
a.
K-Map:
- K-Map stands for Karnaugh Map which is used to reduce the logic functions more easily and quickly.
- By using K-Map, the Boolean expressions with two to four variables are easily reduced.
Explanation of Solution
Simplification of K-Map using Boolean identities:
Given:
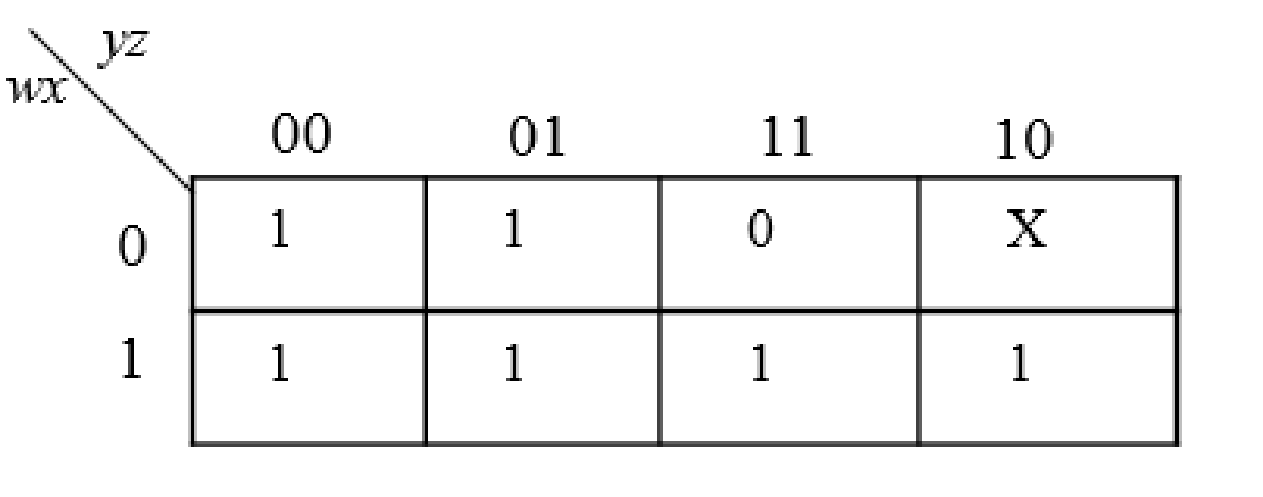
Solution:
The simplified expression using K-Map is
The following steps are used to obtain the Boolean expressions using Boolean identities.
Step1:
The group the 1’s in the table. Then write the Boolean expression according to the mapping. Write 0 term’s as complemented variable like x’ and 1 term’s as it is like x. Here “X” variable denotes don’t care which means the user will take the “X” value as either 0 or 1.
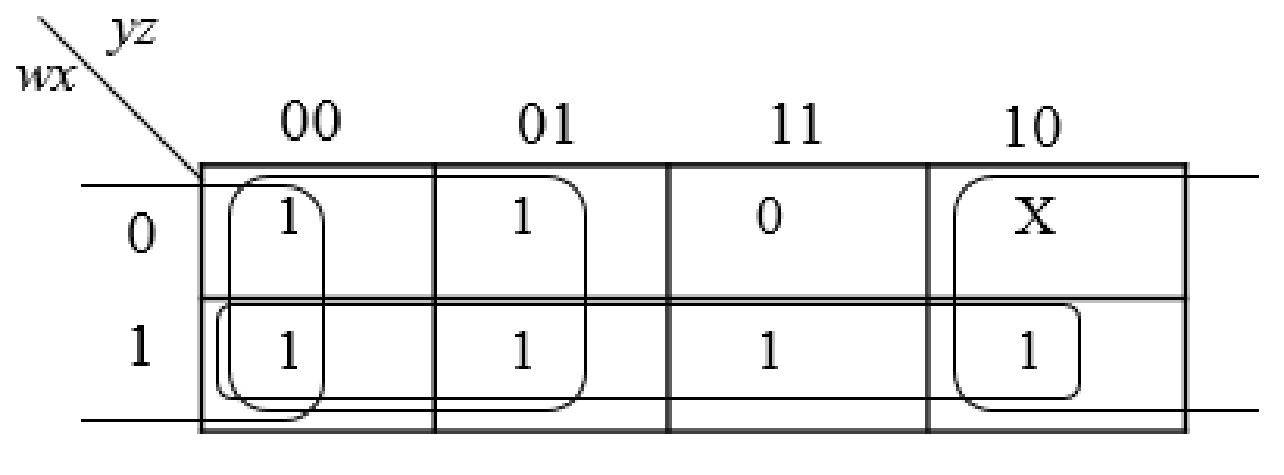
The below expression is obtained from the K-Map
Step2:
The group the 1’s in the table. Then write the Boolean expression according to the mapping. Write 0 term’s as complemented variable like x’ and 1 term’s as it is like x. Here “X” variable denotes don’t care which means the user will take the “X” value as either 0 or 1.
