
Concept explainers
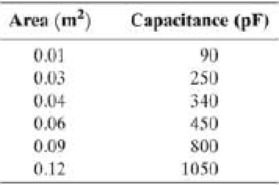
(II) Six physics students were each given an air filled capacitor. Although the areas were different, the spacing between the plates, d, was the same for all six capacitors, but was unknown. Each student made a measurement of the area A and capacitance C of their capacitor. Below is a Table for their data. Using tie combined data and a graphing program or spreadsheet, determine the spacing d between the plates.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- Check Your Understanding When a cylindrical capacitor is given a charge of 0.500 nC, a potential difference of 20.0 V is measured between the cylinders, (a) What is the capacitance of this system? (b) If the cylinders are 1.0 m long, what is the ratio of their radii?arrow_forwardCheck Your Understanding Determine the net capacitance C of each network of capacitors shown below. Assume the C1= 1.0 pF, C2=2.0pF, C3=4.0pF, and C4=5.0 pF. Find the charge on each capacitor, assuming there is a potential difference of 12.0 V across each network.arrow_forward(i) Rank the following five capacitors from greatest to smallest capacitance, noting any cases of equality, (a) a 20-F capacitor with a 4-V potential difference between its plates (b) a 30-F capacitor with charges of magnitude 90 C on each plate (c) a capacitor with charges of magnitude 80 C on its plates, differing by 2 V in potential. (d) a 10-F capacitor storing energy 125 J (e) a capacitor storing energy 250 J with a 10-V potential difference (ii) Rank the same capacitors in part (i) from largest to smallest according to the potential difference between the plates, (iii) Rank the capacitors in part (i) in the order of the magnitudes of the charges on their plates, (iv) Rank the capacitors in part (i) in the order of the energy they store.arrow_forward
- (i) A battery is attached to several different capacitors connected in parallel. Which of the following statements is true? (a) All capacitors have the same charge, and the equivalent capacitance is greater than the capacitance of any of the capacitors in the group, (b) The capacitor with the largest capacitance carries the smallest charge, (c) The potential difference across each capacitor is the same, and the equivalent capacitance is greater than any of the capacitors in the group. (d) The capacitor with the smallest capacitance carries the largest charge. (e) The potential differences across the capacitors are the same only if the capacitances are the same, (ii) The capacitors are reconnected in series, and the combination is again connected to the battery. From the same choices, choose the one that is true.arrow_forwardCheck Your Understanding The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is 2.0 pF. If the area of each plate is 2.4 cm2, what is the plate separation?arrow_forwardCheck Your Understanding The potential difference across a 5.0-pF capacitor is 0.40 V. (a) What is the energy stored in this capacitor? (b) The potential difference is now increased to 1.20 V. By what factor is the stored energy increased?arrow_forward
- What If? The two capacitors of Problem 13 (C1 = 5.00 F and C2 = 12.0 F) are now connected in series and to a 9.00-Y battery. Find (a) the equivalent capacitance of the combination. (b) the potential difference across each capacitor, and (c) the charge on each capacitor.arrow_forwardCheck Your Understanding Continuing with Example 8.12, show that when the battery is connected across the plates the energy stored in dielectric-filled capacitor is U=kU0 (larger than the energy U0 of an empty capacitor kept at the same voltage). Compare this result with the result U=U0/K found previously for an isolated, charged capacitor.arrow_forwardSuppose that the capacitance of a variable capacitor can be manually changed from 100 pF to 800 pF by turning a dial, connected to one set of plates by a shaft from 0° to 180°. With the dial set at 180° (corresponding to C — 800 pF), the capacitor is connected to a 500-V source. After charging, the capacitor is disconnected from the source, and the dial is turned to 0°. If friction is negligible, how much work is required to turn the dial from 180° to 0°?arrow_forward
- (a) Regarding (lie Earth and a cloud layer 800 m above the Earth as the plates of a capacitor, calculate the capacitance of the Earth-cloud layer system. Assume the cloud layer has an area of 1.00 km2 and the air between the cloud and the ground is pure and dry'. Assume charge builds up on the cloud and on the ground until a uniform electric field of 3.00 106 N/C throughout the space between them makes the air break down and conduct electricity as a lightning bolt, (b) What is the maximum charge the cloud can hold?arrow_forwardThe dielectric to be used in a parallel-plate capacitor has a dielectric constant of 3.60 and a dielectric strength of 1.60107 V/m. The capacitor has to have a capacitance of 1.25 nF and must be able to withstand a maximum potential difference 5.5 kV. What is the minimum area the plates of the capacitor may have?arrow_forward(a) Find the equivalent capacitance between points a and b for the group of capacitors connected as shown in Figure P25.12 (page 686). Take C1 = 5.00 F, C2 = 10.0 F, and C3 = 2.00 F. (b) What charge is stored on C3 if the potential difference between points a and b is 60.0 V? Figure P25.12arrow_forward

 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





