
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 28, Problem 7Q
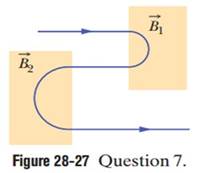 |
Figure 28-27 Question 7.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Checkpoint 4
The figure shows four orientations of an electric di-
pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta-
tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque
on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di-
pole, greatest first.
(1)
(2)
E
(4)
What is integrated science.
What is fractional distillation
What is simple distillation
19:39 ·
C
Chegg
1 69%
✓
The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take
F=1700 lb. (Figure 1)
Figure
800 lb
||-5-
F
600 lb
بتا
D
E
C
BO
10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft-
Solved Part A The compound
beam is fixed at E and...
Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm
Problem
A-12
% Chia sẻ
kip
800 lb
Truy cập )
D Lưu
of
C
600 lb
|-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft
D
E
5 ft-
Trying
Cheaa
Những kết quả này có
hữu ích không?
There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!)
Chegg
Solved The compound b...
Có Không ☑
|||
Chegg
10
וח
Chapter 28 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 28 - Prob. 1QCh. 28 - Prob. 2QCh. 28 - Prob. 3QCh. 28 - Prob. 4QCh. 28 - In Module 28-2, we discussed a charged particle...Ch. 28 - Figure 28-26 shows crossed uniform electic and...Ch. 28 - Figure 28-27 shows the path of an electron that...Ch. 28 - Figure 28-28 shows the path of an electron in a...Ch. 28 - a In Checkpoint 5, if the dipole moment is rotated...Ch. 28 - Particle round about. Figure 28-29 shows 11 paths...
Ch. 28 - Prob. 11QCh. 28 - Prob. 12QCh. 28 - Prob. 1PCh. 28 - A particle of mass 10 g and charge 80 C moves...Ch. 28 - An electron that has an instantaneous velocity of...Ch. 28 - An alpa particle travels at a velocity of...Ch. 28 - GO An electron moves through a unifrom magnetic...Ch. 28 - GO A proton moves through a uniform magnetic field...Ch. 28 - Prob. 7PCh. 28 - An electric field of 1.50 kV/m and a perpendicular...Ch. 28 - ILW In Fig. 28-32, an electron accelerated from...Ch. 28 - A proton travels through uniform magnetic and...Ch. 28 - Prob. 11PCh. 28 - Go At time t1 an electron is sent along the...Ch. 28 - Prob. 13PCh. 28 - A metal strip 6.50 cm long, 0.850 cm wide, and...Ch. 28 - Prob. 15PCh. 28 - Prob. 16PCh. 28 - An alpha particle can be produced in certain...Ch. 28 - Prob. 18PCh. 28 - Prob. 19PCh. 28 - Prob. 20PCh. 28 - SSM An electron of kinetic energy 1.20 keV circles...Ch. 28 - In a nuclear experiment a proton with kinetic...Ch. 28 - What uniform magnetic field, applied perpendicular...Ch. 28 - An electron is accelerated from rest by a...Ch. 28 - a Find the frequency of revolution of an electron...Ch. 28 - Prob. 26PCh. 28 - A mass spectrometer Fig. 28-12 is used to separate...Ch. 28 - A particle undergoes uniform circular motion of...Ch. 28 - An electron follows a helical path in a uniform...Ch. 28 - GO In Fig. 28-40. an electron with an initial...Ch. 28 - A particular type of fundamental particle decays...Ch. 28 - An source injects an electron of speed v = 1.5 ...Ch. 28 - Prob. 33PCh. 28 - An electron follows a helical path in a uniform...Ch. 28 - A proton circulates in a cyclotron, beginning...Ch. 28 - Prob. 36PCh. 28 - Prob. 37PCh. 28 - In a certain cyclotron a proton moves in a circle...Ch. 28 - SSM A horizontal power line carries a current of...Ch. 28 - A wire 1.80 m long carries a current of 13.0 A and...Ch. 28 - Prob. 41PCh. 28 - Prob. 42PCh. 28 - A single-turn current loop, carrying a current of...Ch. 28 - Prob. 44PCh. 28 - ACA /ACwire 50.0 cm long carries a 0.500 A current...Ch. 28 - In Fig. 28-44, a metal wire of mass m = 24.1 mg...Ch. 28 - GO A 1.0 kg copper rod rests on two horizontal...Ch. 28 - GO A long, rigid conductor, lying along an x axis,...Ch. 28 - Prob. 49PCh. 28 - An electron moves in a circle of radius r = 5.29 ...Ch. 28 - Prob. 51PCh. 28 - Prob. 52PCh. 28 - Prob. 53PCh. 28 - A magnetic dipole with a dipole moment of...Ch. 28 - Prob. 55PCh. 28 - Prob. 56PCh. 28 - Prob. 57PCh. 28 - Prob. 58PCh. 28 - A Current loop, carrying a current of 5.0 A, is in...Ch. 28 - Prob. 60PCh. 28 - Prob. 61PCh. 28 - Prob. 62PCh. 28 - A circular loop of wire having a radius of 8.0 cm...Ch. 28 - GO Figure 28-52 gives the orientation energy U of...Ch. 28 - Prob. 65PCh. 28 - Prob. 66PCh. 28 - A stationary circular wall clock has a face with a...Ch. 28 - A wire lying along a y axis from y = 0 to y =...Ch. 28 - Atom 1 of mass 35 u and atom 2 of mass 37 u are...Ch. 28 - Prob. 70PCh. 28 - Physicist S. A. Goudsmit devised a method for...Ch. 28 - A beam of electrons whose kinetic energy is K...Ch. 28 - Prob. 73PCh. 28 - Prob. 74PCh. 28 - Prob. 75PCh. 28 - Prob. 76PCh. 28 - Prob. 77PCh. 28 - In Fig. 28-8, show that the ratio of the Hall...Ch. 28 - Prob. 79PCh. 28 - An electron is moving at 7.20 106 m/s in a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 81PCh. 28 - Prob. 82PCh. 28 - Prob. 83PCh. 28 - A write lying along an x axis from x = 0 to x =...Ch. 28 - At one instant, m/s is the velocity of a proton in...Ch. 28 - An electron has velocity km/s as it enters a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 87PCh. 28 - Prob. 88PCh. 28 - In Fig. 28-58, an electron of mass m, charge e,...Ch. 28 - Prob. 90PCh. 28 - Prob. 91PCh. 28 - An electron that is moving through a uniform...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
With the initial appearance of the feature we call Now Solve This, a short introduction is in order. The featur...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
24. Convert the following to SI units:
a. 8.0 in b. 66 ft/s
c. 60 mph d. 14 in2
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Some organizations are starting to envision a sustainable societyone in which each generation inherits sufficie...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Why is turbidity not an accurate measurement of viable bacteria in a culture?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
In Example 2.lb, is there any mass at the indicated specific volume? Explain.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY