
Capital rationing decision for a service company involving four proposals
Clearcast Communications Inc. is considering allocating a limited amount of capital investment funds among four proposals. The amount of proposed investment, estimated income from operations, and net cash flow for each proposal are as follows:
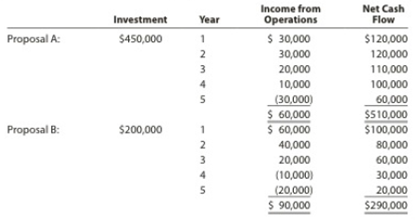
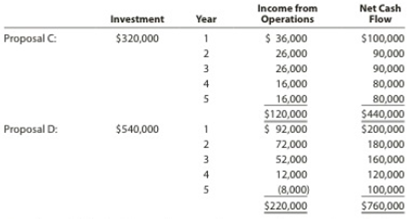
The company’s capital rationing policy requires a maximum cash payback period of three yean. In addition, a minimum average
Instructions
- 1. Compute the cash payback period for each of the four proposals.
- 2. Giving effect to straight-line depreciation on the investments and assuming no estimated residual value, compute the average rate of return for each of the four proposals. (Round to one decimal place.)
- 3. Using the following formal, summarize the results of your computations in parts (l) and (2). By placing the calculated amounts in the first two columns on the left and by placing a check mark in the appropriate column to the right, indicate which proposals should he accepted for further analysis and which should be rejected.

- 4. For the proposals accepted for further analysts in part (3), compute the net present value. Use a rate of 12% and the present value of $1 table appearing in this chapter (Exhibit 2).
- 5. Compute the present value index for each of the proposals in part (4). (Round to two decimal places.)
- 6. Rank the proposals from most attractive to least attractive, based on the present values of net
cash flows computed in part (4). - 7. Rank the proposals from most attractive to least attractive, based on the present value indexes computed in part (5).
- 8. Based on the analyses, comment on the relative attractiveness of the proposals ranked in parts (6) and (7).
1.
Cash payback method:
Cash payback period is the expected time period which is required to recover the cost of investment. It is one of the capital investment method used by the management to evaluate the long-term investment (fixed assets) of the business.
Average rate of return method:
Average rate of return is the amount of income which is earned over the life of the investment. It is used to measure the average income as a percent of the average investment of the business, and it is also known as the accounting rate of return.
The average rate of return is computed as follows:
Average rate of return =Estimated average annual incomeAverage investment
Net present value method:
Net present value method is the method which is used to compare the initial cash outflow of investment with the present value of its cash inflows. In the net present value, the interest rate is desired by the business based on the net income from the investment, and it is also called as the discounted cash flow method.
Present value index:
Present value index is a technique, which isused to rank the proposals of the business. It is used by the management when the business has more investment proposals, and limited fund.
The present value index is computed as follows:
Present value index =Total present value of net cash flowAmount to be invested
The cash payback period for the given proposals.
Explanation of Solution
The cash payback period for the given proposals is as follows:
Proposal A:
Initial investment=$450,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal A | ||||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows | ||
| 1 | 120,000 | 120,000 | ||
| 2 | 120,000 | 240,000 | ||
| 3 | 110,000 | 350,000 | ||
| 4 | 100,000 | 450,000 | ||
Table (1)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal A is 4 years.
Proposal B:
Initial investment=$200,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal B | ||||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows | ||
| 1 | 100,000 | 100,000 | ||
| 2 | 80,000 | 180,000 | ||
| 4 months(1) | 20,000 | 200,000 | ||
Table (2)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal B is 2 years and 4 months.
Working note:
1. Calculate the no. of months in the cash payback period:
No. of months = (Balance amount of intital investmentTotal cash flow for particular year)×No. of months in a year=$20,000$60,000×12 months= 4 months (1)
Proposal C:
Initial investment=$320,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal C | ||||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows | ||
| 1 | 100,000 | 100,000 | ||
| 2 | 90,000 | 190,000 | ||
| 3 | 90,000 | 280,000 | ||
| 6 months (2) | 40,000 | 320,000 | ||
Table (3)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal C is 3 years and 6 months.
