
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133918922
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.9, Problem 25FP
Determine the angle θ between the force and the line AO.
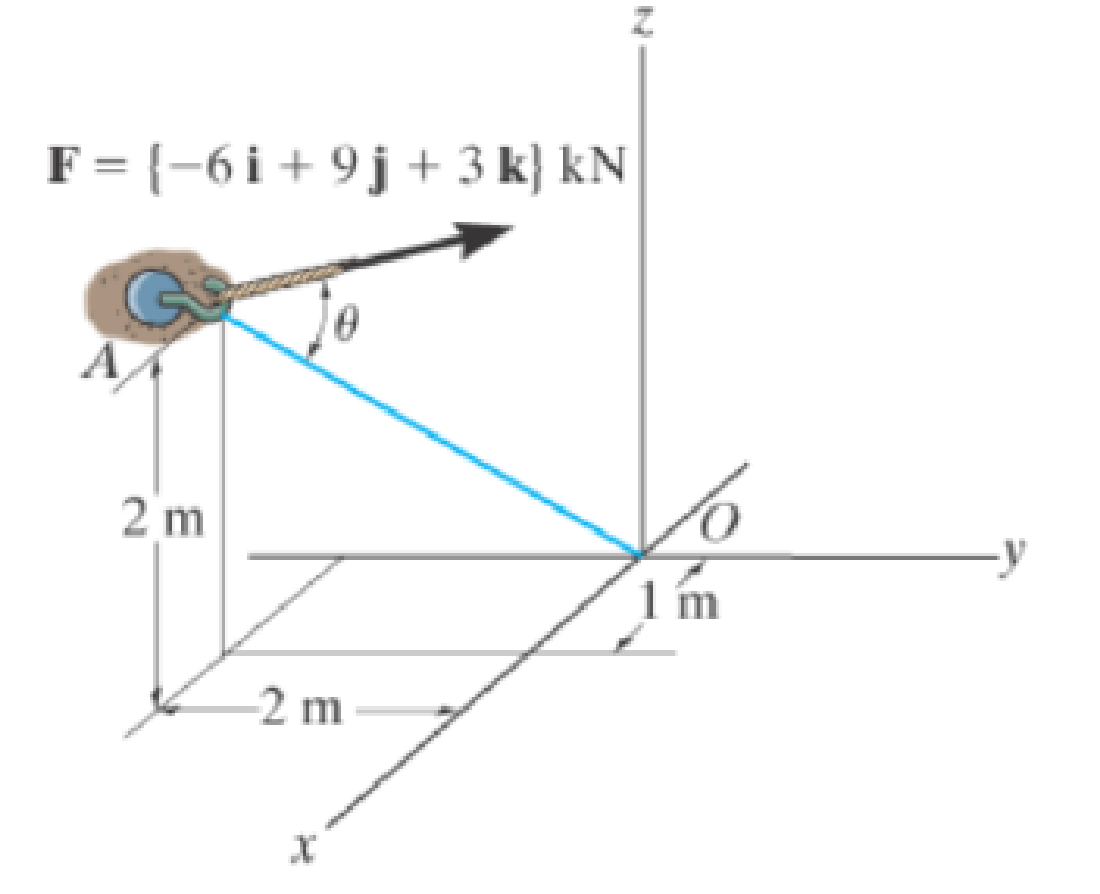
Prob. F2-25
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule05:09
Students have asked these similar questions
2 A metal block of mass m = 10 kg is sliding along a frictionless surface with an initial speed
Vo, as indicated below. The block then slides above an electromagnetic brake that applies a
force FEB to the block, opposing its motion. The magnitude of the electromagnetic force
varies quadratically with the distance moved along the brake (x):
10
FEB = kx²,
with k
= 5
N
m²
V₁ = 8 m/s
m = 10 kg
FEB
Frictionless surface
Electromagnetic brake
⇒x
Determine how far the block slides along the electromagnetic brake before stopping, in m.
