
(a)
Interpretation:
Identify the monomer required for making the given alternating copolymer
Concept introduction:
To explain : To explain why two different repeating units are present in the polymer.
(b)
Interpretation:
Identify the monomer required for making the given alternating copolymer
Concept introduction:
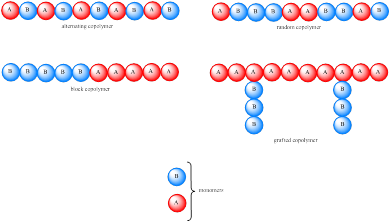
Polymer constructed from a single type of monomer is known as homopoylmers. If the polymer is constructed from two or more type of monomer then they are called as copolymers. Carbocation is initially formed, which undergo rearrangement to a more stable carbocation. Copolymers are usually classified based on the distribution of monomer units. If the monomer unit is present in an alternating fashion then it is known as alternating copolymer while if it is in random fashion then it is known as random copolymer. If the copolymer consists of homopolymer subunits connected in a block fashion then it is known as block copolymer. If the homopolymer subunit is grafted onto another homopolymer subunit then it is known as grafter copolymer. These four types of copolymer can be represented as,

To draw: To draw the structure of the repeating unit of random copolymer.
(c)
Interpretation:
Identify the monomer required for making the given alternating copolymer
Concept introduction:
Polymer constructed from a single type of monomer is known as homopoylmers. If the polymer is constructed from two or more type of monomer then they are called as copolymers. Carbocation is initially formed, which undergo rearrangement to a more stable carbocation. Copolymers are usually classified based on the distribution of monomer units. If the monomer unit is present in an alternating fashion then it is known as alternating copolymer while if it is in random fashion then it is known as random copolymer. If the copolymer consists of homopolymer subunits connected in a block fashion then it is known as block copolymer. If the homopolymer subunit is grafted onto another homopolymer subunit then it is known as grafter copolymer. These four types of copolymer can be represented as,

To justify: To justify whether 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene produce random copolymer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 27 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