Working note:
2. Calculate the no. of months in the cash payback period:
No. of months = (Balance amount of intital investmentTotal cash flow for particular year)×No. of months in a year=$40,000$80,000×12 months= 6 months (2)
Proposal D:
Initial investment=$540,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal D | ||||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows | ||
| 1 | 200,000 | 200,000 | ||
| 2 | 180,000 | 380,000 | ||
| 3 | 160,000 | 540,000 | ||
Table (4)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal D is 3 years.
2.
The average rate of return for the give proposals.
Explanation of Solution
The average rate of return for the given proposals is as follows:
Proposal A:
Average rate of investment = (Income from operationsUseful life of years)(Cost of investment2)=($60,0005 years)($450,0002)=$12,000$225,000=0.053In percentage 0.053×100 = 5.3%
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal A is 5.3%.
Proposal B:
Average rate of investment = (Income from operationsUseful life of years)(Cost of investment2)=($90,0005 years)($200,0002)=$18,000$100,000=0.18In percentage 0.18×100 = 18.0%
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal B is 18.0%.
Proposal C:
Average rate of investment = (Income from operationsUseful life of years)(Cost of investment2)=($120,0005 years)($320,0002)=$24,000$160,000=0.15In percentage 0.15×100 = 15.0%
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal C is 15.0%.
Proposal D:
Average rate of investment = (Income from operationsUseful life of years)(Cost of investment2)=($220,0005 years)($540,0002)=$44,000$270,000=0.163In percentage 0.163×100 = 16.3%
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal D is 16.3%.
3.
To indicate: The proposals which should be accepted for further analysis, and which should be rejected.
Explanation of Solution
The proposals which should be accepted for further analysis, and which should be rejected is as follows:
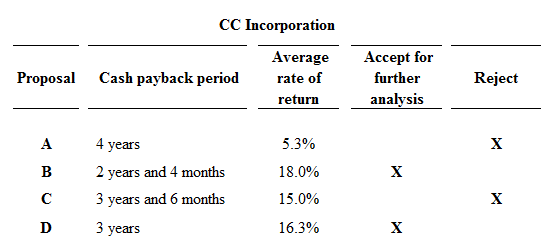
Figure (1)
Proposals A and C are rejected, because proposal A and C fails to meet the required maximum cash back period of 3 years, and they has less rate of return than the other proposals. Hence, Proposals B and D are preferable.
4.
The net present value of preferred proposals.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the net present value of the proposals which has 12% rate of return as follows:
Proposal B:
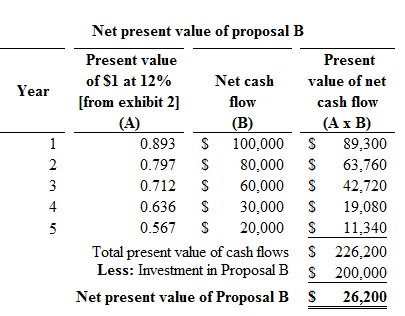
Figure (2)
Hence, the net present value of proposal B is $26,200.
Proposal D:
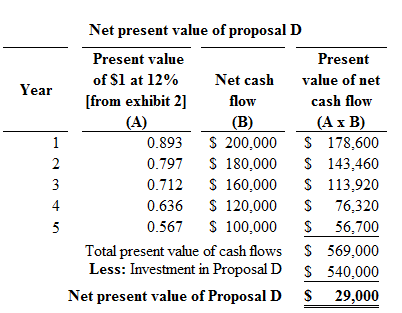
Figure (3)
Hence, the net present value of proposal D is $29,000.
5.
To determine: The present value index for each proposal.
Explanation of Solution
The present value index for each proposal is as follows:
Proposal B:
Calculate the present value index for proposal B:
Present value index for proposal B = Total presest value of cash flowAmount to be invested=$226,200$200,000=1.13
Hence, the present value index for proposal B is 1.13.
Proposal D:
Calculate the present value index for proposal D:
Present value index for proposal D= Total presest value of cash flowAmount to be invested=$569,000$540,000=1.05
Hence, the present value index for proposal Dis 1.05.