Q1: Determine the length, angle of contact, and width of a 9.75 mm thick
leather belt required to transmit 15 kW from a motor running at 900 r.p.m. The
diameter of the driving pulley of the motor is 300 mm. The driven pulley runs at
300 r.p.m. and the distance between the centers of two pulleys is 3 meters. The
density of the leather is 1000 kg/m³. The maximum allowable stress in the
leather is 2.5 MPa. The coefficient of friction between the leather and pulley is
0.3. Assume open belt drive.
5. A 15 kW and 1200 r.p.m. motor drives a compressor at 300 r.p.m. through a pair of spur gears having
20° stub teeth. The centre to centre distance between the shafts is 400 mm. The motor pinion is made
of forged steel having an allowable static stress as 210 MPa, while the gear is made of cast steel
having allowable static stress as 140 MPa. Assuming that the drive operates 8 to 10 hours per day
under light shock conditions, find from the standpoint of strength,
1. Module; 2. Face width and 3. Number of teeth and pitch circle diameter of each gear.
Check the gears thus designed from the consideration of wear. The surface endurance limit may be
taken as 700 MPa. [Ans. m = 6 mm; b= 60 mm; Tp=24; T=96; Dp = 144mm; DG = 576 mm]
Chapter 2 Solutions
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Ch. 2.3 - Then establish the triangle rule, where FR = F1 +...Ch. 2.3 - Then establish the triangle rule to show FR = FU +...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force....Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the 30-lb force into components along the...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve this force into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - along the v axis. Prob. F2-6Ch. 2.3 - If = 60 and F = 450 N, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the magnitude of the resultant force is to be...
Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the two components of...Ch. 2.3 - Solve with F = 350 lb. Prob. 2-4/5Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F1 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F2 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force acting on the support is to...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - If = 60, determine the magnitude of the resultant...Ch. 2.3 - Also, what is the magnitude of the resultant...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve this force into two components acting...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of F and its component...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of F and its direction ....Ch. 2.3 - Determine the required angle (0 45) and the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - What is the component of force acting along member...Ch. 2.3 - Take = 30. Probs. 2-19/20Ch. 2.3 - FR measured counterclockwise from the positive x...Ch. 2.3 - Solve I by first finding the resultant F = F2 + F3...Ch. 2.3 - If F1 = 400 N and F2 = 600 N, determine the angle...Ch. 2.3 - If their lines of action are at an angle apart...Ch. 2.3 - If F1 = 30 lb and F2 = 40 lb, determine the angles...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of FA SO...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction, measured...Ch. 2.3 - What is the minimum magnitude of FR?Ch. 2.3 - directed along the positive x axis, determine the...Ch. 2.3 - If FB = 3 kN and = 45, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the post into its x...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - determine the magnitude of F and its direction ....Ch. 2.4 - If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve F1 and F2 into their x and y components.Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the gusset plate into...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - Express each of the three forces acting on the...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the x and y components of F1 and F2....Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and orientation of FB so...Ch. 2.4 - measured counterclockwise from the positive y...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant fore and...Ch. 2.4 - Show that the resultant force is zero. Prob. 2-52Ch. 2.4 - Express F1 and F2 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - What is the magnitude of the resultant force?...Ch. 2.4 - If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.4 - Set = 30. Probs. 2-56/57Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of F so...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 59PCh. 2.6 - Show , , . a) F = {50i + 60j 10k} kN b) F = {40i ...Ch. 2.6 - In each case, establish F as a Cartesian vector,...Ch. 2.6 - Set up the calculation used to find the magnitude...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Determine the resultant force acting on the hook....Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitudes of the x, y, z components...Ch. 2.6 - If the magnitude of F is 80 N, and = 60 and =...Ch. 2.6 - The component of F in the x-y plane is 7 kN. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Specify the coordinate direction angles of F1 and...Ch. 2.6 - Express each force in Cartesian vector form and...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of F1....Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Note that F1 lies in the x-y plane.Ch. 2.6 - If the resultant force FR has a magnitude of 150...Ch. 2.6 - Express each force in Cartesian vector form.Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Express each force as a Cartesian vector.Ch. 2.6 - Determine the resultant of the two forces and...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 78PCh. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - Express each force in Cartesian vector form and...Ch. 2.6 - If the coordinate direction angles for F1 are 3 =...Ch. 2.6 - If the coordinate direction angles for F1 are 3 =...Ch. 2.6 - If the direction of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 84PCh. 2.6 - If = 75, determine the magnitudes of F and Fy....Ch. 2.8 - In each case, establish a position vector from...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, express F as a Cartesian vector....Ch. 2.8 - Express the position vector rAB in Cartesian...Ch. 2.8 - What is the angle ? Prob. F2-20Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 21FPCh. 2.8 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force at...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the resultant force at A. Prob. F2-24Ch. 2.8 - Determine the length of the connecting rod AB by...Ch. 2.8 - Express force F as a Cartesian vector; then...Ch. 2.8 - Express each of the forces in Cartesian vector...Ch. 2.8 - If F = {350i 250j 450k} N and cable AB is 9 m...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 90PCh. 2.8 - If z = 5 m, determine the location +x, +y of point...Ch. 2.8 - Express each of the forces in Cartesian vector...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 560 N and FC = 700 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 700 N, and FC = 560 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - Express each force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Represent each force as a Cartesian vector. Probs....Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Express this force as a Cartesian vector acting on...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - Represent each force as a Cartesian vector and...Ch. 2.8 - The anticipated loading in two of the struts is...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - If the force in each cable tied to the bin is 70...Ch. 2.8 - Due to symmetry, the tension in the four cables is...Ch. 2.9 - Do not calculate the result. Prob. P2-8Ch. 2.9 - P2.9. In each case, set up the dot product to find...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the projected component of the force...Ch. 2.9 - Find the magnitude of the projected component of...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the components of the force acting...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Express the force F in Cartesian vector form if it...Ch. 2.9 - Express force F in Cartesian vector form if point...Ch. 2.9 - If the force in each chain has a magnitude of 60...Ch. 2.9 - If the resultant force at O has a magnitude of 130...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the length of the chain, and express the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the length of the cable and express the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 112PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of F =...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables. Prob....Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the y axis of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the projected...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 119PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of force...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between pipe segments BA and...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 128PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angles and made between the axes...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 131PCh. 2.9 - Express this component as a Cartesian vector....Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 133PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 134PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the projected...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 137PCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables....Ch. 2.9 - Express the result as a Cartesian vector.Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.9 - Resolve F into components along the u and v axes...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 4RPCh. 2.9 - The cable attach to the tractor at B exerts a...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 6RPCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the edges of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the projection of the force F along the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
For metal-cutting tools, what is the most important material property (i.e., the most critical characteristic)?...
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
What populates the Smalltalk world?
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Summarize the booting process.
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
In each case, determine the internal bending moment as a function of x, and state the necessary boundary and/or...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Describe two properties that each candidate key must satisfy.