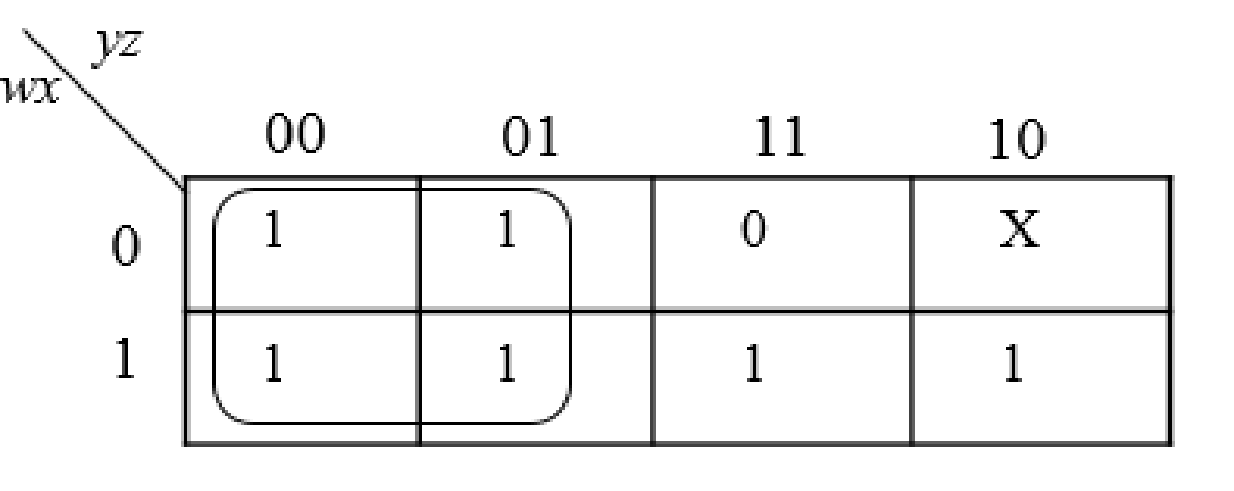
The below expression is obtained from the K-Map
Step3:
The group the 1’s in the table. Then write the Boolean expression according to the mapping. Write 0 term’s as complemented variable like x’ and 1 term’s as it is like x. Here “X” variable denotes don’t care which means the user will take the “X” value as either 0 or 1.
