
DRAW IT Ø Label a hydrogen bond and a polar covalent bond in the diagram of live water molecules. Is a hydrogen bond a covalent bond? Explain.
To label: The hydrogen bond and covalent bonds in water molecules.
Introduction:
Water is a polar molecule consisting of an oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms.
Explanation of Solution
Water (H2O) consists of an oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms. Hydrogen and oxygen share their valence electrons to form a strong bond that known as a covalent bond (Fig.1). As oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, the shared electrons in the H-O bond tend to be pulled towards the oxygen atom. There are two regions of partial negative charge on oxygen and a partial positive charge on each hydrogen atom. Thus, the covalent bond between H-O in the water molecule is a polar bond.
Water is a polar molecule due to the difference in electronegativity between O and H atoms. The partial negatively charged oxygen atom of a water molecule is attracted to the partial positively charged hydrogen atom of an adjacent water molecule (Fig.1). This forms the hydrogen bond among different water molecules.
Pictorial representation:
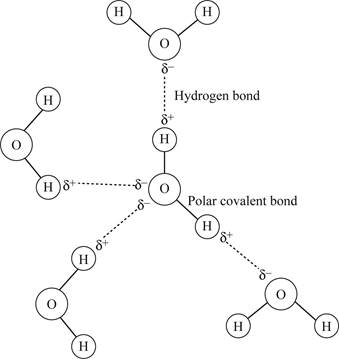
Fig. 1 Interactions among water molecules
To explain: The hydrogen bonds are not covalent bonds.
Introduction: Covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of valence electrons between two atoms. Hydrogen bonds are formed due to the attraction between two adjacent atoms due to partial charges.
Explanation of Solution
Covalent bonds are strong bonds, formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. Hydrogen bonds do not involve the sharing of valence electrons. They are formed on the basis of attraction due to partial charges on neighboring atoms, and are hence very weak bonds. Therefore, a hydrogen bond is not a covalent bond.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Campbell Biology (10th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Organic Chemistry
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Question 2. same chromosome. For all parts of this question, the E and G genes are 8 map units apart on the a) An EG/eg individual is test crossed. What proportion of the progeny will exhibit 1 dominant trait and 1 recessive trait? b) An EG/eg individual is crossed with an Eg/eG individual. What proportion of the progeny will be homozygous recessive for both traits? c) An EG/eg individual is crossed with an Eg/eG individual. What proportion of the progeny will be heterozygous for both genes?arrow_forwardhow do plants integrate diverse signals into appropriate cellular and developmental responses to abiotic stress? I am aware of how they work in isolation e.g response to temperature, light, salinity, drought, nutrients and toxins, but not how the signalling occurs simultanously i.e transcription factors or ezymes present in two systems at once protecting the plant from both things.arrow_forwardtended Response (F24) O 3:58:01 remai Use the table below to construct a phylogenetic tree for a group of alien organisms found on the planet Kepler 22B by the astronomer D. Liscious. Ph.D. The common ancestor of all these organisms was green, silicon-based, with 2 legs, 4 dataports, 1 sex, and did not possess powered flight, x-ray vision, or interdimensional awareness. Assume the hypothesis of parsimony is valid and that all taxa are extant except for Taxon A, which is extinct. (10 pts) You should draw your tree on a piece of paper. Then, take a photo of it, save as a file, and upload it here. Please make sure your tree is neat and easy to read. Table 1. Kepler 22B taxonomic diversity with derived characters. Taxon Skin Basis for building # Legs # Data- # Sexes Powered X-ray Interdimensional Color macromolecules ports Flight? Vision Awareness? A Green Carbon 4 4 2 N N N B Green Carbon 2 4 2 N N Narrow_forward
- Match the following graphs with their likely p-values. 45 4 3.5 3 I Mean Height (SD) S 2 1 05 0 Control Phosphoru く Phosphorus Nitrogen Mean Height (SD) m 2 O Control Nitrogen 1. p=0.0001 2. p=0.1439arrow_forwardTable 1. Kepler 22B taxonomic diversity with derived characters. Taxon Skin Basis for building # Legs # Data- # Sexes Powered X-ray Interdimensional Color macromolecules ports Flight? Vision Awareness? A Green Carbon 4 4 2 N N N B Green Carbon 2 4 2 N N N C Green Silicon 2 4 1 N N N D Green Silicon 2 4 2 N Y N E Purple Silicon 2 4 2 N Y N F Purple Silicon 2 4 2 N Y Y G Purple Silicon 2 5 2 N Y Y H Purple Silicon 2 5 2 Y Y Yarrow_forwardGlobal climate change is expected to result in drastic changes in precipitation patterns. This might mean that, due to the rain shadow effect, the windward sides of mountains might be wetter, while the leeward sides of mountains might be drier. Using what you know about plant taxonomy and ecological relationships, propose a justified, ecological hypothesis on how plant community composition would change on each side of the mountain. Your answer should contain two parts: The hypothesis and the ecological justification addressing the bold points above.arrow_forward
- Explain why homologies are used in constructing phylogenetic trees (2 pts). Give two specific examples of how using analogous characters would result in a tree depicting incorrect evolutionary relationships (4 pts). Aarrow_forwardD B - E C - A - Farrow_forwardDiscuss briefly the research on the effects of marijuana smoking on the functioning of the immune system.arrow_forward
- 1) Describe how you would test the hypothesis that lobe eyes are a dominant lethal gene. Run the experiment and see if your hypothesis is correct. b) What are the possible body colors in fruit flies? Place an asterisk next to the wild type body color. c) Draw a fly with star-shaped eyes next to one with lobe eyes and insert your drawing below.arrow_forwardUtilizing the following pedigree, and the key for phenotypes, to the right of it, determine the genotypes of the individuals in the pedigree for blood type inheritance. Individual Blood Type I1 I2 II1 II2 II3 II4 III1 III2 III3 III4 III5 III6arrow_forwarda)At what wavelength (nm) on a spectrometer can this color be quantified? b) Record your results. Indicate on this page which boxes turned color. A B C + - 1:2 1:10 1:100 c) Based on these results, which patient(s) definitely have lupus, which definitely do not, and which require further testing?arrow_forward

 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College



