
Practical Management Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781305250901
Author: Wayne L. Winston, S. Christian Albright
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 3, Problem 1C
Summary Introduction
Case summary:
The case discusses the details about the Company SS, which would manufacture two types of shelves for the grocery stores. The essential details are given below:
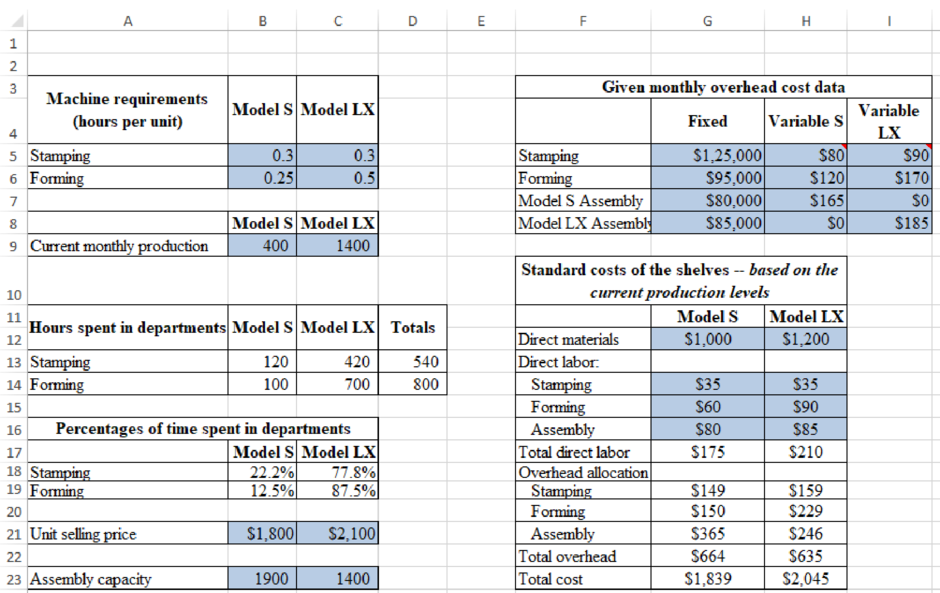
Figure (1)
To determine: The LP model of the problem.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Help with question?
What are some good examples of bullet points on a resume for a Christian Elementary School?
What is an example of a cover letter for a Christian School Long-Term Substitute Teaching position?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Practical Management Science
Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 1PCh. 3.6 - Prob. 2PCh. 3.6 - Prob. 3PCh. 3.6 - Prob. 4PCh. 3.6 - Prob. 5PCh. 3.6 - Prob. 6PCh. 3.6 - Prob. 7PCh. 3.6 - Prob. 8PCh. 3.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 3.7 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 11PCh. 3.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 3.7 - Prob. 13PCh. 3.7 - Prob. 14PCh. 3.7 - Prob. 15PCh. 3.7 - Prob. 16PCh. 3.7 - Prob. 17PCh. 3.8 - The Pigskin Company produces footballs. Pigskin...Ch. 3.8 - The Pigskin Company produces footballs. Pigskin...Ch. 3.8 - The Pigskin Company produces footballs. Pigskin...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 21PCh. 3.8 - Prob. 22PCh. 3.8 - Prob. 23PCh. 3.8 - Prob. 24PCh. 3 - Prob. 25PCh. 3 - Prob. 26PCh. 3 - Prob. 27PCh. 3 - Prob. 28PCh. 3 - Prob. 29PCh. 3 - Prob. 30PCh. 3 - Prob. 31PCh. 3 - Prob. 32PCh. 3 - Prob. 33PCh. 3 - Prob. 34PCh. 3 - Prob. 35PCh. 3 - Prob. 36PCh. 3 - Prob. 37PCh. 3 - Prob. 38PCh. 3 - Prob. 39PCh. 3 - Prob. 40PCh. 3 - Prob. 41PCh. 3 - Prob. 42PCh. 3 - Prob. 43PCh. 3 - Prob. 44PCh. 3 - Prob. 45PCh. 3 - Prob. 46PCh. 3 - Prob. 47PCh. 3 - Prob. 48PCh. 3 - Prob. 49PCh. 3 - Prob. 50PCh. 3 - Prob. 51PCh. 3 - Prob. 52PCh. 3 - Prob. 1CCh. 3 - Prob. 2.1CCh. 3 - Prob. 2.2CCh. 3 - Prob. 2.3CCh. 3 - Prob. 2.4CCh. 3 - Prob. 2.5CCh. 3 - Prob. 2.6CCh. 3 - Prob. 2.7CCh. 3 - Prob. 2.8C
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, operations-management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The supply chain is a conventional notion, but organizations are only really interested in making products that they can sell to customers. Provided they have reliable supplies of materials and reasonable transport for finished products, logistics is irrelevant. Do you think this is true? If yes, explain, and if no, clearly explain as well.arrow_forwardworking as a program operations managerarrow_forward12 X1, X230 1 x =0x2 write the Following linear Programming model by 1- general Form Canonical Forms Canonical formY 2- Standard Form Max Z=35X+ 4 X 2 +6 X3 ST. X+2X2-5x3 = 40 3X, + 6X2 + 7x 3 = 30 7x, +lox2 x3 = 50 X3 X 2 X 3 <0arrow_forward
