
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780133942651
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 13EAP
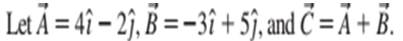
a. Write vector
b. Draw a coordinate system and on it show vectors
c. What are the magnitude and direction of vector
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Relating linear and Angular kinematics
At t=3 s, a point on the rim of a .20m radius wheel has a tangential speed of 50 m/s as the wheel.
calculate the wheel's constant angular acceleration?
calculate the angular velocities at t=3 seconds and t=0 seconds.
through what angle did the wheel turn between t=0seconds and t=3 seconds?
at what time will the radical acceleration equal g?
Please solve with steps and final answer
please help with 27 part A.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Ch. 3 - Can the magnitude of the displacement vector be...Ch. 3 - If C=A+B, can C = A + B? Can C>A + B? For each,...Ch. 3 - If C=A+B can C = 0? Can C< O? For each, show how...Ch. 3 - Is it possible to add a scalar to a vector? If so,...Ch. 3 - How would you define the zero vector ?Ch. 3 - Can a vector have a component equal to zero and...Ch. 3 - Can a vector have zero magnitude if one of its...Ch. 3 - Suppose two vectors have unequal magnitudes. Can...Ch. 3 - Are the following statements true or false?...Ch. 3 - I. Trace the vectors in FIGURE EX3.1 onto your...
Ch. 3 - Trace the vectors in FIGURE EX3.2 onto your paper....Ch. 3 - a. What are the x- and v-components of vector E...Ch. 3 - A velocity vector 40° below the positive x-axis...Ch. 3 - A position vector in the first quadrant has an...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors. Then find its...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors. Then find its...Ch. 3 - Let C = (3.15 m, 15° above the negative x-axis)...Ch. 3 - A runner is training for an upcoming marathon by...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors, label an angle...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors, label an angle...Ch. 3 - Let a. Write Vector Cin component form. b. Draw a...Ch. 3 - a. Write vector Cin component form. b. Draw a...Ch. 3 - a. Write vector Din component form. b. Draw a...Ch. 3 - Let A = 4î - 2j, B = -3î + 5j, and E = 2 A + 3 B...Ch. 3 - Let A = 41 - 2j, B = -3î + 5j, and F = A -4 B . a....Ch. 3 - 17. Let = 2î + 3? and = 2î — 2?. Find the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 3 - 19. What are the x– and y- components of the...Ch. 3 - 20. For the three vectors shown Figure EX3.20, + +...Ch. 3 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 3 - 22. Let = (3.0 m, 20° south of east), = (2.0 m,...Ch. 3 - The position of a particle as a function of time...Ch. 3 - a. What is the angle between vectors E and F in...Ch. 3 - FIGURE P3.25 shows vectors A and B . Find vector C...Ch. 3 - Prob. 26EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 3 - The minute hand on a watch is 2.0 cm in length....Ch. 3 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 3 - Ruth sets out to visit her friend Ward, who lives...Ch. 3 - A cannon tilted upward at 30° fires a cannonball...Ch. 3 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 34EAPCh. 3 - A pine cone falls straight down from a pine tree...Ch. 3 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 3 - Your neighbor Paul has rented a truck with a...Ch. 3 - Tom is climbing a 3.0-m-long ladder that leans...Ch. 3 - The treasure map in FIGURE P3.40 gives the...Ch. 3 - The bacterium E. coli is a single-cell organism...Ch. 3 - A flock of ducks is trying to migrate south for...Ch. 3 - FIGURE P3.43 shows three ropes tied together in a...Ch. 3 - I Four forces are exerted on the object shown in...Ch. 3 - FIGURE P3.45 shows four electric charges located...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- solve 27 Barrow_forwardCalf muscle Lower leg bones B A C d AB A- dBC Ꮎ B The top left figure shows an anatomical structure in the lower leg and foot that are involved in standing on tiptoe, with the heel raised slightly off the floor so that the foot effectively contacts the floor only at point C. The calf muscle pulls on the foot at point A, which is rotating around point B where the foot contacts the lower leg bones. We want to compute the pulling force FA of the calf muscle necessary for the person to stand on tiptoe as well as the force FB on the lower leg bones from the foot. For simplicity we will assume that the points A, B and C lie on a single line as shown on the simplified diagram on the right. Assume distance dAB = 5.00 cm, distance dBC = 15.0 cm, the angle between the floor and the foot is 0 = 10.0°, and the person's mass m = 80.0 kg. We will neglect the weight of the foot. a) Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the foot. (1 point) b) Assuming rotational equilibrium compute the calf…arrow_forward3. You are in a tall building located near the equator. As you ride an elevator from the ground floor to the top floor, your tangential speed due to the earth's rotation a. increases b. decreases increases when the speed of the elevator increases and decreases when the speed of the elevator decreases d. does not changearrow_forward
