
Concept explainers
The unadjusted
PS Music
Unadjusted Trial Balance
July 31, 2018
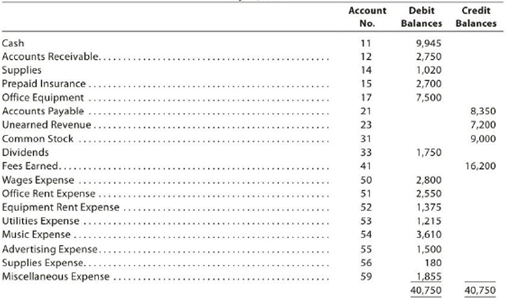
The data needed to determine adjustments are as follows:
- During July, PS Music provided guest disc jockeys for KXMD for a total of 115 hours. For information on the amount of the accrued revenue to be billed to KXMD, see the contract described in the July 3 transaction at the end of Chapter 2.
- Supplies on hand at July 31, $275.
- The balance of the prepaid insurance account relates to the July 1 transaction at the end of Chapter 2.
Depreciation of the office equipment is $50.- The balance of the unearned revenue account relates to the contract between PS Music and KXMD, described in the July 3 transaction at the end of Chapter 2.
- Accrued wages as of July 31 were $140.
Instructions
- 1. Prepare adjusting
journal entries. You will need the following additional accounts:18
Accumulated Depreciation —Office Equipment22 Wages Payable
57 Insurance Expense
58 Depreciation Expense
- 2.
Post the adjusting entries , inserting balances in the accounts affected. - 3. Prepare an adjusted trial balance.
1.
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. All adjusting entries affect at least one income statement account (revenue or expense), and one balance sheet account (asset or liability).
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts, and it contains the balances of all the accounts after the adjustment entries are journalized, and posted.
To prepare: The adjusting entries in the books of Company PS at the end of the July 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
| Journal Page 18 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Accounts receivable | 12 | 1,400 | ||
| July | 31 | Fees earned (1) | 41 | 1,400 | |
| (To record the fees earned at the end of July) | |||||
| 31 | Supplies expense (2) | 56 | 745 | ||
| Supplies | 14 | 745 | |||
| (To record supplies expense incurred at the end of the July) | |||||
| 31 | Insurance expense (3) | 57 | 225 | ||
| Prepaid insurance | 15 | 225 | |||
| (To record insurance expense incurred at the end of the July) | |||||
| 31 | Depreciation expense | 58 | 50 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation-Office equipment | 18 | 50 | |||
| (To record depreciation expense incurred at the end of the July) | |||||
| 31 | Unearned revenue (4) | 23 | 3,600 | ||
| Fees earned | 41 | 3,600 | |||
| (To record the service performed to the customer at the end of the July) | |||||
| 31 | Wages expense | 50 | 140 | ||
| Wages payable | 22 | 140 | |||
| (To record wages expense incurred at the end of the July) | |||||
Table (1)
Working notes:
1. Calculated the value of accrued fees during the July
Hence, fees earned during the July are $1,400.
2. Calculate the value of supplies expense
Hence, supplies expense during the July is $745.
3. Calculate the value of insurance expense
Hence, insurance expense during the July is $745.
4. Calculate the value of unearned fees at the end of the July
Hence, unearned fees at the end of the July are $3,600.
2.
To post: The adjusting entries to the ledger in the books of Company PS.
Explanation of Solution
Post the adjusting entries to the ledger account as follows:
| Account: Cash Account no. 11 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 3,920 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 5,000 | 8,920 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 1,750 | 7,170 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 2,700 | 4,470 | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 1,000 | 5,470 | ||||
| 3 | 1 | 7,200 | 12,670 | ||||
| 3 | 1 | 250 | 12,420 | ||||
| 4 | 1 | 900 | 11,520 | ||||
| 8 | 1 | 200 | 11,320 | ||||
| 11 | 1 | 1,000 | 12,320 | ||||
| 13 | 1 | 700 | 11,620 | ||||
| 14 | 1 | 1,200 | 10,420 | ||||
| 16 | 2 | 2,000 | 12,420 | ||||
| 21 | 2 | 620 | 11,800 | ||||
| 22 | 2 | 800 | 11,000 | ||||
| 23 | 2 | 750 | 11,750 | ||||
| 27 | 2 | 915 | 10,835 | ||||
| 28 | 2 | 1,200 | 9,635 | ||||
| 29 | 2 | 540 | 9,095 | ||||
| 30 | 2 | 500 | 9,595 | ||||
| 31 | 2 | 3,000 | 12,595 | ||||
| 31 | 2 | 1,400 | 11,195 | ||||
| 31 | 2 | 1,250 | 9,945 | ||||
Table (2)
| Account: Accounts Receivable Account no. 12 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 1,000 | |||
| 2 | 1 | 1,000 | |||||
| 23 | 2 | 1,750 | 1,750 | ||||
| 30 | 2 | 1,000 | 2,750 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 1,400 | 4,150 | |||
Table (3)
| Account: Supplies Account no. 14 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 170 | |||
| 18 | 850 | 1,020 | |||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 745 | 275 | ||||
Table (4)
| Account: Prepaid Insurance Account no. 15 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | 1 | 2,700 | 2,700 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 225 | 2,475 | |||
Table (5)
| Account: Office equipment Account no. 17 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 5 | 1 | 7,500 | 7,500 | |||
Table (6)
| Account: Accumulated Depreciation Account no. 18 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 50 | 50 | ||
Table (7)
| Account: Accounts Payable Account no. 21 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 250 | |||
| 3 | 1 | 250 | |||||
| 5 | 1 | 7,500 | 7,500 | ||||
| 18 | 2 | 850 | 8,350 | ||||
Table (8)
| Account: Wages Payable Account no. 22 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 140 | 140 | ||
Table (9)
| Account: Unearned revenue Account no. 23 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | 1 | 7,200 | 7,200 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 3,600 | 3,600 | |||
Table (10)
| Account: P’s capital Account no. 31 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 4,000 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 5,000 | 9,000 | ||||
