
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119304142
Author: Connie Allen, Valerie Harper
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 25, Problem 1.1BGL
Summary Introduction
To label: The major endocrine glands in the given figure.
Introduction: The endocrine system is the collection of the endocrine glands. There are two types of glands found in the human body, namely endocrine or ductless glands and exocrine or duct glands. The secretions of the endocrine glands are called hormones. They are secreted directly into the bloodstream and are found to regulate the metabolisms of the body. The endocrine system is under the control of the hypothalamus.
Expert Solution & Answer
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
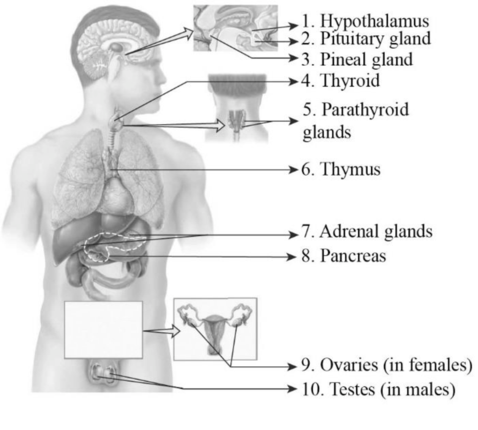
Fig.1: Major endocrine glands
Explanation of Solution
- 1. Hypothalamus: It is located in the brain below the thalamus and acts as a control center that connects the functions of the nervous system with the endocrine system. It regulates the secretion of the anterior pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is extended to form the posterior pituitary.
- 2. Pituitary gland: It is situated at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland is divided into anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis). The secretions of the anterior pituitary gland are called tropic hormones, which stimulate the secretion of other endocrine glands.
- 3. Pineal gland: It is a small gland located in the brain. It is also called conarium or epiphysis cerebri. The secretion of the pineal gland is called melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which regulates the sleep cycle.
- 4. Thyroid gland: The thyroid gland is located at the base of the neck (below Adam’s apple). It is a butterfly-shaped organ having two lobes (left and right) connected by an isthmus. The thyroid gland secretes triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and calcitonin. Thyroid hormones regulate the
metabolism of body. - 5. Parathyroid glands: The parathyroid glands are found in the neck region behind the thyroid gland. There are four parathyroid glands, each pair located above (superior parathyroid glands) and below (inferior parathyroid glands). The parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH).
- 6. Thymus gland: The thymus gland is located in the area between the lungs behind the sternum. It secretes thymosin, which induces the development of T lymphocytes, which plays a major role in the immune system.
- 7. Adrenal glands: They are triangular-shaped glands and are called suprarenal glands since they are found on the top of the renal system. The adrenal gland is divided into two portions, adrenal cortex, and adrenal medulla. Hormones secreted by adrenal glands play a role in regulating metabolism, stress, immune system, and blood pressure by maintaining the salt level in blood.
- 8. Pancreas: The pancreas is a dual or heterocrine gland, which secretes hormones (endocrine) and enzymes (exocrine). It is located behind the stomach as a long flattened gland. The main function of the pancreas is to regulate the blood glucose level.
- 9. Ovaries: Ovaries are the part of the female reproductive system situated along the left and right side of the uterus. At puberty, ovaries secrete hormones, namely estrogen, testosterone, progesterone, and inhibin. These hormones play a vital role in menstruation and fertility.
- 10. Testes: Testes are the male reproductive gland located within the scrotum. Testes secrete hormones like androgens. Testosterone is the primary androgen produced by the testes. The main function of testes is the production of sperm.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Chapter 25 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion
Ch. 25 - Prob. 1.1BGLCh. 25 - Label the drawing and photomicrographs of the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 3.1BGLCh. 25 - Label the photomicrographs of the sections of...Ch. 25 - Observe the location of the adrenal glands in the...Ch. 25 - Label the terms in Figure 25.6(a), (b), and...Ch. 25 - Observe the location of the pancreas in the...Ch. 25 - Label the structures on the drawing in Figure...Ch. 25 - Using the labeled line drawing in Figure 25.8(b),...Ch. 25 - ACTH ________________________________
Ch. 25 - ADH ________________________________
Ch. 25 - Prob. 4HACh. 25 - Prob. 5HACh. 25 - LH ________________________________
Ch. 25 - Prob. 7HACh. 25 - Prob. 8HACh. 25 - Prob. 9HACh. 25 - PTH ________________________________
Ch. 25 - T3 ________________________________
Ch. 25 - T4 ________________________________
Ch. 25 - Prob. 13HACh. 25 - MSH ________________________________
Ch. 25 - TH ________________________________
Ch. 25 - ACTH ____________________
Ch. 25 - ADH ____________________
Ch. 25 - aldosterone ____________________
Ch. 25 - Prob. 4MEGHCh. 25 - calcitonin ____________________
Ch. 25 - Prob. 6MEGHCh. 25 - epinephrine/NE ____________________
Ch. 25 - estrogen; progesterone ____________________
Ch. 25 - FSH ____________________
Ch. 25 - Prob. 10MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 11MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 12MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 13MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 14MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 15MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 16MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 17MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 18MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 19MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 20MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 21MEGHCh. 25 - Prob. 22MEGHCh. 25 - _______ Stimulates uterine contractions and milk...Ch. 25 - Prob. 2HFCh. 25 - Prob. 3HFCh. 25 - Prob. 4HFCh. 25 - Prob. 5HFCh. 25 - Prob. 6HFCh. 25 - Prob. 7HFCh. 25 - Prob. 8HFCh. 25 - Prob. 9HFCh. 25 - Prob. 10HFCh. 25 - Prob. 11HFCh. 25 - Prob. 12HFCh. 25 - _______________ Helps to set the biological...Ch. 25 - Prob. 14HFCh. 25 - Prob. 15HFCh. 25 - Prob. 16HFCh. 25 - _______________ Promotes the maturation of T cells...Ch. 25 - Prob. 18HFCh. 25 - Prob. 19HFCh. 25 - Prob. 20HFCh. 25 - Prob. 21HFCh. 25 - Prob. 22HFCh. 25 - Prob. 23HFCh. 25 - Prob. 24HFCh. 25 - Prob. 25HFCh. 25 - Prob. 26HFCh. 25 - Prob. 27HFCh. 25 - Prob. 1ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 2ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 3ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 4ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 5ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 6ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 7ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 8ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 9ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 10ESSCh. 25 - Prob. 1UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 2UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 3UYKCh. 25 - Using your textbook or another reference book,...Ch. 25 - Prob. 5UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 6UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 7UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 8UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 9UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 10UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 11UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 12UYKCh. 25 -
Hypothalamus and tropic hormones.
Ch. 25 - Prob. 14UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 15UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 16UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 17UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 18UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 19UYKCh. 25 - Prob. 20UYK
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education
Great Glands - Your Endocrine System: CrashCourse Biology #33; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WVrlHH14q3o;License: Standard Youtube License