
To answer:
What is a competitive market and how it is described by the
Concept Introduction:
Competitive market: The competitive market is a market where there is large number of buyers and sellers in the, the sellers are profit motive and the buyers want to maximise their satisfaction. In a competitive market no single produce can influence the price of the commodities. If one producer increases the price of his good no one will follow him and the producer may incur losses. In a
Explanation:
The competitive market is a place where there are large number of buyers and sellers in the economy. And they are selling homogenous products in the economy. The sellers are profit oriented and the buyers want maximum satisfaction from the products. There is rivalry in the competitive market the actions of one firm affects the decision of another firm so it leads to rivalry in the markets.
Another feature of competitive market is excludability. The firms may exclude the consumers from enjoying their goods or service for an example the movies are only shown to the persons who buy movie tickets, if there is no excludability the consumers become free riders. Another feature of competitive market is the available information is fully reflected in the market for example there is report that hamburger consumption creates more health problems to the people, so due to this report there will be decreased demand for hamburgers in the market. So the available information is fully reflected in the market. The very important feature of competitive market is there is no barriers to entry that means firms can enter and leave the market at any time, there is complete freedom of firms to enter or leave the market.
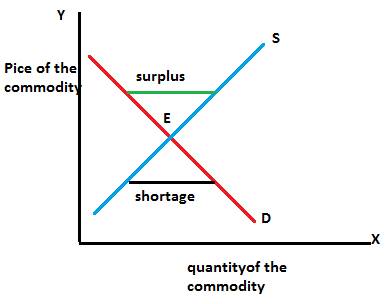
The above graph shows the supply and demand model in a competitive market, the demand curve will be downward sloping one indicates the negative relationship between the price and quantity demanded, if the prices are high the people will buy less of the product. The supply curve will be upward sloping one indicates the direct relationship between demand and supply. If the prices are high the producers will supply more of their products in the market. The intersection between the demand and supply curve is the equilibrium where the demand and supply are equal. There will be a surplus in the economy when the supply of goods and services exceeds the demand for goods and services and there will be also shortages in the economy when there is demand for goods and services exceeds the supply of goods and services.
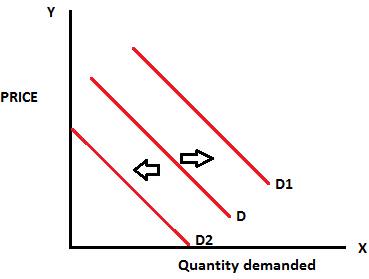
The shifts in the demand curve is shown by the above graph, a right ward shift from D to D1 shows increase in the quantity demanded of the commodity and the left ward shift from D to D2 shows the decrease in the quantity demanded. Changes in the price of commodity can only create movement along the demand curve and it cannot shift the demand curve, changes in income, tastes and preferences, fashion, changes in the prices of other goods can shift the demand curve.
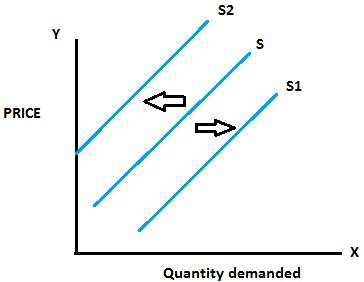
The shifts in the supply curve is shown by the above graph a right ward shift from S to S1 shows the increase in the quantity supplied and a leftward shift from S to S2 shows the decrease in the quantity supplied. Changes in input prices, expectations, technology can shift the supply curve; price only can result in a movement in the supply curve.
Explanation of Solution
The competitive market is a place where there are large number of buyers and sellers in the economy. And they are selling homogenous products in the economy. The sellers are profit oriented and the buyers want maximum satisfaction from the products. There is rivalry in the competitive market the actions of one firm affects the decision of another firm so it leads to rivalry in the markets.
Another feature of competitive market is excludability. The firms may exclude the consumers from enjoying their goods or service for an example the movies are only shown to the persons who buy movie tickets, if there is no excludability the consumers become free riders. Another feature of competitive market is the available information is fully reflected in the market for example there is report that hamburger consumption creates more health problems to the people, so due to this report there will be decreased demand for hamburgers in the market. So the available information is fully reflected in the market. The very important feature of competitive market is there is no barriers to entry that means firms can enter and leave the market at any time, there is complete freedom of firms to enter or leave the market.

The above graph shows the supply and demand model in a competitive market, the demand curve will be downward sloping one indicates the negative relationship between the price and quantity demanded, if the prices are high the people will buy less of the product. The supply curve will be upward sloping one indicates the direct relationship between demand and supply. If the prices are high the producers will supply more of their products in the market. The intersection between the demand and supply curve is the equilibrium where the demand and supply are equal. There will be a surplus in the economy when the supply of goods and services exceeds the demand for goods and services and there will be also shortages in the economy when there is demand for goods and services exceeds the supply of goods and services.

The shifts in the demand curve is shown by the above graph, a right ward shift from D to D1 shows increase in the quantity demanded of the commodity and the left ward shift from D to D2 shows the decrease in the quantity demanded. Changes in the price of commodity can only create movement along the demand curve and it cannot shift the demand curve, changes in income, tastes and preferences, fashion, changes in the prices of other goods can shift the demand curve.

The shifts in the supply curve is shown by the above graph a right ward shift from S to S1 shows the increase in the quantity supplied and a leftward shift from S to S2 shows the decrease in the quantity supplied. Changes in input prices, expectations, technology can shift the supply curve; price only can result in a movement in the supply curve.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forwardMake a clear distinction and similarities between economic conditions of public, economics policy and economic systemarrow_forward← >>> Content → C វា Q Search this course ? Mind Tap - Cengage Learning x b Home | bartleby ChatGPT - Microeconomics G Welfare effects of a tariff in a ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?deploymentId=5832655719808280021166203&elSBN 9781337914413&id=2125010357&snapshotId=4041364& ☆ CENGAGE MINDTAP Aplia Homework: International Trade On the following grapn, use the green triangle (triangle symbols) to snage the area representing consumer surpius (CS) when the economy is at the free-trade equilibrium. Then, use the purple triangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing producer surplus (PS). 590 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 560 530 500 470 PRICE (Dollars per ton) 440 410 380 350 320 Pu 290 02 46 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of maize) CS PS Σ C C × A-Z Dec 13 9:33 bongoarrow_forward
- Sarth is single and has three children solve this accounting questionsarrow_forward← >>> Content → C A ChatGPT - Microeconomics Mind Tap - Cengage Learning b Answered: - Content - C>>> X + C × ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?deploymentId=5832655719808280021166203&elSBN 9781337914413&id=2125010357&snapshotId=4041364& ☆ ☑ Q Search this course ? CENGAGE MINDTAP Aplia Homework: International Trade 300 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of tangerines) tons of When Guatemala allows free trade of tangerines, the price of a ton of tangerines in Guatemala will be $500. At this price, 300,000 tangerines will be demanded in Guatemala, and 200,000 tons will be supplied by domestic suppliers. Therefore, Guatemala will import 100,000 tons of tangerines. Using the information from the previous tasks, complete the following table to analyze the welfare effect of allowing free trade. Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus Without Free Trade (Millions of dollars) With Free Trade (Millions of dollars) When Guatemala allows free trade, the…arrow_forward← Content → C >>> វា Q Search this course ? Mind Tap - Cengage Learning x b Answered: - MyHarper | Stud × | ChatGPT - Microeconomics G Welfare effects of a tariff in a ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?deploymentId=5832655719808280021166203&elSBN 9781337914413&id=2125010357&snapshotId=4041364& ☆ CENGAGE MINDTAP Aplia Homework: International Trade i 2. Welfare effects of free trade in an importing country Consider the Guatemalan market for tangerines. The following graph shows the domestic demand and domestic supply curves for tangerines in Guatemala. Suppose Guatemala's government currently does not allow the international trade in tangerines. Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium price of a ton of tangerines and the equilibrium quantity of tangerines in Guatemala in the absence of international trade. Then, use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade the area representing consumer surplus in equilibrium. Finally, use the purple point (diamond…arrow_forward
- ← MyHarper | Students Content → с ChatGPT - Microeconomics Mind Tap - Cengage Learning x b Answered: - Q Search this ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?deploymentId=5832655719808280021166203&elSBN 9781337914413&id=2125010357&snapshotId=4041364& ☆ វា Q Search this course >>> CENGAGE MINDTAP Aplia Homework: International Trade rmany, use the purple point (aramona sympory to shave the area representing producer surplus in equimonium. Note: Select and drag a fill area point from the palette to the graph. To fill in regions on the graph, merely drop the fill area point on the desired region. 800 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 750 700 650 PRICE (Dollars per ton) 600 550 500 450 400 350 300 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of tangerines) + No Trade Equilibrium Δ Consumer Surplus ? Producer Surplus Σ m Q ? C × A-Z Dec 13 8:00 bongoarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardPlease show a separate supply and demand diagram for a,b,c,d clearly label FRA, WTP, Consumer Surplus, Producer Surplus and Social Welfare for the intial WQ level as well as P* and Q* for each: (a) In the diagram below, show and explain the initial level of forest recreation area (FRA) when there is no price charged for using it (i.e., it is free). Show/explain the total willingness to pay (WTP), consumer surplus (CS), producer surplus (PS), and social welfare (SW) for the initial WQ level. (b) In a new diagram, show what happens to WTP, CS, PS, and SW as FRA deteriorates (e.g., the supply of FRA becomes smaller from development). Then in another diagram, show/explain what happens to WTP, CS, PS, and SW as population grows. (c) Suppose a perfectly competitive market was created for FRA. In a new diagram, show/explain what happens to the FRA level, Price, WTP, CS, PS, and SW. Compare your answers to part (a). (d) Suppose that, instead of a market for FRA, the government…arrow_forward
- The Figure 2 portrays. MC ATC Price P 0 Q₁ Q Quantity 02 MR Figure 2 a competitive firm which should shut down in the short run the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run a competitive firm which is realizing an economic profit the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short runarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardRefer to the Figure 1. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce MC Dollars 0 C H A B Figure1 K units at price C OD units at price J E units at price B E units at price A(EH) KDE Quantity G ATC AVC MRarrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