Modern Database Management
Consider a class characteristic that will be used in an online dating service to assess how compatible two peop...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. G A micarta pinion rotating at 1200 r.p.m. is to transmit 1 kW to a cast iron gear at a speed of 192 r.p.m. Assuming a starting overload of 20% and using 20° full depth involute teeth, determine the module, number of teeth on the pinion and gear and face width. Take allowable static strength for micarta as 40 MPa and for cast iron as 53 MPa. Check the pair in wear.arrow_forwardI want to solve these choicesarrow_forward2. A spur gear made of bronze drives a mid steel pinion with angular velocity ratio of 32: 1. The pressure angle is 14½. It transmits 5 kW at 1800 r.p.m. of pinion. Considering only strength, design the smallest diameter gears and find also necessary face width. The number of teeth should not be less than 15 teeth on either gear. The elastic strength of bronze may be taken as 84 MPa and of steel as 105 MPa. Lewis factor for 14½½ pressure angle may be taken 0.684 0.124 y = No. of teeth as [Ans. m 3 mm; b= 35 mm; Dp = 48 mm; D= 168 mm]arrow_forward
- Q2. Determine the safety factors for the bracket rod shown in Figure 2 based on both the distortion-energy theory and the maximum shear theory and compare them. Given: The material is 2024-T4 aluminum with a yield strength of 47 000 psi. The rod length /= 6 in. and arm a = 8 in. The rod outside diameter od 1.5 in., id = 1 in, h=2 in., t=0.5 in., Load F= 1000 lb. Assumptions: The load is static and the assembly is at room temperature. Consider shear due to transverse loading as well as other stresses. (Note: solve in SI units) wall tube Figure 2 armarrow_forwardThe question has been set up with all the cuts needed to accurately derive expressions for V(x) and M(x). Using the cuts free body diagrams set up below, derive expressions for V(x) and M(x). If you use the method of cuts then validate your answers using calculus or vice versa.arrow_forwardIt is required to treat 130 kmol/hr of chloroform-air feed gas mixture that contains 12% chloroform. It is required to remove 93% of chloroform using 150 kmol/hr of solvent that contains 99.6% water and 0.4% chloroform. The cross sectional area of the column is 0.8 m². Calculate the column height using the following data; kx'.a = 1.35 (kmol/m³.s (Ax)), and ky'.a = 0.06 (kmol/m³.s (Ay)), kx/ky = 1.35, and the equilibrium data are: X 0 0.0133 0.033 y 0 0.01 0.0266 0.049 0.064 0.0747 0.0933 0.1053 0.0433 0.06 0.0733 0.111 0.1 0.12 0.14arrow_forward
- ४ B: Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps). (Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix) [T1] T₂ T3 [T] 1 = [0] 0 0 d dx dx) (ka)+4(ka) = dy -20xy, k = 1 + 0.3 T ge L=3cm, 4x= Ay B.Cs.: at x=0=LT=0°C at y=0-L T=10°C Fig. (2)arrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only Two rods fins) having same dimensions, one made orass (k = 85 Wm K) and the mer of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having of their ends inserted into a furna. At a section 10.5 cm a way from furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120 Find the distance at which the ame temperature would be reached in the per rod ? both ends are ex osed to the same environment. ns 2.05 ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forwardFor the beam show below, draw A.F.D, S.F.D, B.M.D 6 kN/m 1 M B. 3 M Marrow_forward
- 1. Two long rods of the same diameter-one made of brass (k=85w/m.k) and the other made of copper (k=375 w/m.k) have one of their ends inserted into a furnace (as shown in the following figure). Both rods are exposed to the same environment. At a distance of 105 mm from the furnace, the temperature of the brass rod is 120°C. At what distance from the furnace will the same temperature be reached in the copper rod? Furnace 105 mm T₁ Brass rod ⑪ h Too- x2- Ti Copper rodarrow_forward: +0 العنوان use only Two rods fins) having same dimensions, one made orass (k = 85 Wm K) and the mer of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having of their ends inserted into a furna. At a section 10.5 cm a way from furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120 Find the distance at which the ame temperature would be reached in the per rod ? both ends are ex osed to the same environment. ns 2.05 ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forwardمشر on ۲/۱ Two rods (fins) having same dimensions, one made of brass(k=85 m K) and the other of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having one of their ends inserted into a furnace. At a section 10.5 cm a way from the furnace, the temperature brass rod 120°C. Find the distance at which the same temperature would be reached in the copper rod ? both ends are exposed to the same environment. 22.05 ofthearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Introduction To Engg Mechanics - Newton's Laws of motion - Kinetics - Kinematics; Author: EzEd Channel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ksmsp9OzAsI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY