
Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design (McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398204
Author: Richard G Budynas, Keith J Nisbett
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 120P
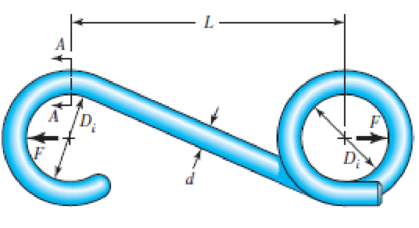
A utility hook was formed from a round rod of diameter d = 20 mm into the geometry shown in the figure. What are the stresses at the inner and outer surfaces at section A–A if F = 4 kN, L = 250 mm, and Di = 75 mm?
Problem 3–120
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q6] (20 Marks) Select the most suitable choice for the following statements: modo digi
-1A 10 af5
1 -The copper-based alloy which is responded to age hardening is
a) copper-nickel
b) aluminum bronze c) copper - beryllium d) brass besincaluy
2- Highly elastic polymers may experience elongations to greater than....
b) 500%
bromsia-P
c) 1000%. d) 1200% 15m or -2
a)100%
3- The cooling rate of quenching the steel in saltwater will be ......the cooling rate of quenching ir
c) faster than sold) none of them
a) slower than
4- Adding of
a) Cr
b) the same as
...... Will lead to stabilize the
b) Mo
10
austenite in steel.
c) Nimble avolls 1d) Sized loloin nl
5- The adjacent linear chains of crosslinked polymers are joined one to another at various positic
DIR...
by.........bonds
c) covalent noisqo gd) ionic lg 120M
6- For the ceramic with coordination number 6 the cation to anion radius ratio will be
a) Van der Waals
a) 0.155-0.225
a) linear
b) hydrogen
(b) 0.225-0.414
c) 0.414 0.732
..polymers.…
Examine
Notes: Attempt Six Questions Only.
rever necessa ,
Q1] (20 Marks) Answer with true (T) or false (F), corrects the wrong phrases, and gives sho
reasons for correct and corrected statements:
1- High chromium irons are basically grey cast irons alloyed with 12 to 30 % Cr.
yous board-19qgo orT-1
2- The drawbacks of Al- Li alloys are their high young modulus and high density.&M 0) (0
3- Vulcanized rubbers are classified under thermoplastic polymers.
4- Diamond is a stable carbon polymorph at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. (
5- The metallic ions of ceramic are called anions, and they are positively charged.
yldgiH-S
69001(6
H.W 5.4
Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E-228GPa. The diameters
of the rods are as shown in fig. below.
2P-
PA
50mm
B
200mm
2P
0.9m
1.3m
Chapter 3 Solutions
Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design (McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering)
Ch. 3 - 31 to 34 Sketch a free-body diagram of each...Ch. 3 - 31 to 34 Sketch a free-body diagram of each...Ch. 3 - Sketch a free-body diagram of each element in the...Ch. 3 - 3-1 to 3-4 Sketch a free-body diagram of each...Ch. 3 - 35 to 38 For the beam shown, find the reactions at...Ch. 3 - 35 to 38 For the beam shown, find the reactions at...Ch. 3 - 35 to 38 For the beam shown, find the reactions at...Ch. 3 - For the beam shown, find the reactions at the...Ch. 3 - For the beam shown, find the reactions at the...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 36 using singularity functions...
Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 37 using singularity functions...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 38 using singularity functions...Ch. 3 - For a beam from Table A9, as specified by your...Ch. 3 - A beam carrying a uniform load is simply supported...Ch. 3 - For each of the plane stress states listed below,...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 315 for: (a)x = 28 MPa, y = 7 MPa, xy...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 315 for: a) x = 12 kpsi, y = 6 kpsi,...Ch. 3 - For each of the stress states listed below, find...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 318 for: (a)x = 10 kpsi, y = 4 kpsi...Ch. 3 - The state of stress at a point is x = 6, y = 18, z...Ch. 3 - The state of stress at a point is x = 6, y = 18, z...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 320 with x = 10, y = 40, z = 40, xy =...Ch. 3 - A 34-in-diameter steel tension rod is 5 ft long...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 323 except change the rod to aluminum...Ch. 3 - A 30-mm-diameter copper rod is 1 m long with a...Ch. 3 - A diagonal aluminum alloy tension rod of diameter...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 326 with d = 16 mm, l = 3 m, and...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 326 with d = 58 in, l = 10 ft, and...Ch. 3 - Electrical strain gauges were applied to a notched...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 329 for a material of aluminum. 3-29...Ch. 3 - The Roman method for addressing uncertainty in...Ch. 3 - Using our experience with concentrated loading on...Ch. 3 - The Chicago North Shore Milwaukee Railroad was an...Ch. 3 - For each section illustrated, find the second...Ch. 3 - 3-35 to 3-38 For the beam illustrated in the...Ch. 3 - 3-35 to 3-38 For the beam illustrated in the...Ch. 3 - 3-35 to 3-38 For the beam illustrated in the...Ch. 3 - 3-35 to 3-38 For the beam illustrated in the...Ch. 3 - The figure illustrates a number of beam sections....Ch. 3 - A pin in a knuckle joint canning a tensile load F...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-40 for a = 6 mm, b = 18 mm. d = 12...Ch. 3 - For the knuckle joint described in Prob. 3-40,...Ch. 3 - The figure illustrates a pin tightly fitted into a...Ch. 3 - For the beam shown, determine (a) the maximum...Ch. 3 - A cantilever beam with a 1-in-diameter round cross...Ch. 3 - Consider a simply supported beam of rectangular...Ch. 3 - In Prob. 346, h 0 as x 0, which cannot occur. If...Ch. 3 - 348 and 349 The beam shown is loaded in the xy and...Ch. 3 - The beam shown is loaded in the xy and xz planes....Ch. 3 - Two steel thin-wall tubes in torsion of equal...Ch. 3 - Consider a 1-in-square steel thin-walled tube...Ch. 3 - The thin-walled open cross-section shown is...Ch. 3 - 3-53 to 3-55 Using the results from Prob. 3-52,...Ch. 3 - 3-53 to 3-55 Using the results from Prob. 3-52,...Ch. 3 - 3-53 to 3-55 Using the results from Prob. 3-52,...Ch. 3 - Two 300-mm-long rectangular steel strips are...Ch. 3 - Using a maximum allowable shear stress of 70 Mpa,...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 357 with an allowable shear stress of...Ch. 3 - Using an allowable shear stress of 50 MPa,...Ch. 3 - A 20-mm-diameter steel bar is to be used as a...Ch. 3 - A 2-ft-long steel bar with a 34-in diameter is to...Ch. 3 - A 40-mm-diameter solid steel shaft, used as a...Ch. 3 - Generalize Prob. 3-62 for a solid shaft of...Ch. 3 - A hollow steel shaft is to transmit 4200 N m of...Ch. 3 - The figure shows an endless-bell conveyor drive...Ch. 3 - The conveyer drive roll in the figure for Prob....Ch. 3 - Consider two shafts in torsion, each of the same...Ch. 3 - 3-68 to 3-71 A countershaft two V-belt pulleys is...Ch. 3 - 3-68 to 3-71 A countershaft two V-belt pulleys is...Ch. 3 - 3-68 to 3-71 A countershaft two V-belt pulleys is...Ch. 3 - A countershaft carrying two V-belt pulleys is...Ch. 3 - A gear reduction unit uses the countershaft shown...Ch. 3 - Prob. 73PCh. 3 - Prob. 74PCh. 3 - Prob. 75PCh. 3 - Prob. 76PCh. 3 - Prob. 77PCh. 3 - Prob. 78PCh. 3 - Prob. 79PCh. 3 - The cantilevered bar in the figure is made from a...