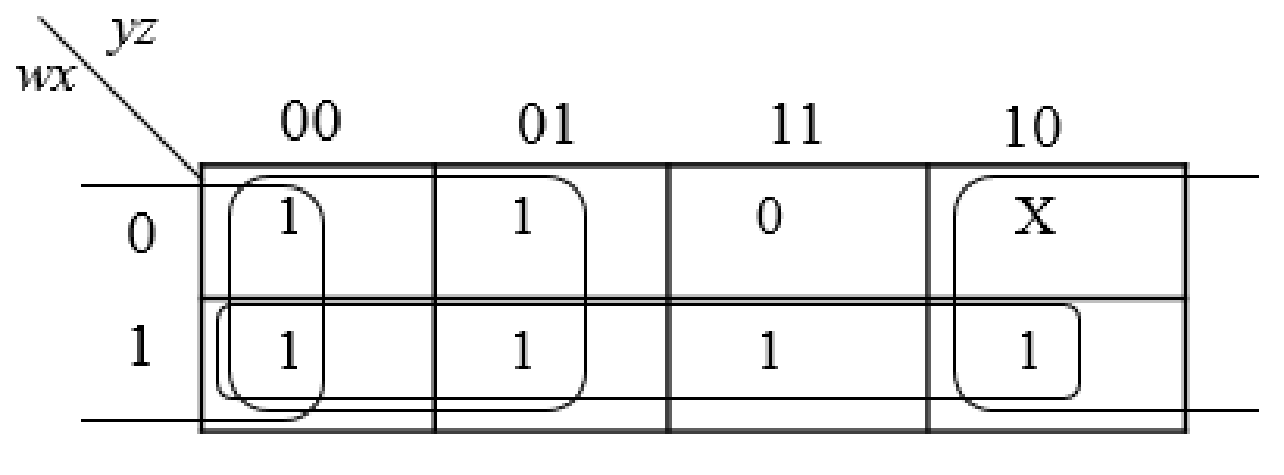
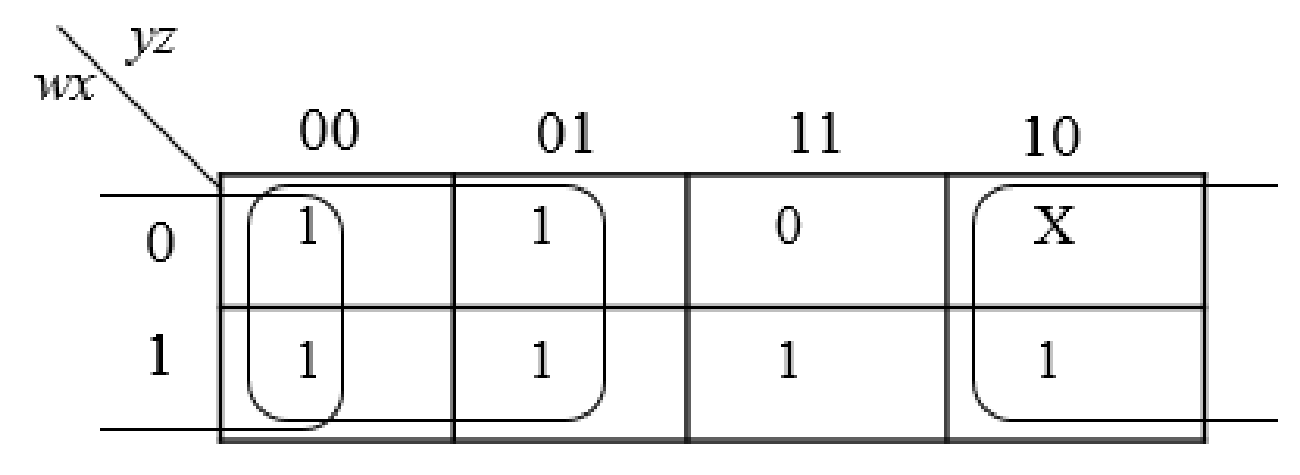
The below expression is obtained from the K-Map
Step4:
Group all the expressions
Therefore, the simplified expression using Boolean identities is “
b.
K-Map:
- K-Map stands for Karnaugh Map which is used to reduce the logic functions more easily and quickly.
