
To review:
The represented data are given in the graph and the purpose of reverse development in some cnidarians.
Introduction:
Cnidarians are marine, invertebrate, and radially symmetrical animals that belong to phylum Cnidaria. These animals do not have a complete gut instead have a blind sac called the gastrovascular cavity, which is connected to the single opening called the mouth. The cnidarians exhibit two distinct stages during its life cycle.
Explanation of Solution
The life cycle of all cnidarians involves the formation of two distinct body forms: one sessile (immobile) and other motile. The sessile stage is known as the polyp, which is cylindrical in structure and is attached to a substratum, while the motile stage is known as the medusa, which is umbrella or bell shaped and is free swimming in the sea. The polyp stage exhibits the asexual young stage that converts into the medusa stage representing the sexual mature phase of the organism.
Some cnidarians such as Turritopsis dohrnii shows the reversal of sexual mature phase into young asexual phase. This reversal process is referred to as the reduction. The medusa stage under reduction into its younger version is called as the reducing medusa. Such cnidarians are regarded as “immortal jellies.” Research has shown that this revert back process occurs when the organism faces stress conditions in its surrounding such as unavailability of food, injury, and unfavorable conditions to sexually reproduce.
The following graph represents the data generated when the Turritopsis dohrnii species were incubated under different concentrations of cesium chloride (CsCl) for 3 hours, as a part of a study of reversion phenomenon shown by this species.
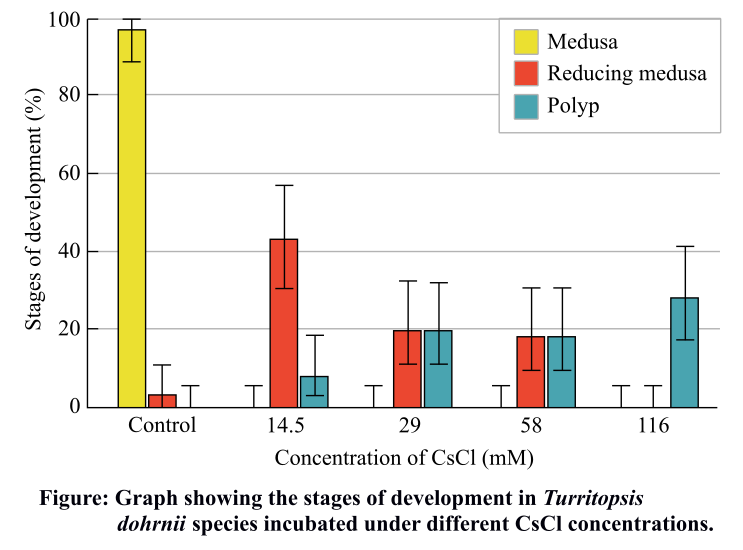
From the graph, it is clear that at CsCl concentration of 14.5 mM (low), maximum number of reducing medusa stages were recovered as compared to the control where no stress is given and maximum number of normal medusa stages were seen. At intermediate CsCl concentrations (29 Mm and 58 mM), equal number of reducing medusa stages and polyp stages were seen. However, at very high CsCl concentration (116 mM), absence of reducing medusa was seen while maximum number of polyp stages were recovered. This represents the reversion of all the medusa stages into the polyp stage.