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-80 with Fx = 0, Fy = 175 lbf, and...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-80 with Fx = 75 lbf, Fy= 200 lbf,...Ch. 3 - For the handle in Prob. 3-80, one potential...Ch. 3 - The cantilevered bar in the figure is made from a...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-84 with Fx = 300 lbf, Fy = 250 lbf,...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-84 with Fx = 300 lbf, Fy = 250 lbf,...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-84 for a brittle material,...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-84 with Fx = 300 lbf, Fy = 250 lbf,...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-84 with Fx = 300 lbf, Fy = 250 lbf,...Ch. 3 - The figure shows a simple model of the loading of...Ch. 3 - Develop the formulas for the maximum radial and...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 391 where the cylinder is subject to...Ch. 3 - Develop the equations for the principal stresses...Ch. 3 - 3-94 to 3-96 A pressure cylinder has an outer...Ch. 3 - 3-94 to 3-96 A pressure cylinder has an outer...Ch. 3 - 3-94 to 3-96A pressure cylinder has an outer...Ch. 3 - 3-97 to 3-99 A pressure cylinder has an outer...Ch. 3 - 3-97 to 3-99 A pressure cylinder has an outer...Ch. 3 - 3-97 to 3-99 A pressure cylinder has an outer...Ch. 3 - An AISI 1040 cold-drawn steel tube has an OD = 50...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-100 with an OD of 2 in and wall...Ch. 3 - Prob. 102PCh. 3 - Prob. 103PCh. 3 - A thin-walled cylindrical Steel water storage tank...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3-104 with the tank being pressurized...Ch. 3 - Find the maximum shear stress in a 512-in-diameter...Ch. 3 - The maximum recommended speed for a...Ch. 3 - An abrasive cutoff wheel has a diameter of 5 in,...Ch. 3 - A rotary lawnmower blade rotates at 3500 rev/min....Ch. 3 - 3110 to 3115 The table lists the maximum and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 111PCh. 3 - Prob. 112PCh. 3 - 3110 to 3115 The table lists the maximum and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 114PCh. 3 - Prob. 115PCh. 3 - 3116 to 3119 The table gives data concerning the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 117PCh. 3 - Prob. 118PCh. 3 - 3116 to 3119 The table gives data concerning the...Ch. 3 - A utility hook was formed from a round rod of...Ch. 3 - A utility hook was formed from a round rod of...Ch. 3 - The steel eyebolt shown in the figure is loaded...Ch. 3 - For Prob. 3122 estimate the stresses at the inner...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3122 with d = 14 in, Ri = 12 in, and...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3123 with d = 14 in, Ri = 12 in, and...Ch. 3 - Shown in the figure is a 12-gauge (0.1094-in) by...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3126 with a 10-gauge (0.1406-in)...Ch. 3 - Prob. 128PCh. 3 - The cast-iron bell-crank lever depicted in the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 130PCh. 3 - Prob. 131PCh. 3 - A cast-steel C frame as shown in the figure has a...Ch. 3 - Two carbon steel balls, each 30 mm in diameter,...Ch. 3 - A carbon steel ball with 25-mm diameter is pressed...Ch. 3 - Repeat Prob. 3134 but determine the maximum shear...Ch. 3 - A carbon steel ball with a 30-mm diameter is...Ch. 3 - An AISI 1018 steel ball with 1-in diameter is used...Ch. 3 - An aluminum alloy cylindrical roller with diameter...Ch. 3 - A pair of mating steel spur gears with a 0.75-in...Ch. 3 - 3140 to 3142 A wheel of diameter d and width w...Ch. 3 - 3140 to 3142 A wheel of diameter d and width w...Ch. 3 - 3140 to 3142 A wheel of diameter d and width w...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- d₁ = = Two solid cylindrical road AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown. Knowing that 30mm (for AB) and d₂ 50mm (for BC), find the average normal stress in each road and the total deformation of road AB and BC. E=220GPa H.W 5.3 60kN A For the previous example calculate the value of force P so that the point A will not move, and what is the total length of road AB at that force? P◄ A 125kN 125kN 0.9m 125kN 125kN 0.9m B B 1.3m 1.3marrow_forwardClass: B Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E-228GPa The cross sections of the rods are as shown in fig. below. 183 P- Solution 1.418mm 200mm 80mm 3P- 18.3 A 080mm B 200mm 3P- 0.9m إعدادات العرض 1.3m 4.061mmarrow_forwardH.W6 Determine the largest weight W that can be supported by two wires shown in Fig. P109. The stress in either wire is not to exceed 30 ksi. The cross- sectional areas of wires AB and AC are 0.4 in2 and 0.5 in2, respectively. 50° 30° Warrow_forward