6.
To rank: The proposal from most attractive to least attractive, based on the present value of net cash flows.
Explanation of Solution
Proposals are arranged by rank is as follows:
| Proposals | Net present value | Rank |
| Proposal D | $ 29,000 | 1 |
| Proposal B | $ 26,200 | 2 |
Table (5)
7.
To rank: The proposal from most attractive to least attractive, based on the present value of index.
Explanation of Solution
Proposals are arranged by rank is as follows:
| Proposals | Present value index | Rank |
| Proposal B | 1.13 | 1 |
| Proposal D | 1.05 | 2 |
Table (6)
8.
To analysis: The proposal which is favor to investment, and comment on the relative
attractiveness of the proposals based on the rank.
Explanation of Solution
On the basis of net present value:
The net present value of Proposal B is $26,200, and Proposal D is $29,000. In this case, the net present value of proposal D is more than the net present value of proposal B. Hence, investment in Proposal D is preferable.
On the basis of present value index:
The present value index of Proposal B is 1.13, and the present value index of Proposal D is 1.05. In this case, Proposal B has the favorable present value index, because the present value index of Proposal B (1.13) is more than Proposal D (1.05). Thus, the investment in Proposal B is preferable (favorable).
Every business tries to getmaximum profit with minimum investment. Hence, the cost of investment in Proposal B is less than the proposal D. Thus, investment in Proposal B is preferable
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting
- Repsola is a drilling company that operates an offshore Oilfield in Feeland. Five yearsago, Feeland had a major oil discovery and granted licenses to drill oil to reputable,experienced drilling companies. The licensing agreement requires the company toremove the oil rig at the end of production and restore the seabed. Ninety percent ofthe eventual costs of undertaking the work relate to the removal of the oil rig andrestoration of damage caused by building it and ten percent arise through theextraction of the oil. At the Statement of Financial Position (SOFP) date (December 312025), the rig has been constructed but no oil has been extractedOn January 1st 2023, Repsola obtained the license to construct an oil rig at a cost of$500 million. Two years later the oil rig was completed. The rig is expected to beremoved in 20 years from the date of acquisition. The estimated eventual cost is 100million. The company’s cost of capital is 10% and its year end is December 31st. Repsolauses…arrow_forwardRepsola is a drilling company that operates an offshore Oilfield in Feeland. Five yearsago, Feeland had a major oil discovery and granted licenses to drill oil to reputable,experienced drilling companies. The licensing agreement requires the company toremove the oil rig at the end of production and restore the seabed. Ninety percent ofthe eventual costs of undertaking the work relate to the removal of the oil rig andrestoration of damage caused by building it and ten percent arise through theextraction of the oil. At the Statement of Financial Position (SOFP) date (December 312025), the rig has been constructed but no oil has been extractedOn January 1st 2023, Repsola obtained the license to construct an oil rig at a cost of$500 million. Two years later the oil rig was completed. The rig is expected to beremoved in 20 years from the date of acquisition. The estimated eventual cost is 100million. The company’s cost of capital is 10% and its year end is December 31st. Repsolauses…arrow_forwardMaharaj Garage & Car Supplies sells a variety of automobile cleaning gadgets including a variety of hand vacuums. The business began the first quarter (January to March) of 2024 with 20 (Mash up Dirt) deep clean, cordless vacuums at a total cost of $126,800. During the quarter, the business completed the following transactions relating to the "Mash up Dirt" brand. January 8 January 31 February 4 February 10 February 28 March 4 March 10 March 31 March 31 105 vacuums were purchased at a cost of $6,022 each. In addition, the business paid a freight charge of $518 cash on each vacuum to have the inventory shipped from the point of purchase to their warehouse. The sales for January were 85 vacuums which yielded total sales revenue of $768,400. (25 of these units were sold on account to Mandys Cleaning Supplies, a longstanding customer) A new batch of 65 vacuums was purchased at a total cost of $449,800 8 of the vacuums purchased on February 4 were returned to the supplier, as they were…arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





