
(a)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is D or L should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Monosaccharides: (single sugar unit) simple sugars units are the most basic units of carbohydrates.
Structure and nomenclature: Monosaccharide has this chemical formula:
Monosaccharides can be classified by the number x of carbon atoms. If they contain three carbon atom and is called triose. If they contain four carbon and is called tetrose, if they contain five carbon and is called pentose, if they contain six carbon and is called hexose and so on.
Aldose: A monosaccharide in which carbon serves as a backbone and contains an
Ketose: A ketose is a simple sugar unit (monosaccharide) containing one
D and L enantiomers: L isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the left side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
R isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the right side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
To find: Type of enantiomers.
(a)
Answer to Problem 42PP
Answer
The given compound is D-aldotetrose (a).
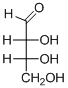
Explanation of Solution
The OH group connected to C3 is pointing to the right side, so it is called as D-sugar. The
(b)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is D or L should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Monosaccharides: (single sugar unit) simple sugars units are the most basic units of carbohydrates.
Structure and nomenclature: Monosaccharide has this chemical formula:
Monosaccharides can be classified by the number x of carbon atoms. If they contain three carbon atom and is called triose. If they contain four carbon and is called tetrose, if they contain five carbon and is called pentose, if they contain six carbon and is called hexose and so on.
Aldose: A monosaccharide in which carbon serves as a backbone and contains an aldehyde group at the beginning.
Ketose: A ketose is a simple sugar unit (monosaccharide) containing one ketone group per molecule.
D and L enantiomers: L isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the left side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
R isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the right side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
To find: Type of enantiomers.
(b)
Answer to Problem 42PP
Answer
The given compound is L-aldopentose (b).
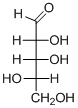
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is L-aldopentose.
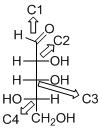
The OH group connected to C4 is pointing to the left side, so it is called as L-sugar. The functional group at Cl is an aldehyde group, so the compound is an aldose. Finally, the compound has five carbon atoms, so it is a pentose. The given compound is an L-aldopentose
(c)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is D or L should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Monosaccharides: (single sugar unit) simple sugars units are the most basic units of carbohydrates.
Structure and nomenclature: Monosaccharide has this chemical formula:
Monosaccharides can be classified by the number x of carbon atoms. If they contain three carbon atom and is called triose. If they contain four carbon and is called tetrose, if they contain five carbon and is called pentose, if they contain six carbon and is called hexose and so on.
Aldose: A monosaccharide in which carbon serves as a backbone and contains an aldehyde group at the beginning.
Ketose: A ketose is a simple sugar unit (monosaccharide) containing one ketone group per molecule.
D and L enantiomers: L isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the left side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
R isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the right side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
To find: Type of enantiomers.
(c)
Answer to Problem 42PP
Answer
The given compound is D-aldopentose (c).
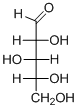
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is D-aldopentose.
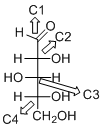
The OH group connected to C4 is pointing to the right side, so this is a D-sugar. The functional group at Cl is an aldehyde group, so the compound is an aldose. Finally, the compound has five carbon atoms, so it is a pentose. The given compound is a D-aldopentose.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is D or L should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Monosaccharides: (single sugar unit) simple sugars units are the most basic units of carbohydrates.
Structure and nomenclature: Monosaccharide has this chemical formula:
Monosaccharides can be classified by the number x of carbon atoms. If they contain three carbon atom and is called triose. If they contain four carbon and is called tetrose, if they contain five carbon and is called pentose, if they contain six carbon and is called hexose and so on.
Aldose: A monosaccharide in which carbon serves as a backbone and contains an aldehyde group at the beginning.
Ketose: A ketose is a simple sugar unit (monosaccharide) containing one ketone group per molecule.
D and L enantiomers: L isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the left side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
R isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the right side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
To find: Type of enantiomers.
(d)
Answer to Problem 42PP
Answer
The given compound is D-aldohexose (d).
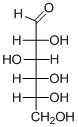
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is D-aldohexose.
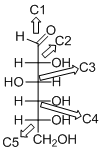
The OH group connected to C5 is pointing to the right side, so this is a D-sugar. The functional group at Cl is an aldehyde group, so the compound is an aldose. Finally, the compound has six carbon atoms, so it is called as a hexose. The given compound is a D-aldohexose
(e)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is D or L should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Monosaccharides: (single sugar unit) simple sugars units are the most basic units of carbohydrates.
Structure and nomenclature: Monosaccharide has this chemical formula:
Monosaccharides can be classified by the number x of carbon atoms. If they contain three carbon atom and is called triose. If they contain four carbon and is called tetrose, if they contain five carbon and is called pentose, if they contain six carbon and is called hexose and so on.
Aldose: A monosaccharide in which carbon serves as a backbone and contains an aldehyde group at the beginning.
Ketose: A ketose is a simple sugar unit (monosaccharide) containing one ketone group per molecule.
D and L enantiomers: L isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the left side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
R isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the right side of the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl.
To find: Type of enantiomers.
(e)
Answer to Problem 42PP
Answer
The given compound is D-ketopentose (e).
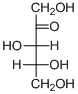
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is D-ketopentose.
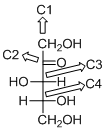
The OH group connected to C4 is pointing to the right side, so this is a D-sugar. The functional group at C2 is a ketone group, so the compound is a ketose. Finally, the compound has five carbon atoms, so it is a pentose. The given compound is a D-ketopentose.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