- Find equation of motion and natural frequency for the system shown in fig. by energy method. H.W2// For the system Fig below find 1-F.B.D 2-Eq.of motion 8wn 4-0 (5) m. Jo marrow_forward2. Read the following Vernier caliper measurements. (The scales have been enlarged for easier reading.) The Vernier caliper is calibrated in metric units. (a) 0 1 2 3 4 5 سلسلسله (b) 1 2 3 4 5 6 سلسل (c) 1 23456 (d) 1 2 3 4 5 6 سلسلسarrow_forwardExplain why on the interval 0<x<1000 mm and 1000<x<2000mm, Mt is equal to positive 160 Nm, but at x= 0mm and x=1000mm Mt is equal to -160 Nm (negative value!). What is the reason for the sign change of Mt?arrow_forward
- 20 3. 2-233 2520 Тр Gears 1079 A pair of helical gears consist of a 20 teeth pinion meshing with a 100 teeth gear. The pinion rotates at Ta 720 r.p.m. The normal pressure angle is 20° while the helix angle is 25°. The face width is 40 mm and the normal module is 4 mm. The pinion as well as gear are made of steel having ultimate strength of 600 MPa and heat treated to a surface hardness of 300 B.H.N. The service factor and factor of safety are 1.5 and 2 respectively. Assume that the velocity factor accounts for the dynamic load and calculate the power transmitting capacity of the gears. [Ans. 8.6 kWarrow_forward4. A single stage helical gear reducer is to receive power from a 1440 r.p.m., 25 kW induction motor. The gear tooth profile is involute full depth with 20° normal pressure angle. The helix angle is 23°, number of teeth on pinion is 20 and the gear ratio is 3. Both the gears are made of steel with allowable beam stress of 90 MPa and hardness 250 B.H.N. (a) Design the gears for 20% overload carrying capacity from standpoint of bending strength and wear, (b) If the incremental dynamic load of 8 kN is estimated in tangential plane, what will be the safe power transmitted by the pair at the same speed?arrow_forwardDetermine the stress in each section of the bar shown in Fig. when subjected to an axial tensile load shown in Fig. The central section is 30 mm hollow square cross- section; the other portions are of circular section, their diameters being indicated What will be the total deformation of the bar? For the bar material E = 210GPa. 20mi О 30mm 30mmm 2.6 15mm 30kN 1 2 10kN - 20kN 3 -329 91mm 100mm 371mmarrow_forward
- Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E=228GPa. The diameters of the rods are as shown in fig. below. 2P- PA 80mm B 200mm 2P 0.9m 1.3m.arrow_forwardIf the rods are made from a square section with the dimension as shown. Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E=228GPa. 2P- P A 80mm B 200mm 2P 0.9m 1.3marrow_forward3. 9. 10. The centrifugal tension in belts (a) increases power transmitted (b) decreases power transmitted (c) have no effect on the power transmitted (d) increases power transmitted upto a certain speed and then decreases When the belt is stationary, it is subjected to some tension, known as initial tension. The value of this tension is equal to the (a) tension in the tight side of the belt (b) tension in the slack side of the belt (c) sum of the tensions in the tight side and slack side of the belt (d) average tension of the tight side and slack side of the belt The relation between the pitch of the chain (p) and pitch circle diameter of the sprocket (d) is given by 60° (a) p=d sin (c) p=d sin (120° T where T Number of teeth on the sprocket. 90° (b) p=d sin T 180° (d) p=d sin Tarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Pressure Vessels Introduction; Author: Engineering and Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z1J97IpFc2k;License: Standard youtube license