Table (11)
| Account: P’s drawings Account no. 32 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 500 | |||
| 31 | 2 | 1,250 | 1,750 | ||||
Table (12)
| Account: Fees earned Account no. 41 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 6,200 | |||
| 11 | 1 | 1,000 | 7,200 | ||||
| 16 | 2 | 2,000 | 9,200 | ||||
| 23 | 2 | 2,500 | 11,700 | ||||
| 30 | 2 | 1,500 | 13,200 | ||||
| 31 | 2 | 3,000 | 16,200 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 1,400 | 17,600 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 3,600 | 21,200 | |||
Table (13)
| Account: Wages expense Account no. 50 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 400 | |||
| 14 | 1 | 1,200 | 1,600 | ||||
| 28 | 2 | 1,200 | 2,800 | ||||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 140 | 2,940 | |||
Table (14)
| Account: Office rent expense Account no. 51 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 800 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 1,750 | 2,550 | ||||
Table (15)
| Account: Equipment rent expense Account no. 52 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 675 | |||
| 13 | 1 | 700 | 1,375 | ||||
Table (16)
| Account: Utilities expense Account no. 53 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 300 | |||
| 27 | 2 | 915 | 1,215 | ||||
Table (17)
| Account: Music expense Account no. 54 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 1,590 | |||
| 21 | 2 | 620 | 2,210 | ||||
| 31 | 2 | 1,400 | 3,610 | ||||
Table (18)
| Account: Advertising expense Account no. 55 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 500 | |||
| 8 | 1 | 200 | 700 | ||||
| 22 | 2 | 800 | 1,500 | ||||
Table (19)
| Account: Supplies expense Account no. 56 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 180 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 745 | 925 | |||
Table (20)
| Account: Insurance expense Account no. 57 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 225 | 225 | ||
Table (21)
| Account: Depreciation expense Account no. 58 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 50 | 50 | ||
Table (22)
| Account: Miscellaneous expense Account no. 59 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| July | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 415 | |||
| 4 | 900 | 1,315 | |||||
| 29 | 540 | 1,855 | |||||
Table (23)
3.
To prepare: An adjusted trial balance of Company PS at July 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an adjusted trial balance of Company PS at July 31, 2019 as follows:
| Company PS | |||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | |||
| July 31, 2019 | |||
| Particulars | Account No. |
Debit $ | Credit $ |
| Cash | 11 | 9,945 | |
| Accounts receivable | 12 | 4,150 | |
| Supplies | 14 | 275 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 15 | 2,475 | |
| Office equipment | 17 | 7,500 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Equipment | 18 | 50 | |
| Accounts payable | 21 | 8,350 | |
| Wages payable | 22 | 140 | |
| Unearned revenue | 23 | 3,600 | |
| P's capital | 31 | 9,000 | |
| P's drawings | 32 | 1750 | |
| Fees earned | 41 | 21,200 | |
| Wages expense | 50 | 2,940 | |
| Office rent expense | 51 | 2,550 | |
| Equipment rent expense | 52 | 1,375 | |
| Utilities expense | 53 | 1,215 | |
| Music expense | 54 | 3,610 | |
| Advertising expense | 55 | 1,500 | |
| Supplies expense | 56 | 925 | |
| Insurance expense | 57 | 225 | |
| Depreciation expense | 58 | 50 | |
| Miscellaneous expense | 59 | 1,855 | |
| 42,340 | 42,340 | ||
Table (24)
The debit column and credit column of the adjusted trial balance are agreed, both having the balance of $42,340.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial and Managerial Accounting - With CengageNow
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics of Money, Banking and Financial Markets, The, Business School Edition (5th Edition) (What's New in Economics)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Macroeconomics
Management (14th Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
- The next dividend payment by Skippy Inc. will be $3.45. The dividends are anticipated to maintain a growth rate of 4.2% forever. If the stock currently sells for $37.95 per share, what is the required rate of return? Comprehensive Holdings just paid a dividend of $2.95 per share on its stock. The dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 4.8% forever. If investors require a return of 12% on the stock, what is the current price? What will be the price in 3 years? In 7 years? Citibank expects to pay a dividend of $2 per share on its common stock at the end of this year. The growth rate of the dividend is 8% for the next 2 years. After that, the dividends are expected to grow at a constant growth rate of 5% per year forever. The required rate of return on the company’s stock is 11%. What is the price of Citibank stock today? A firm pays a current dividend of $3, which is expected to grow at a rate of 4% indefinitely. If the current value of the firm’s shares is $53,…arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forwardThe stock P/E ratio.??arrow_forward
- provide correct answer mearrow_forwardHyundai Company had beginning raw materials inventory of $29,000. During the period, the company purchased $115,000 of raw materials on account. If the ending balance in raw materials was $18,500, the amount of raw materials transferred to work in process inventory is?arrow_forwardComputing the gross profit percentage Edible Art earned net sales revenue of $75,050,000 in 2019. The cost of goods sold was $55,650,000, and net income reached $13,000,000, the company s highest ever. Compute the company s gross profit percentage for 2019.arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





