
Review Figure 3.4. Suppose the price of gasoline is
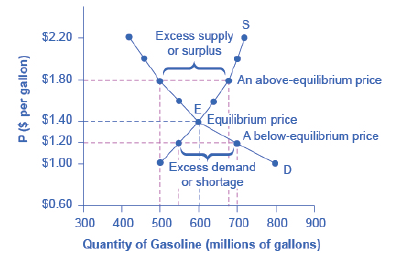
Figure 3.4
If the price of gasoline is $1.60 per gallon and the equilibrium price is $1.40 per gallon. Comment whether the quantity demanded and supplied is higher or lower at $1.60 per gallon. Is there a shortage or surplus?
Explanation of Solution
As per the diagram, the equilibrium price is $1.40 per gallon in the market. Any price above the equilibrium price level in the market creates surplus of the product in the market and any price below the equilibrium price creates a shortage of the product in the market.
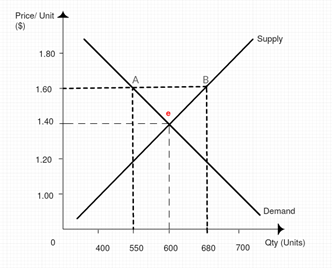
In the above figure, at price level $1.60 per gallon, the quantity demand is 550 millions of gallons and quantity supply is 680 million gallons, represented by point A and B in the diagram. Clearly, we can see that quantity supply is more than quantity demand and there is a surplus of the product.
If the price is below the equilibrium price, then there will be shortage of the product.
Equilibrium Price: It is that level of price where demand of a product is equal to the supply of a product.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS (OER)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Cost Accounting (15th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
Construction Accounting And Financial Management (4th Edition)
- what are Factors affecting the demand of gasolinearrow_forwardThe table below illustrates the market's demand and supply for cheddar cheese. Price Per Pound[$] Quantity demanded Quantity Supplied 3.00 320 200 3.50 280 220 4.00 240 240 4.50 200 260 5.00 160 280 A new study says that eating cheese is good for your health, so that demand increases by 30% at every price. What is the equilibrium quantity in the market after the study?arrow_forwardOnly typed answer and please answer correctlyarrow_forward
- Price ($/cup) 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 0 10 20 Original Supply A decrease in the price of coffee beans. New Demand Original Demand 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Quantity (cups/hour) New Supply The figure above refers to the market for coffee. What might cause a shift from the original demand curve to the new demand curve? Check all that apply. An increase in the price of tea (a substitute for coffee). A decrease in income if coffee is an inferior good. An expectation that coffee prices will fall in the future. A decrease in the price of cream (a complement to coffee)arrow_forwardThe table shows the quantity of tablets that is demanded and supplied at various prices. Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied Price 50 75 100 125 120,000 112,500 105,000 97,500 100,000 102,500 105,000 107,500 Assume that the new equilibrium price is $50. How much would quantity supplied need to increase at each price to reach this equilibrium? A) 2550 B) 5050 C) 20,000 D) 112,499arrow_forwardExplain the impact of higher corn prices on consumers. Draw a graph explaining the impact of higher corn prices on consumers. Explain which curve will shift on your graph and the change in price and quantity demanded. Explain the impact of higher corn prices on producers. Draw a graph explaining the impact of higher corn prices on producers. Explain which curve will shift on your graph and the change in price and quantity supplied.arrow_forward
- The table gives the demand and supply schedules for milkshakes. What is the equilibrium price of a milkshake and the equilibrium quantity of milkshakes per day? The equilibrium quantity of milkshakes is The equilibrium price is $ a milkshake. a day. This question: 1 point(s) possible Price (dollars per milkshake) 4 5 6 Quantity demanded (per day) 120 120 105 90 75 60 45 Quantity supplied (per day) 30 45 60 75 90 105arrow_forwardSuppose the price of gasoline is $1.60 per gallon. Is the quantity demanded higher or lower than at the equilibrium price of $1.40 per gallon? What about the quantity supplied? Is there a shortage or a surplus in the market? If so, how much?arrow_forwardUsing the following schedule, (5) find the equilibrium price and quantity. (6) Describe the situation at a price of $10. What will occur to price? (7) Describe the situation at a price of $2. What will occur to price? price Quantity demanded Quantity supplied $ 1 500 100 $2 400 120 $3 350 150 $4 320 200 $5 300 300 $6 275 410 $7 260 500 $8 230 650 $9 200 800 $10 150 975arrow_forward
- 1. Demand terminology Complete the following table by selecting the term that matches each definition. Definition The claim that, with other things being equal, the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of that good rises A table showing the relationship between the price of a good and the amount that buyers are willing and able to purchase at various prices A graphical object showing the relationship between the price of a good and the amount of the good that buyers are willing and able to purchase at various prices The amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase at a given price Law of Quantity Demand Demand Demanded Curve Schedule Demand O O O O O O O O O Apply your understanding of the previous key terms by completing the following scenario with the appropriate terminology. Your friend Bob struggles with understanding graphs. He shows you the following illustration and asks for your help interpreting it: O O Oarrow_forwardDraw a supply and demand graph for the market for air travel. Analyze the impact of an increase in the cost of jet fuel. Be sure to use just one graph, shifting either the demand curve or the supply curve the correct direction. Show the impact on equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.arrow_forwardPlease don't give an handmade diagram. Make diagram with a digital tool.arrow_forward
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