- By using K-Map, the Boolean expressions with two to four variables are easily reduced.
Explanation of Solution
Simplification of K-Map using Boolean identities:
Given:
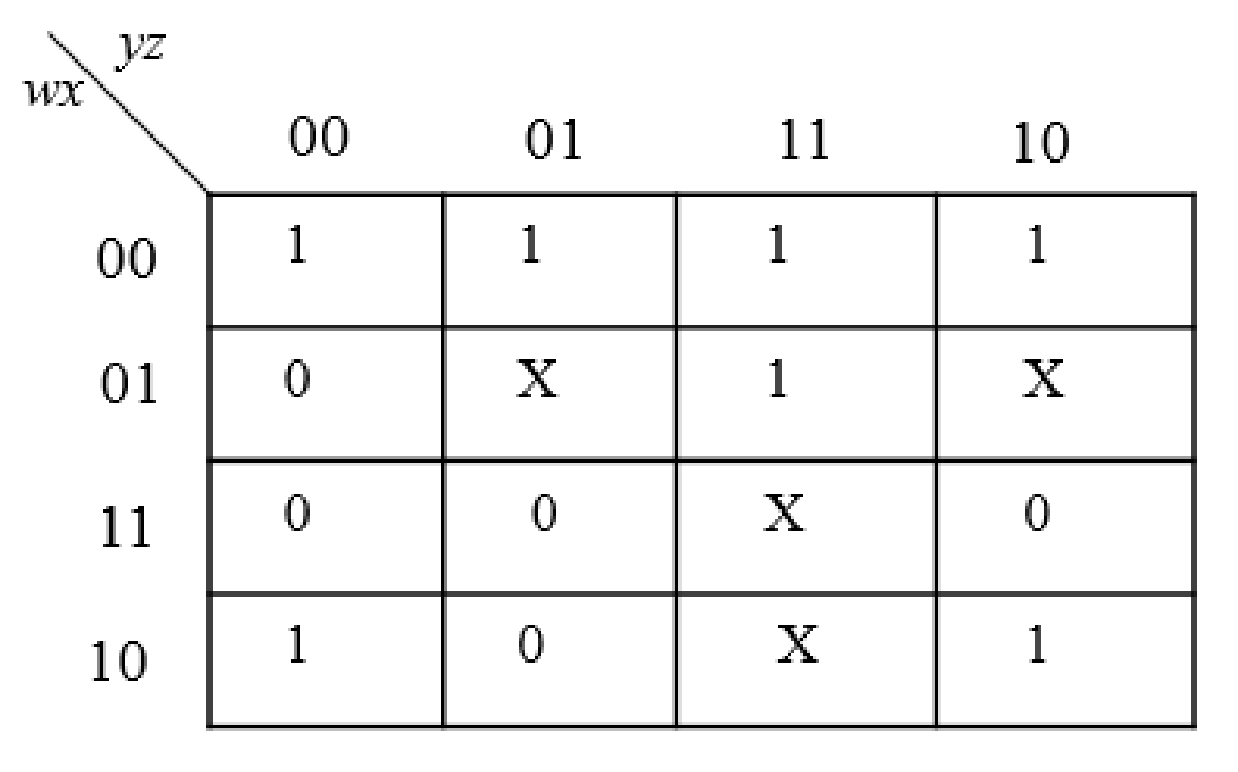
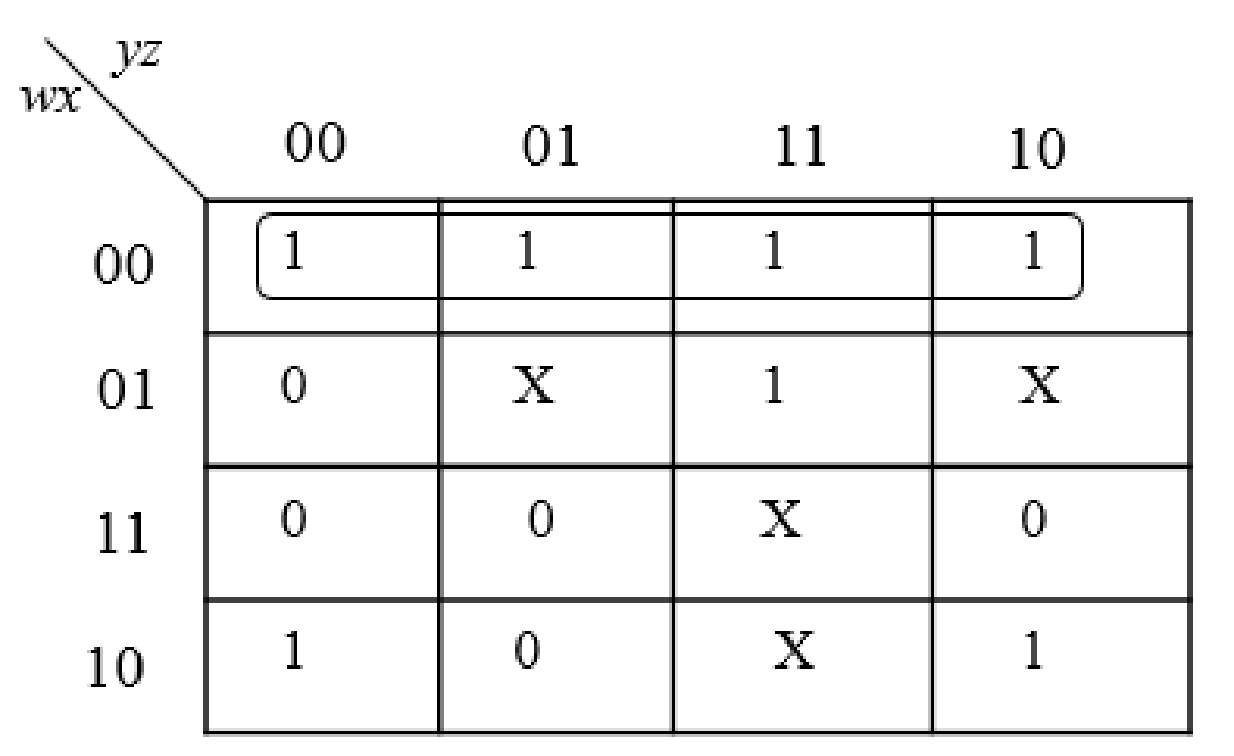
Solution:
The simplified expression using K-Map is
The following steps are used to obtain the Boolean expressions using Boolean identities.