- a/ a Minimum cost assign each worker for one job at Jobs J1 12 33 WI 2 4 6 W2 5 W3 5 33 6 7arrow_forwardوبة واضافة هذه القيمة الى القيم Ex: Assign each job for each worker at minimum total Cost عمل لكل عامل وبأقل كلفة ممكنة obs الأعمال Workors العمال J1 J2 J3 J4 W₁ 15 13 14 12 W2 11 12 15 13 W3 13 12 10 11 W4 15 17 14 16arrow_forwardThe average completion time (flow time) for the sequence developed using the FCFS rule = 11.75 days (round your response to two decimal places). The percentage utilization for the sequence developed using the FCFS rule = 42.55 % (enter your response as a percentage rounded to two decimal places). b) Using the SPT (shortest processing time) decision rule for sequencing the jobs, the order is (to resolve a tie, use the order in which the jobs were received): An Alabama lumberyard has four jobs on order, as shown in the following table. Today is day 205 on the yard's schedule. In what sequence would the jobs be ranked according to the decision rules on the left: Job Due Date A 212 B 209 C 208 D 210 Duration (days) 6 3 3 8 Sequence 1 Job B 2 3 4 A D The average tardiness (job lateness) for the sequence developed using the SPT rule = 5.00 days (round your response to two decimal places). The average completion time (flow time) for the sequence developed using the SPT rule = 10.25 days…arrow_forward
- With the aid of examples, fully discuss any five (5) political tactics used in organisations.arrow_forwarda. With the aid of examples, define discrimination. b. Fully discuss any four (4) types of discrimination in the workplacearrow_forwardRead the Following Extract and Answer the Questions that Follows:The word politics has a somewhat negative connotation. It suggests that someone is attempting touse means or to gain ends that are not sanctioned by the organisation. Political behaviour, as we’vedefined it is quite neutral. Similarly, power is not inherently negative. Whether a person viewspower and politics as unsavoury topics depends on several considerations, most important perhapsbeing where the individual stands on a specific issue in each situation. Nonetheless, most managersare reluctant to admit to political character of their own work settings.Discuss any Five (5) Political tactics you know.arrow_forward
- Describe current features of Cigna Accredo pharmacy own appraisal forms and compare the system used against the textbook’s description of desirable features of appraisal forms. What improvements would you recommend and why?arrow_forwardProvide a recommendation of a combination of different methods of performance data that could be used to arrive at an overall score for each person being rated in cigna Accredo pharmacy. Explain the comprehensive system you have recommended and why you have chosen this combination of tools. Support your answer with research.arrow_forwardAlready got wrong answer Plz Don't use chatgptarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:Cengage,