Therefore, it can be concluded that as the stress conditions increase in the environment of cnidaria, the revert back phenomenon is more as more number of medusa stages starts reverting back to the young polyp stages. This reversion process contributes to the immortality of these animals.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
- What is the formula of Evolution? Define each item.arrow_forwardDefine the following concepts from Genetic Algorithms: Mutation of an organism and mutation probabilityarrow_forwardFitness 6. The primary theory to explain the evolution of cooperation among relatives is Kin Selection. The graph below shows how Kin Selection theory can be used to explain cooperative displays in male wild turkeys. B When paired, subordinant males increase the reproductive success of their solo, dominant brothers. 0.9 C 0 Dominant Solo EVOLUTION Se, Box 13.2 © 2023 Oxford University Press rB rB-C Direct Indirect Fitness fitness fitness gain Subordinate 19 Fitness After A. H. Krakauer. 2005. Nature 434: 69-72 r = 0.42 Subordinant Dominant a) Use Hamilton's Rule to show how Kin Selection can support the evolution of cooperation in this system. Show the math. (4 b) Assume that the average relatedness among male turkeys in displaying pairs was instead r = 0.10. Could kin selection still explain the cooperative display behavior (show math)? In this case, what alternative explanation could you give for the behavior? (4 pts) 7. In vampire bats (pictured below), group members that have fed…arrow_forward
- Examine the following mechanism and classify the role of each labeled species in the table below. Check all the boxes that applyarrow_forward1. Define and explain the two primary evolutionary consequences of interspecific competitionarrow_forward2 A linear fragment of DNA containing the Insulin receptor gene is shown below, where boxes represent exons and lines represent introns. Assume transcription initiates at the leftmost EcoRI site. Sizes in kb are indicated below each segment. Vertical arrows indicate restriction enzyme recognition sites for Xbal and EcoRI in the Insulin receptor gene. Horizontal arrows indicate positions of forward and reverse PCR primers. The Horizontal line indicates sequences in probe A. Probe A EcoRI Xbal t + XbaI + 0.5kb | 0.5 kb | 0.5 kb | 0.5kb | 0.5 kb | 0.5 kb | 1.0 kb EcoRI On the gel below, indicate the patterns of bands expected for each DNA sample Lane 1: EcoRI digest of the insulin receptor gene Lane 2: EcoRI + Xbal digest of the insulin receptor gene Lane 3: Southern blot of the EcoRI + Xbal digest insulin receptor gene probed with probe A Lane 4: PCR of the insulin receptor cDNA using the primers indicated Markers 6 5 4 1 0.5 1 2 3 4arrow_forward
- 4. (10 points) woman. If both disease traits are X-linked recessive what is the probability A man hemizygous for both hemophilia A and color blindness mates with a normal hemophilia A nor colorblindness if the two disease genes show complete that a mating between their children will produce a grandson with neither a. linkage? (5 points) that a mating between their children will produce a grandson with both hemophilia A and colorblindness if the two disease genes map 40 cM apart? (5 points)arrow_forward2 2 1.5 1.0 0.67 5. (15 points) An individual comes into your clinic with a phenotype that resembles Down's syndrome. You perform CGH by labeling the patient's hobe DNA red and her mother's DNA green. Plot the expected results of the Red:Green ratio if: A. The cause of the syndrome was an inversion on one chromosome 21 in the child 0.5 1.5 1.0 0.67 0.5 21 p 12345678910 CEN q 123456789 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 B. The cause of the syndrome was a duplication of the material between 21q14 and 21q18 on one chromosome in the child 21 p 123456789 10 CEN q 12345678910 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 C. The mother carried a balanced translocation that segregated by adjacent segregation in meiosis I and resulted in a duplication in the child of the material distal to the translocation breakpoint at 21q14. 1.5 1.0 0.67 0.5 21 p 12345678910 CEN q 123456789 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 mom seal bloarrow_forward4. You find that all four flower color genes map to the second chromosome, and perform complementation tests with deletions for each gene. You obtain the following results: (mutant a = blue, mutant b = white, mutant c = pink, mutant d = red) wolod Results of Complementation tests suld Jostum Mutant a b с Del (2.2 -2.6) blue white pink purple Del (2.3-2.8) blue white pink red Del (2.1 -2.5) blue purple pink purple Del (2.4-2.7) purple white pink red C d Indicate where each gene maps: a b ori ai indW (anioq 2) .8arrow_forward
- lon 1. Below is a pedigree of a rare trait that is associated with a variable number repeat. PCR was performed on individuals using primers flanking the VNR, and results are shown on the agarose gel below the pedigree. I.1 1.2 II.1 II.2 II.3 II.4 II.5 II.6 11.7 III.1 III.2 III.3 III.4etum A. (5 points) What is the mode of inheritance? B. (10 points) Fill in the expected gel lanes for II.1, II.5, III.2, III.3 and III.4 C. (5 points) How might you explain the gel results for II.4?arrow_forwardTo study genes that create the purple flower color in peas, you isolate 4 amorphic mutations. Each results in a flower with a different color, described mutant a = blue mutant c = pink mutant b = white mutant d = red A. In tests of double mutants, you observe the following phenotypes: mutants a and b = blue mutants b and c = white mutants c and d = pink Assuming you are looking at a biosynthetic pathway, draw the pathway indicating which step is affected by each mutant. B. What is the expected flower color of a double mutant of a and c?arrow_forwardExplain the principle of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