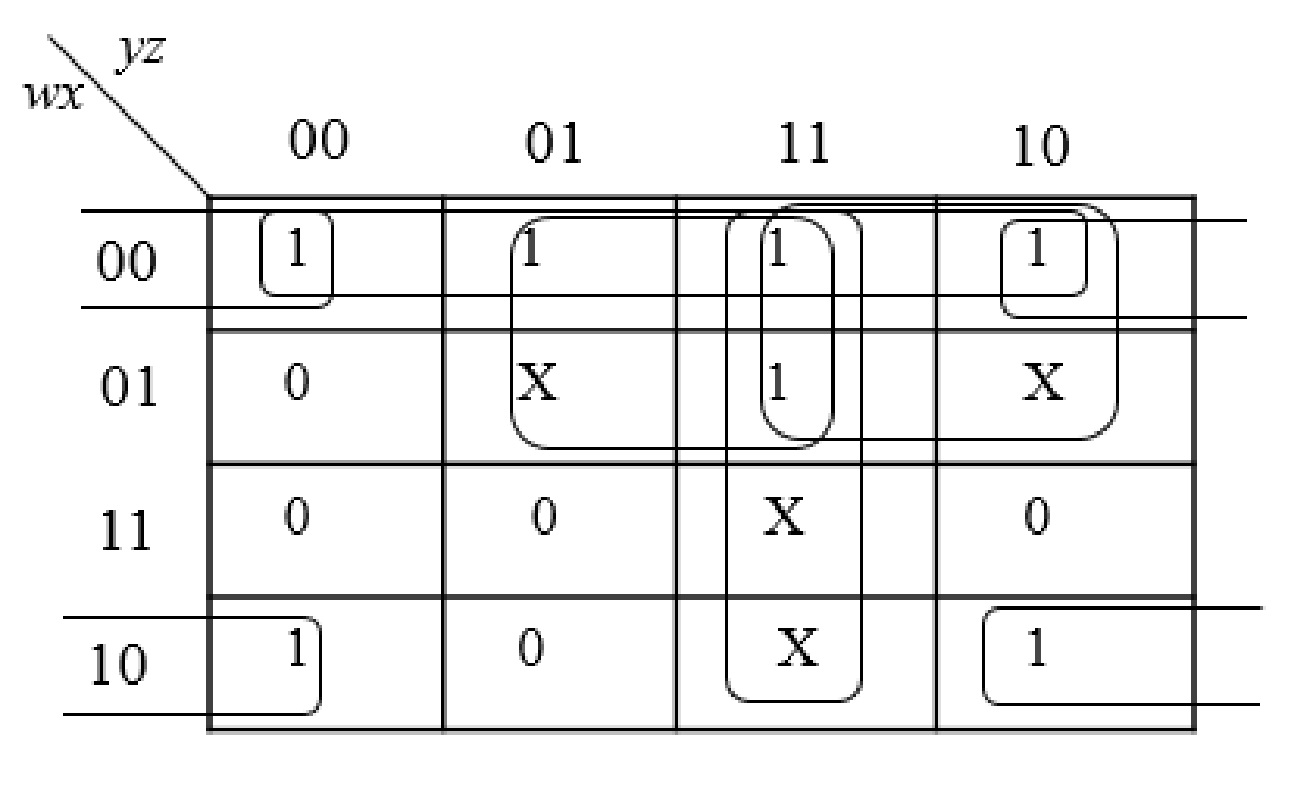
Step1:
The group the 1’s in the table. Then write the Boolean expression according to the mapping. Write 0 term’s as complemented variable like x’ and 1 term’s as it is like x. Here “X” variable denotes don’t care which means the user will take the “X” value as either 0 or 1.
The below expression is obtained from the K-Map
Step2:
The group the 1’s in the table. Then write the Boolean expression according to the mapping. Write 0 term’s as complemented variable like x’ and 1 term’s as it is like x. Here “X” variable denotes don’t care which means the user will take the “X” value as either 0 or 1.