- 2. Two points are located on a rigid wheel that is rotating with decreasing angular velocity about a fixed axis. Point A is located on the rim of the wheel and point B is halfway between the rim and the axis. Which one of the following statements concerning this situation is true? A B Both points have the same centripetal acceleration. b. Both points have the same tangential acceleration. The angular velocity at point A is greater than that of point B. d. Both points have the same instantaneous angular velocity. Each second, point A turns through a greater angle than point B. e.arrow_forward4. Two hoops, starting from rest, roll down identical inclined planes. The work done by nonconservative forces, such as air resistance, is zero (Wnc = 0 J). Both have the same mass M, but, as the drawing shows, one hoop has twice the radius as the other. The moment of inertia for each hoop is I = Mr², where r is its radius. Which, if either, has the greater total kinetic energy (translational plus rotational) at the bottom of the incline? Radius=R Mass = M Radius=R Mass = Marrow_forward5. A uniform disk, a thin hoop, and a uniform solid sphere, all with the same mass and same outer radius, are each free to rotate about a fixed axis through its center. Assume the hoop is connected to the rotation axis by light spokes. With the objects starting from rest, identical forces are simultaneously applied to the rims, as shown. Rank the objects according to their angular velocities after a given time t, least to greatest. a. disk, sphere, hoop b. hoop, sphere, disk c. sphere, disk, hoop d. hoop, disk, sphere e. disk, hoop, spherearrow_forward
- 1. Two cars are traveling at the same constant speed v. As the drawing above indicates, car A is moving along a straight section of the road, while car B is rounding a circular turn. Which statement is true about the accelerations of the cars? B A a. The acceleration of both cars is zero, since they are traveling at a constant speed. b. Car A is accelerating, but car B is not accelerating. c. Car A is not accelerating, but car B is accelerating. d. Both cars are accelerating.arrow_forward6. A wheel rolls without slipping along a horizontal road as shown. The velocity of the center of the wheel is represented by v. Point P is painted on the rim of the wheel. The direction of the instantaneous velocity of point P is: a. b. C. d. öö j e. ↑ ↑ ↓arrow_forwardNo chatgptarrow_forward
- G Remaxi: hatdirkst poed of Cha pital of te wendb axcels does ha taxaxxeaza s in Kirarais Avite v) askaly fearbe Add to search 4) Kom me TUTHICAL NOW HISE is the ball moving at the highest point in its trajectory if air resistance is negligible? 3) Constant Acceleration Kinematics: In a ballistics test, a bullet moving horizontally with a speed of 500 m/s strikes a sandbag and penetrates a distance of 10.0 cm. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of the bullet in the sandbag? (b) How many milliseconds does it take the bullet to come to rest in the sandbag? 4) Constant Acceleration Kinematics: A car with good tires on a dry road can decelerate (slow down) at a steady rate of about 5.0 m/s2 when braking. If a car is initially traveling at 55 mi/h (a) how much time does it take the car to stop? (b) what is its stopping distance? XA Translate Q Search Homework Best Wishes < 7:01 Google Lens 100 5G+ 43arrow_forwardan with an mal velocity of 32 m/s at 35° from the vertical. How fast is the ball moving at the highest point in its trajectory if air resistance is negligible? 3) Constant Acceleration Kinematics: In a ballistics test, a bullet moving horizontally with a speed of 500 m/s strikes a sandbag and penetrates a distance of 10.0 cm. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of the bullet in the sandbag? (b) How many milliseconds does it take the bullet to come to rest in the sandbag? 4) Constant Acceleration Kinematics: A car with good tires on a dry road can decelerate (slow down) at a steady rate of about 5.0 m/s2 when braking. If a car is initially traveling at 55 mi/h di bawa (a) how much time does it take the car to stop? (b) what is its stopping distance? 2)」 3) 2 9 6) 4) - Best Wishesarrow_forward6. A meter stick whose mass is 0.200 kg is supported at the zero cm mark by a knife edge and a force F at the 100 cm point. A mass of 700 grams is attached to the stick at the 40 cm mark. Find the magnitude of N and F in Newtons. Magnitude of N N Newtons, Magnitude of F Newtons F itions for 40 cm 700 gm 100 cmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Introduction to Vectors and Their Operations; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KBSCMTYaH1s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY