
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given compound should be filled whether it is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure.
Concept introduction:
Isomer: Molecule has same molecular formula but different structural arrangement is called isomer.
Geometric isomerism (also known as E-Z isomerism or cis-trans isomerism): same molecular formula but different arrangement in the space. These isomers happen where you have restricted rotation in a molecule (double bond in the molecule). The
Constitutional isomer: (or structural) isomers differ in the connectivity they contain different functional groups and / or bonding patterns is called constitutional isomer.
Resonance: it is a process of delocalization electrons with in the molecule.
Chiral: Absence of a plane of symmetry or a center of symmetry is called chiral molecule, a non-superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral. A carbon atom is attached by the four different groups is called chiral carbon.
Enantiomers: Two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable.
Diastereomers: Two stereoisomers that are non-mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable.
(a)
Answer to Problem 23.86QP
The given compound is diastereomers (a)
Explanation of Solution
To find: The given compound is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure
The given compound is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure needs to be known.
The given compound is diastereomers which is shown below.
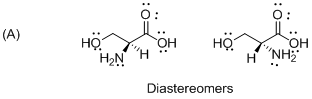
The above compounds are non-mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable therefore the given compound diastereomers.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given compound should be filled whether it is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure.
Concept introduction:
Isomer: Molecule has same molecular formula but different structural arrangement is called isomer.
Geometric isomerism (also known as E-Z isomerism or cis-trans isomerism): same molecular formula but different arrangement in the space. These isomers happen where you have restricted rotation in a molecule (double bond in the molecule). The functional groups are same side in the molecule is cis, the functional groups are opposite side is called trans isomer.
Constitutional isomer: (or structural) isomers differ in the connectivity they contain different functional groups and / or bonding patterns is called constitutional isomer.
Resonance: it is a process of delocalization electrons with in the molecule.
Chiral: Absence of a plane of symmetry or a center of symmetry is called chiral molecule, a non-superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral. A carbon atom is attached by the four different groups is called chiral carbon.
Enantiomers: Two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable.
Diastereomers: Two stereoisomers that are non-mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable.
(b)
Answer to Problem 23.86QP
The given compound is diastereomers (b)
Explanation of Solution
To find: The given compound is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure
The given compound is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure needs to be known.
The given compound is diastereomers which is shown below.
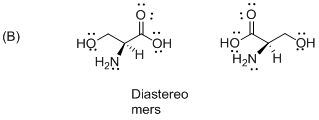
The above compounds are non-mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable therefore the given compound diastereomers.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given compound should be filled whether it is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure.
Concept introduction:
Isomer: Molecule has same molecular formula but different structural arrangement is called isomer.
Geometric isomerism (also known as E-Z isomerism or cis-trans isomerism): same molecular formula but different arrangement in the space. These isomers happen where you have restricted rotation in a molecule (double bond in the molecule). The functional groups are same side in the molecule is cis, the functional groups are opposite side is called trans isomer.
Constitutional isomer: (or structural) isomers differ in the connectivity they contain different functional groups and / or bonding patterns is called constitutional isomer.
Resonance: it is a process of delocalization electrons with in the molecule.
Chiral: Absence of a plane of symmetry or a center of symmetry is called chiral molecule, a non-superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral. A carbon atom is attached by the four different groups is called chiral carbon.
Enantiomers: Two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable.
Diastereomers: Two stereoisomers that are non-mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable.
(c)
Answer to Problem 23.86QP
The given compound is resonance structure (c)
Explanation of Solution
To find: The given compound is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure
The given compound is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure needs to be known.
The given compound is resonance structure which is shown below.
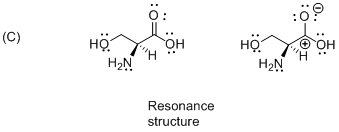
Isomers have different sequence of bond types or connection in different order is called as resonance structure therefore the given molecule is resonance structure.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given compound should be filled whether it is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure.
Concept introduction:
Isomer: Molecule has same molecular formula but different structural arrangement is called isomer.
Geometric isomerism (also known as E-Z isomerism or cis-trans isomerism): same molecular formula but different arrangement in the space. These isomers happen where you have restricted rotation in a molecule (double bond in the molecule). The functional groups are same side in the molecule is cis, the functional groups are opposite side is called trans isomer.
Constitutional isomer: (or structural) isomers differ in the connectivity they contain different functional groups and / or bonding patterns is called constitutional isomer.
Resonance: it is a process of delocalization electrons with in the molecule.
Chiral: Absence of a plane of symmetry or a center of symmetry is called chiral molecule, a non-superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral. A carbon atom is attached by the four different groups is called chiral carbon.
Enantiomers: Two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable.
Diastereomers: Two stereoisomers that are non-mirror images of each other and they are non-supposable.
(d)
Answer to Problem 23.86QP
The given compound is constitutional isomer (d)
Explanation of Solution
To find: The given compound is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure
The given compound is resonance structure, constitutional isomer, cis/trans isomer or same structure needs to be known.
The given compound is constitutional isomer which is shown below.
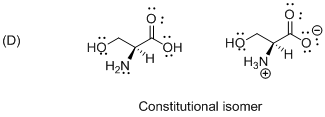
Isomers with the same order of connections and sequence of bond types, but which differ in the spatial arrangement of the atoms therefore the given molecule is called constitutional isomer
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST
- Distinguish between isomerism and resonance. Distinguish between structural and geometric isomerism. When writing the various structural isomers, the most difficult task is identifying which are different isomers and which are identical to a previously written structurethat is, which are compounds that differ only by the rotation of a carbon single bond. How do you distinguish between structural isomers and those that are identical? Alkenes and cycloalkanes are structural isomers of each other. Give an example of each using C4H8. Another common feature of alkenes and cycloalkanes is that both have restricted rotation about one or more bonds in the compound, so both can exhibit cis- trans isomerism. What is required for an alkene or cycloalkane to exhibit cis-trans isomerism? Explain the difference between cis and trans isomers. Alcohols and ethers are structural isomers of each other, as are aldehydes and ketones. Give an example of each to illustrate. Which functional group in Table 21-4 can be structural isomers of carboxylic acids? What is optical isomerism? What do you look for to determine whether an organic compound exhibits optical isomerism? 1-Bromo-1-chloroethane is optically active whereas 1-bromo-2-chloroethane is not optically active. Explain.arrow_forwardWhat is the correct molecular structure for 1-cyclopropyl-3-ethyl-4-methyl hexane?arrow_forward1-bromo-3-ethylcyclopentane exhibits geometrical isomerism. Draw structures of the two geometrical isomersarrow_forward
- 1-Propylamine, propan-1-ol, acetic acid, and butane have about the same molar masses. Which would you expect to have the (a) highest boiling point, (b) lowest boiling point, (c) least solubility in water, and (d) least chemical reactivity? Have each member of your group chose a part to answer, andthen discuss with each other why those answers were chosen.arrow_forwardFor the following, you must draw an appropriate structure that has the chemical formula C5H9NO with the indicated functional group(s) and/or property. In each case, identify any other functional groups in the molecule you draw, that were not indicated in the question. You may use condensed dash or bond-line structure to draw your molecules. c) An acyclic amide that cannot form hydrogen bonds with itselfarrow_forwardHow many structural isomers are there for a five-member straight carbon chain with one double bond? For a six-member straight carbon chain with two double bonds?arrow_forward
- The empirical formula of X is C3H5CIO If X is an optically alkanal, give the structural formula of X and draw this pair of enantiomers.Structural formula of X : If X has a C=C bond and a saturated OH group (i.e. The OH group does not attach to the C=C), give the structural formula of X if X shows cis-trans isomerism. Draw the pair of cis-trans isomers.Structural formula of X :arrow_forwardAre there alkene isomers with the molecular formula C2H3Cl?arrow_forward2-methylhexane & 3,3-dimethylpentane Are the two compounds Constitutional Isomers or Different Compounds? Draw structures for both compounds.arrow_forward
- What is an isomer having the formula C6H12 ?Without using 2-hexenearrow_forward38. Using a catalyst, two gaseous hydrocarbons, X and Y, were produced from heating hexane, C6H14. The gases were individually tested with aqueous bromine. For X, aqueous bromine became colorless, while for Y, the reddish-brown color of aqueous bromine was retained. Which of the following best describes the identity of the two hydrocarbons? (A) X= alkane, Y = alkene (B) X = alkene, Y = alkane (C) Both X and Y contain the same number of carbon atoms. (D) Both X and Y contain the same number of hydrogen atoms.arrow_forwardDraw Three examples of structural isomers that have the chemical formula C6H14.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