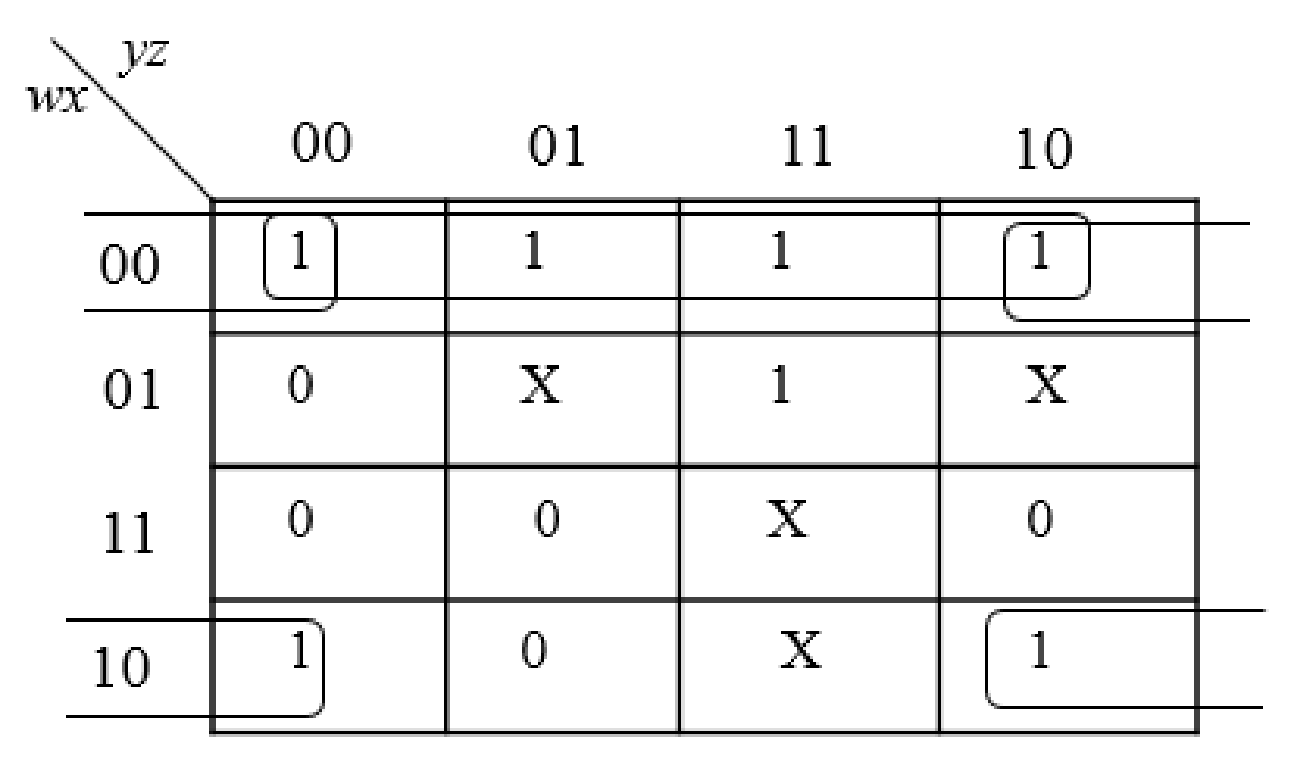
The below expression is obtained from the K-Map
Step3:
The group the 1’s in the table. Then write the Boolean expression according to the mapping. Write 0 term’s as complemented variable like x’ and 1 term’s as it is like x. Here “X” variable denotes don’t care which means the user will take the “X” value as either 0 or 1.
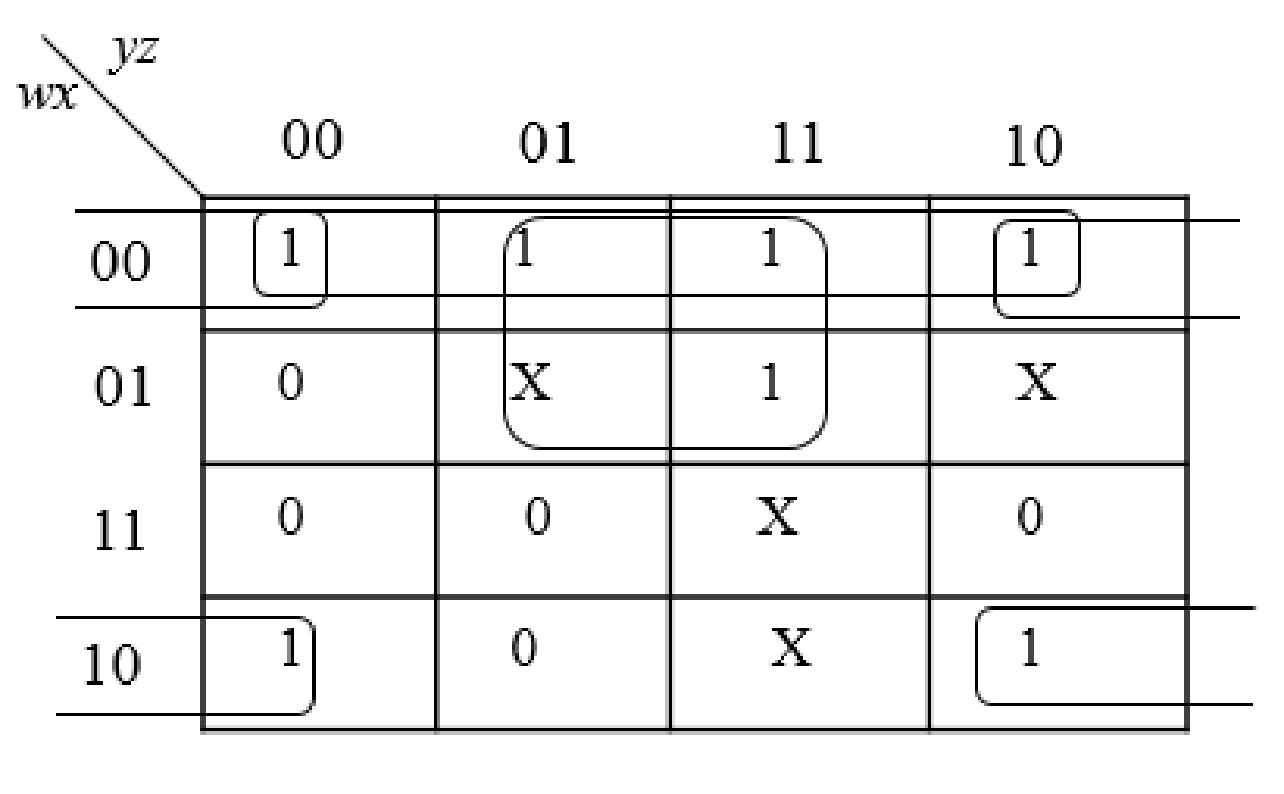
The below expression is obtained from the K-Map
Step4:
The group the 1’s in the table. Then write the Boolean expression according to the