
Identical beams of light are incident on three different pairs of (ideal) polarizers. The double arrow drawn on each polarizer represents its direction of polarization.
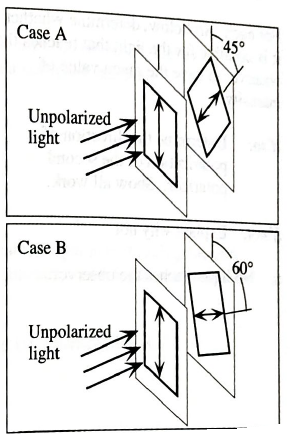
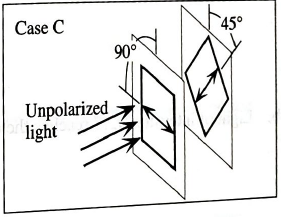
- Suppose that the incident light in each case were unpolarized.
Rank the three cases (A−C) according to the intensity of the light transmitted past the second polarizer, from largest to smallest. If for any case no light is transmitted past the second polarizer, state that explicitly. Explain your reasoning.
The ranking of intensity of light after passing through the second polarizer in each case.
Answer to Problem 1aTH
B<A=C
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The intensity of light passing through a polarizer depends directly on square of cosine of the angle. Smaller the angle between the two polarizer, greater will be the intensity of light passing through the second polarizer.
The angle between the two polariser is smallest in case A. hence the intensity of light is greatest in case A.
For case A and case C, the value of square of cosine of the angle between two polariser is same. Hence the intensity of light is same in case A and case C.
The angle between the two polariser is greatest in case B. hence the intensity of light is smallest in case B.
Conclusion:
Hence the intensity of light after passing through second polarizer is same in case A and case C and is greater than the intensity of light in case B.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
- look at answer show all work step by steparrow_forwardLook at the answer and please show all work step by steparrow_forward3. As a woman, who's eyes are h = 1.5 m above the ground, looks down the road sees a tree with height H = 9.0 m. Below the tree is what appears to be a reflection of the tree. The observation of this apparent reflection gives the illusion of water on the roadway. This effect is commonly called a mirage. Use the results of questions 1 and 2 and the principle of ray reversibility to analyze the diagram below. Assume that light leaving the top of the tree bends toward the horizontal until it just grazes ground level. After that, the ray bends upward eventually reaching the woman's eyes. The woman interprets this incoming light as if it came from an image of the tree. Determine the size, H', of the image. (Answer 8.8 m) please show all work step by steparrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
