
Concept explainers
(a) What is the smallest force parallel to a
(a)
The magnitude of the minimum force required to keep the
Answer to Problem 80SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The weight of the objectis
Coefficient of static friction and kinetic friction between the object and
Formula used:
Write the expression of the coefficient of static friction:
Here,
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Consider,
Draw the free body diagram of the object:
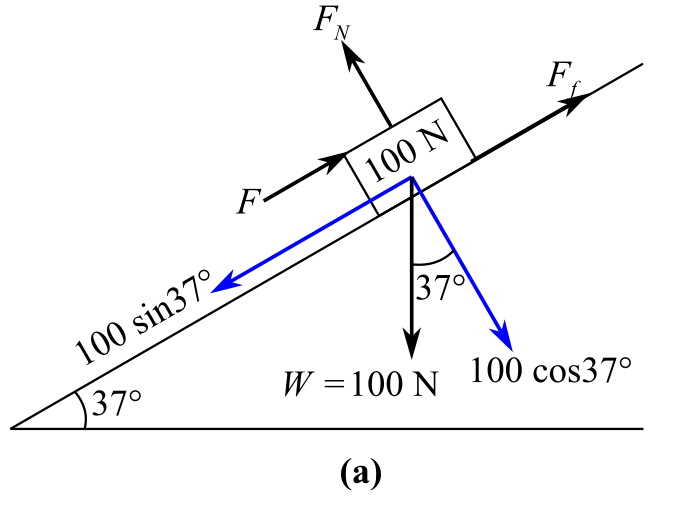
In the above diagram,
Recall the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Considering along the perpendicular to the inclined plane, the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Therefore,
Here, considering coefficient of the static friction force because the object is just sliding down.
Recall the expression of static friction force:
Substitute
Understand that the acceleration of the object will be zero because it will be at rest after the application of force
Rewrite the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Considering along the parallel to the inclined plane, the direction of the rightward forces is positive and the direction of the leftward forces is negative. Therefore,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the minimum force required to keep the object from sliding down the incline plane is
(b)
The magnitude of the forceapplied parallel to the
Answer to Problem 80SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The weight of the object is
Coefficient of static friction and kinetic friction between the object and
The acceleration of the blockis zero because its moves with constant velocity.
Formula used:
Write the expression of the coefficient of static friction:
Here,
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Since the
Draw the free body diagram of the object:
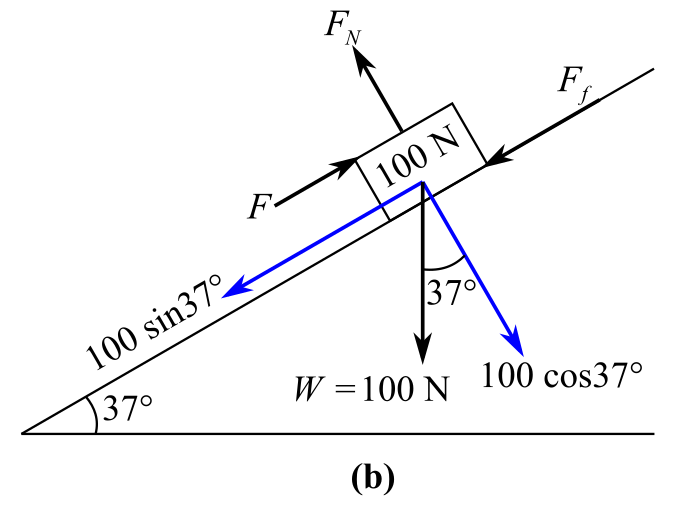
In the above diagram,
The object is moving with constant velocity.
Rewrite the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium.
Considering along the parallel to the inclined plane, the direction of the rightward forces is positive and the direction of the leftward forces is negative. Therefore,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the parallel force needed to keep the objectmoving up the inclineat a constant speed is
(c)
The magnitude of the acceleration of an object if a
Answer to Problem 80SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The weight of the object is
Parallel pushing force is 94N.
Coefficient of static friction and kinetic friction between the object and incline is
Formula used:
Write the expression of the coefficient of the kinetic friction:
From the Newton’s second law of the motion, the expression of the force is
Here,
Write the expression for the weight of the
Here,
Explanation:
Since the
Draw the free body diagram of the object:
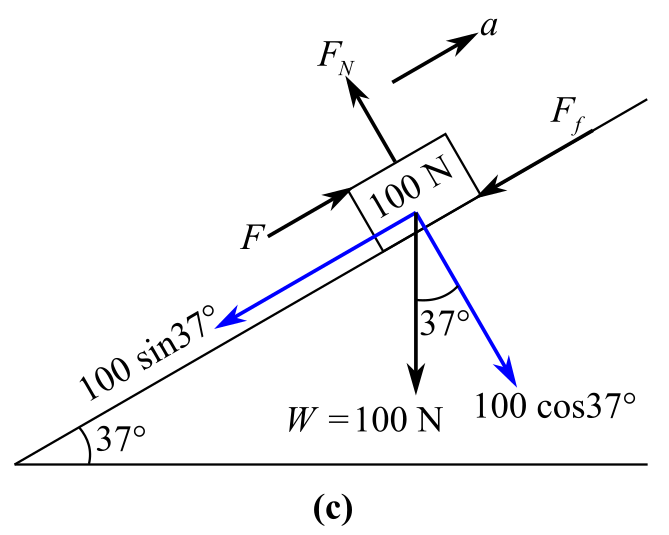
In the above diagram, considering the objectup the incline,
Here, considering the coefficient of the kinetic friction because
Recall the expression of coefficient of kinetic friction:
Here,
Substitute
Recall the expression for the weight of the
Substitute
Recall the expression for Newton’s second law of the motion:
Considering along the parallel to the inclined plane, the direction of the rightward forces is positive and the direction of the leftward forces is negative. Therefore,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the acceleration of the object is
(d)
Thedistance coveredby the object after
Answer to Problem 80SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The weight of the object is
Coefficient of static friction and kinetic friction between the object and incline is
Time to considered is
Initial velocity is
Formula used:
Write the expression of the displacement:
Here,
Explanation:
Recall the expression of the displacement:
Substitute
Conclusion:
The displacement of the object is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
EBK INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Question B3 Consider the following FLRW spacetime: t2 ds² = -dt² + (dx² + dy²+ dz²), t2 where t is a constant. a) State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat. [2 marks] b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function of time t, starting at t = 0. [3 marks] c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect to galaxy A. d) The Friedmann equations are 2 k 8πG а 4πG + a² (p+3p). 3 a 3 [5 marks] Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page. [5 marks] e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i) radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv) none of the previous. Justify your answer. f) [5 marks] A conformally…arrow_forwardSECTION B Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.] Question B1 Consider the line element where w is a constant. ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx², a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric. [2 marks] b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.] [10 marks] c) Write down the geodesic equations. [5 marks] d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion. [4 marks] e) Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics. [4 marks]arrow_forwardPage 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Iarrow_forwardHow would partial obstruction of an air intake port of an air-entrainment mask effect FiO2 and flow?arrow_forward14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forwardCheckpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