mapping. Write 0 term’s as complemented variable like x’ and 1 term’s as it is like x. Here “X” variable denotes don’t care which means the user will take the “X” value as either 0 or 1.
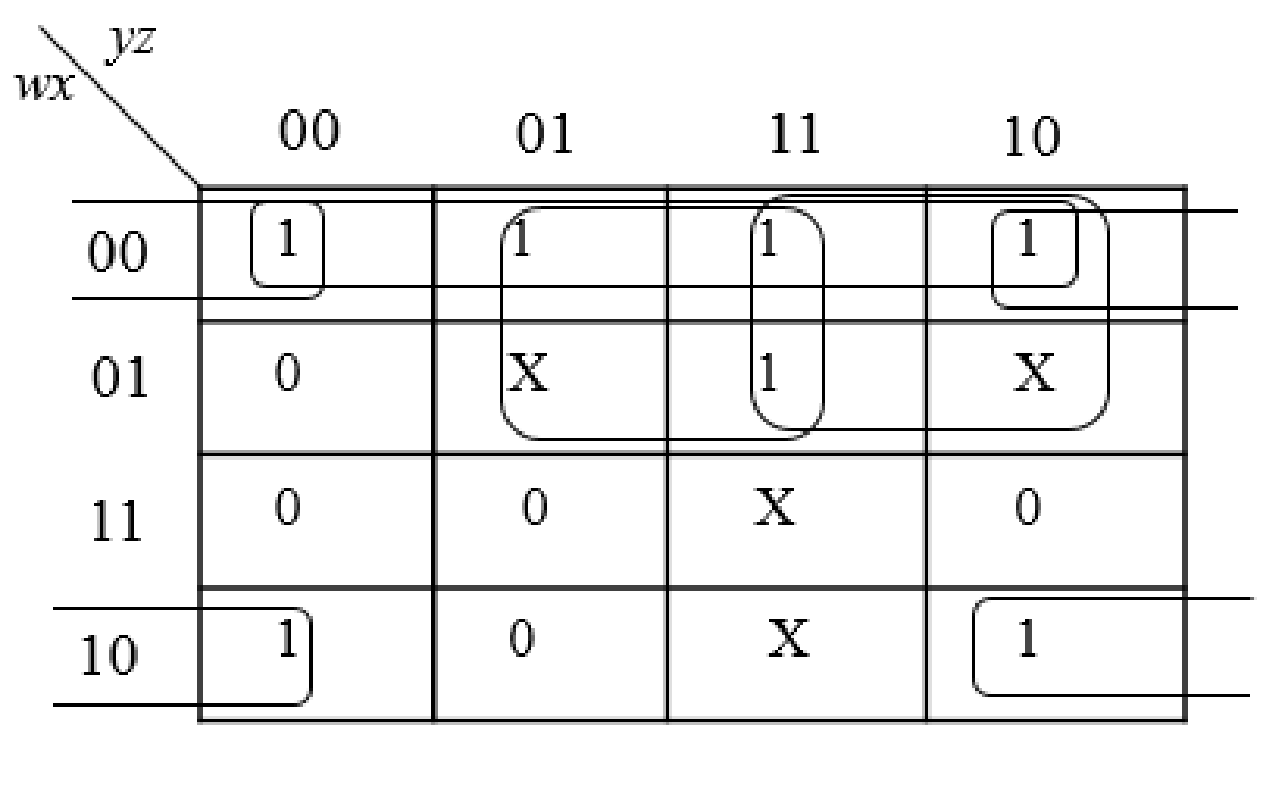
The below expression is obtained from the K-Map
Step5:
The group the 1’s in the table. Then write the Boolean expression according to the mapping. Write 0 term’s as complemented variable like x’ and 1 term’s as it is like x. Here “X” variable denotes don’t care which means the user will take the “X” value as either 0 or 1.
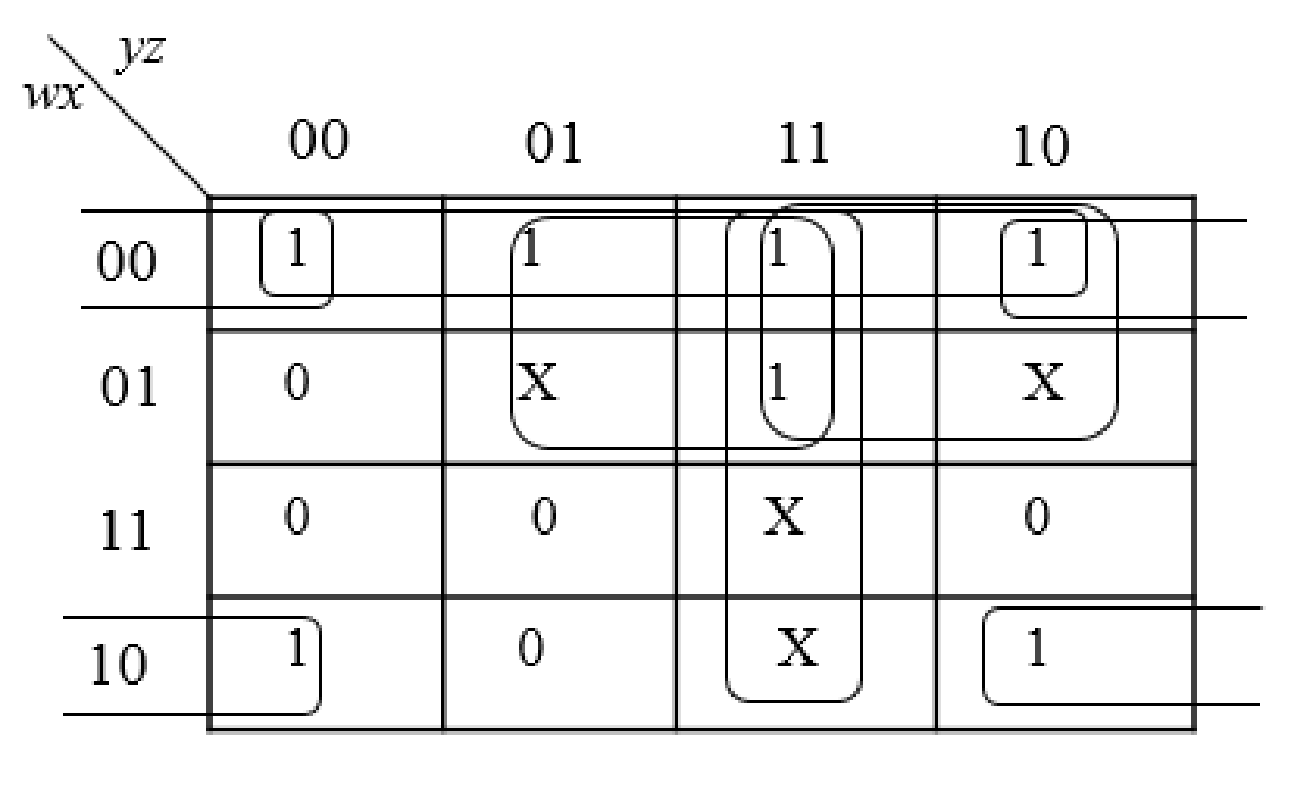
The below expression is obtained from the K-Map
Step6:
Group all the expressions
Therefore, the simplified expression using Boolean identities is “
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Essentials of Computer Organization and Architecture
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





